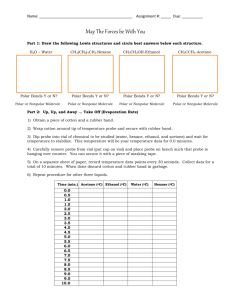
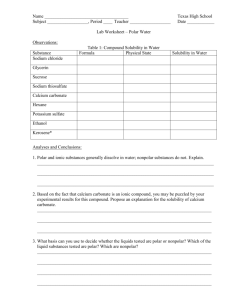
Polar Nonpolar Station Lab
advertisement
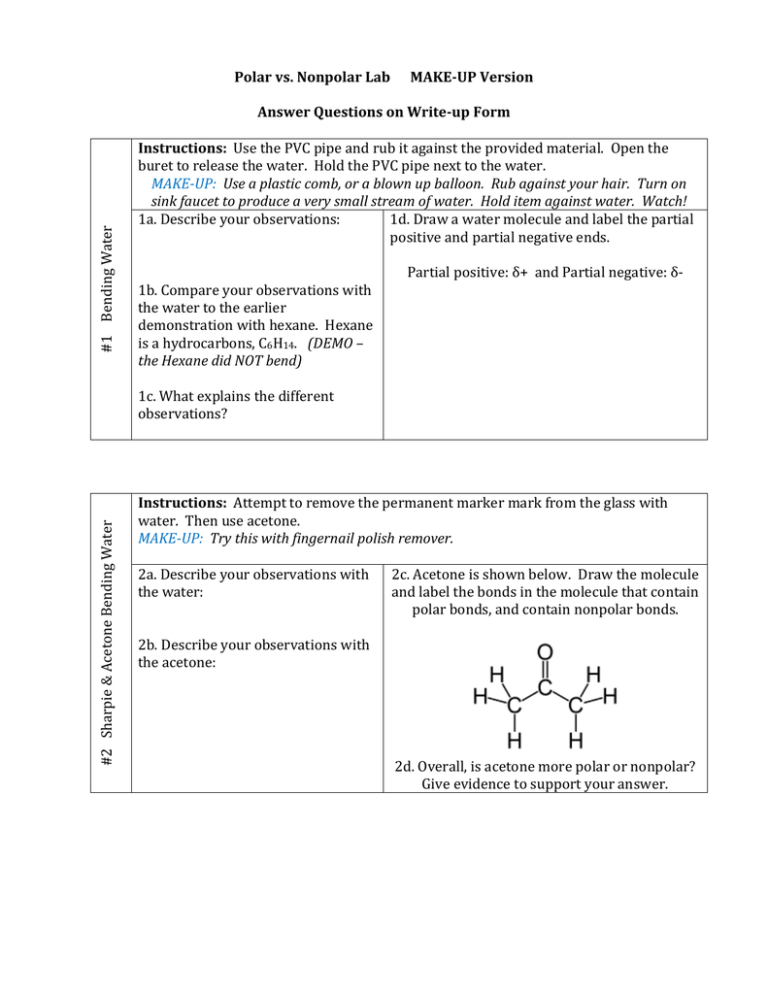
Polar vs. Nonpolar Lab MAKE-UP Version #1 Bending Water Answer Questions on Write-up Form Instructions: Use the PVC pipe and rub it against the provided material. Open the buret to release the water. Hold the PVC pipe next to the water. MAKE-UP: Use a plastic comb, or a blown up balloon. Rub against your hair. Turn on sink faucet to produce a very small stream of water. Hold item against water. Watch! 1a. Describe your observations: 1d. Draw a water molecule and label the partial positive and partial negative ends. 1b. Compare your observations with the water to the earlier demonstration with hexane. Hexane is a hydrocarbons, C6H14. (DEMO – the Hexane did NOT bend) Partial positive: δ+ and Partial negative: δ- #2 Sharpie & Acetone Bending Water 1c. What explains the different observations? Instructions: Attempt to remove the permanent marker mark from the glass with water. Then use acetone. MAKE-UP: Try this with fingernail polish remover. 2a. Describe your observations with the water: 2c. Acetone is shown below. Draw the molecule and label the bonds in the molecule that contain polar bonds, and contain nonpolar bonds. 2b. Describe your observations with the acetone: 2d. Overall, is acetone more polar or nonpolar? Give evidence to support your answer. #3 Polystyrene & Acetone (wear gloves) Instructions: Place a small piece of Styrofoam in the round watch glass. Place a few drops of acetone onto the Styrofoam. Watch! MAKE-UP: Styrofoam and Acetone VIDEO Polystyrene Peanuts are a Polystyrene contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. long chain of styrene Acetone primarily contains carbon and hydrogen atoms. molecules – a Polymer. 3a. The term “Like Dissolves Like” can be used to explain the Acetone observed reaction. What does this phrase mean (use terms “polar” and “nonpolar”)? Use your observations to support your answer. Hint: Look at the polystyrene in water. Polystyrene: A polymer Benzene: The six sided ring with the circle is a benzene ring. Each corner is a carbon atom, and each carbon has a hydrogen (for the 4th bond on carbon). Is polystyrene POLAR or NONPOLAR? Just C & H’s #4 Oil, Water, & Soap Instructions: Place about 3 mL of the colored water into a test tube. Place about 1 mL of oil into the tube. Observe. Next place a piece of wax paper over the top of the tube and mix the contents. Let sit and observe. Next place 2-3 drops of dish soap into the test tube. Again cover the top and mix. Let sit and observe. MAKE-UP: Do this at home in a small clear container. Increase amounts to be able to see the layers. Typical Soap Molecule: 4a. Observations after adding oil to water: Soap primarily contains carbons and hydrogens, but one end contains oxygen. The ends have different polarities. 4b. After mixing oil & water: 4c. After mixing the oil & water with dish soap: 4d. Explain what soap did to the oil and water mixture. What does polarity have to do with it? #5 Water, Hexane & NaCl Instructions: (wear gloves) Place a small amount of water in the petri dish. Dissolve “a pinch” of NaCl in the water. Next place a small amount of hexane in a separate petri dish. Place “a pinch” of NaCl in with the hexane. Stir. MAKE-UP: Salt in Hexane Video How Water Dissolves Salt Video Dispose of the mixtures in the labeled beakers. Illustrate proper dissolving of salt in water: NaCl is an ionic compound – it contains a cation and anion. 5a. Is water polar or nonpolar? What happened to the NaCl in water? 5b. Is hexane polar or nonpolar? What happened to the NaCl in hexane? 5c. Explain this observation! 5d. Draw two water molecules around sodium and two water molecules around chlorine. Na+ Cl- (Hint: Make sure the partial positive and partial negative ends of water are with the correct ion.) MAKE-UP: The following are questions / answer stations, so no special instructions needed! Tug-of-War #6: Tug-of-War What element has the higher “pull” of the electrons in the following bonds? H-H H-Cl C-H Indicate the partial positive and partial negative of each pair. Use the δ+ and δsymbols. More pull = high electronegativity HONORS CHEMISTRY #7: Textbook Questions HONORS CHEMISTRY STATION #7 Chapter 8, pg 270. Answer questions: #75 #76 #77 GENERAL CHEMISTRY STATION #7 #10: Methane #9: Ammonia GENERAL CHEMISTRY #8: Diatomic Molecules #7: Textbook Questions Chapter 8, pg 275. Answer questions: Draw the Lewis Diagrams for the 7 common Diatomic Molecules See your list of “Memorize These!” Identify them as Polar or Nonpolar. Most of the produced ammonia is used in fertilizer. It is also used as a household cleaner. It is known for its streak free shine, so is used for cleaning windows and removing baked on grime. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for ammonia. Is ammonia polar or nonpolar? Instructions: Pretend to light a Bunsen Burner (too much flammable material out today! Draw the Lewis Dot Structure of the methane molecule. Draw in the bond dipoles (the arrows). Is methane polar or nonpolar?