Chemistry - cloudfront.net
advertisement

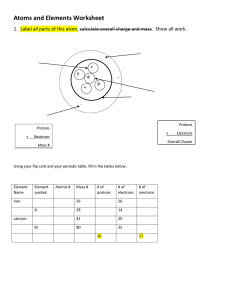
Chemistry • Demetri Mendelev and the Periodic Table Periods and Groups • The Periodic Table arranges elements in rows, called periods, and columns, called groups. The order of the elements is determined by atomic number. Meet the Elements • Meet the Elements Video Types of Matter Atom Types of Matter Atom Element Compound Element Compound Molecule Mixture Molecule Mixture Types of Matter Atom Types of Matter Atom Element Compound Element Compound Molecule Mixture Molecule Mixture Types of Matter Chemistry Unit 1 Structure of an Atom Protons and an Atoms identity Valence Electrons and Reactivity The Periodic Table Chemistry Unit 2 Chemical Formulas Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Law of Conservation of Mass Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 1, part 1 atom: the smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of that element element: a pure substance, made up of similar atoms, that cannot be broken down by chemical means Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 1, part 2 Periodic Table: a logical arrangement of the elements into rows and columns; an element’s position in the Periodic Table can be used to predict its properties group: a column of the Periodic Table; elements in the same group have similar properties nucleus: the center of an atom, which contains protons and neutrons period: a row of the Periodic Table proton: the subatomic particle in the nucleus that has a positive electric charge valence electrons: the outermost electrons of an atom, which help determine an element’s chemical properties neutron: the subatomic particle in the nucleus that has no electric charge metal: an element that is typically dense, shiny, strong, and a good conductor of heat and electricity electron cloud: the region around the nucleus where electrons are found electron: the negatively charged subatomic particle that exists in a cloud surrounding the nucleus unified atomic mass unit (u): the unit for measuring the mass of atoms electric charge: a property of matter that causes it to experience a force near other charged matter valence electrons: the outermost electrons of an atom, which help determine an element’s chemical properties ion: an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons chemical bond: an attractive force between atoms or ions, formed by the sharing or transfer of valence electrons nonmetal: an element that typically is not dense, and is dull, brittle, and a poor conductor of heat and electricity metalloid: an element that has properties between those of a metal and nonmetal; also called a semimetal pure substance: matter that has the same chemical composition throughout compound: a substance that forms when two or more elements join chemically molecule: a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds chemical formula: a group of chemical symbols and numbers that shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule Protons, Neutrons and Electrons The Hierarchical Relationship of Atomic Structure Atoms Molecules Minerals Mineral Rocks Neutrons Electrons Protons Earth Element • A pure substance, made up of similar atoms, that cannot be broken down by chemical means • An element’s identity is determined by the number of protons. • Interactive Periodic Table http://www.ptable.com/ What do you know about chemistry? Atom Nucleus • Nucleus is a term used to describe the control center in an animal cell (Biology) • Nucleus is the term to describe the very dense region at the center of an atom (Chemistry) Is this an animal or a plant cell? Components of an Atom • Proton • Neutron • Electron • All about Atoms Protons • Have a positive charge • Mass =1u or 1amu (unified atomic mass) • Located in the nucleus • The number of protons determines the elements identity Captain Proton A proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark Neutrons • Neutral Charge • Mass 1u • Located in the Nucleus • Elements with a variable number of neutrons are called isotopes Electrons and the Electron Cloud • • • • Electron Mass: Close to 0 u Negative Charge located in the Electron Cloud Atoms with a different number of electrons are called ions. • The Electrons cloud is subdivided into shells • The shells hold a fixed amount of electrons – 1st shell holds 2 electrons – 2nd shell holds 8 electrons – 3rd shell holds 8 electrons How to calculate Atomic Mass and Atomic Number. APE MAN • Atomic Number = #Protons = #Electrons • Mass Number- Atomic Number = Neutrons Atomic Components Sub-Atomic Particle Electrical Charge Mass Location in Atom Proton + 1u Nucleus Neutron neutral 1u Nucleus Electron - 0u Electron Cloud If the number of protons change, you have a different element. If the number of neutrons change, you have an isotope. If the number of electrons change, you have an ion. Bohr Model Bohr Model Bohr Model Bohr Model Name the Atom Draw the Atomic Structure P E N Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Draw the Atomic Structure Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Draw the atomi Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Build the Atom Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dice Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Build the Atom Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Build the Atom Action Metal, Metalloid or Non-Metal? Draw the Atomic Structure What period is the element in? What group is the element in? Draw the Lewis Dot Structure Build the Atom H H H H H He He He He He Li Li Li Li Li B B B B B Be Be Be Be Be C C C C C N N N N N O O O O O F F F F F Ne Ne Ne Ne Ne Na Na Na Na Na Mg Mg Mg Mg Mg Al Al Al Al Al Si Si Si Si Si P P P P P Si Si Si Si Si Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Ar Ar Ar Ar Ar Chemistry Review Stations Review Station 2 sentences Stamp Chemistry Review Stations Review Station Build an Atom Build an Atom Petri Dish Elements Petri Dish Elements Conversation with a Teacher Conversation with a Teacher 2 sentences Stamp Build an Atom Element ` 1. 2. 3. Draw an Element Build the Atom Roll the dice and illustrate your paper Action Build an Atom Element 1. 2. 3. Draw an Element Build the Atom Roll the dice and illustrate your paper Action Subatomic Particle Mass of Particles ____ protons ____electrons _____neutrons Total Mass of Electric Charge Build the Atom The formation of Salt Valence Electrons • Valence Electrons determine an elements chemical properties, including reactivity. • Valence Electrons refer to the number of electrons in their outer shell Lewis Dot Structure Ne Si B H O Be He C Li Valence Electrons • The Lewis dot structure shows just the valence electrons • The valence electrons are the electrons in the out shell • The number valence electrons in the outer shell determine the reactivity Lewis Dot Structure Noble Gases Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 1, Part 2 Periodic Table: a logical arrangement of the elements into rows and columns; an element’s position in the Periodic Table can be used to predict its properties group: a column of the Periodic Table; elements in the same group have similar properties period: a row of the Periodic Table valence electrons: the outermost electrons of an atom, which help determine an element’s chemical properties metal: an element that is typically dense, shiny, strong, and a good conductor of heat and electricity nonmetal: an element that typically is not dense, and is dull, brittle, and a poor conductor of heat and electricity metalloid: an element that has properties between those of a metal and nonmetal; also called a semimetal pure substance: matter that has the same chemical composition throughout compound: a substance that forms when two or more elements join chemically molecule: a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds chemical formula: a group of chemical symbols and numbers that shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a molecule METALS, NONMETALS, METALLOIDS, & NOBLE GASES FOUR SECTION FOLDABLE ADVANCED ORGANIZER Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids • The Periodic Table can be used to predict many properties of elements. – Metals are located on the left side and in the center of the table, while nonmetals are clustered on the right side. – A staircase-like line divides the two groups. – Elements called metalloids, which have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals, are located along this line. Metals Metalloids Non-Metals Metals Color metals non-metals and metalloids. Cut apart the metals, non=metals and metalloids Paste each section under its heading Draw columns to separate the categories. Metalloids Non-Metals Color metals non-metals and metalloids. Cut apart the metals, non=metals and metalloids Paste each section under its heading Draw columns to separate the categories. Examples: Examples: Examples: Examples: Examples: Examples: Groups: Groups: Groups: Groups: Groups: Groups: Properties: Properties: Properties: Properties: Properties: Properties: PROPERTIES OF METALS • Most elements are metals • Metals have few electrons in their outer energy level • Metals are solid at room temperature except Mercury which is a liquid • Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity • Metals are malleable which means they can be flattened into thin sheets • Metals are ductile which means they can be drawn into thin wires • Metals are shiny PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS • Nonmetals are located right of the Zig Zag line • Nonmetals have almost a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level • Nonmetals are mostly gases at room temperature • Nonmetals are not good conductors of heat & electricity • Nonmetals are not malleable • Nonmetals are not ductile – they are brittle and will break or shatter when hit with a hammer • Nonmetals are not shiny PROPERTIES OF METALLOIDS • Metalloids are also called semiconductors • Metalloids border the Stairs • Metalloids have a ½ complete set of electrons in their outer energy level • Metalloids have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. EXAMPLES OF METALLOIDS • Tellurium-shiny but brittle • Silicon-semiconductor • Boron-hard but brittle and a good conductor of electricity PROPERTIES OF NOBLE GASES • Noble Gases are Family 18 • Noble Gases have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level – all but Helium have 8. Helium has 2. • Noble Gases are gases at room temperature • Noble Gases are nonmetals PROPERTIES OF NOBLE GASES • • • • Noble Gases are colorless Noble Gases are odorless Noble Gases are unreactive Noble Gases are found in very small amounts on Earth EXAMPLES OF NOBLE GASES • • • • • Helium Argon Krypton Xenon Radon (Radioactive gas) • The periods grow in size on the table from top to bottom. The first period has only two elements, hydrogen (atomic number 1) and helium (atomic number 2). The second and third periods each contain eight elements, and the next two periods each contain 18 elements. • The last two periods contain 32 elements. To make the table easier to read, some of these elements are placed at the bottom of the table. • The table is organized so that elements with similar configurations of valence electrons are placed in the same column, or group. – Atoms of elements in Group 1 (including hydrogen, lithium, and sodium) each have one valence electron. – Atoms of elements in Group 17 (including fluorine, chlorine, and bromine) each have seven valence electrons. • • Valence electrons help determine the chemical properties of an element. This means that the elements in a group all have similar chemical properties. Metals, Metalloids and Non-Metals Metalloids Noble Gases Metalloids Noble Gases Metals Non-Metals Metals Non-Metals Metals Metalloids Non-Metals Noble Gases Electrons Components of an Atom Protons Neutrons Metalloids Noble Gases Metalloids Noble Gases Metals Non-Metals Metals Non-Metals Glue Nows! Atomic Structure Atomic Structure As you answer these questions, remember that atoms tend to be most stable when their outer energy level is full with electrons. They gain, lose, or share their outer electrons— called valence electrons—to achieve a full outer set. As you answer these questions, remember that atoms tend to be most stable when their outer energy level is full with electrons. They gain, lose, or share their outer electrons— called valence electrons—to achieve a full outer set. 1. Of the 10 atoms you modeled, which 2 are the most stable? Explain. 1. Of the 10 atoms you modeled, which 2 are the most stable? Explain. 2. Look at the electron structures for lithium and fluorine. In a chemical reaction, the valence electron of a lithium atom transfers to the fluorine atom. This changes both atoms into ions. Explain why this reaction occurs. 2. Look at the electron structures for lithium and fluorine. In a chemical reaction, the valence electron of a lithium atom transfers to the fluorine atom. This changes both atoms into ions. Explain why this reaction occurs. 3. When hydrogen and oxygen react, they combine in a 2-to-1 ratio to form a molecule of water (H 2 O). In this reaction, each of the 2 hydrogen atoms shares its valence electron with 1 oxygen atom. Explain why this reaction takes place in terms of the number of valence electrons. 3. When hydrogen and oxygen react, they combine in a 2-to-1 ratio to form a molecule of water (H 2 O). In this reaction, each of the 2 hydrogen atoms shares its valence electron with 1 oxygen atom. Explain why this reaction takes place in terms of the number of valence electrons. Sub-Atomic Particle Electrical Charge Mass Location in Atom Sub-Atomic Particle Electrical Charge Mass Location in Atom SubAtomic Particle Electrical Charge Mass Location in Atom 8. a • • Key Concepts An atom is the basic component of matter. All the atoms of a specific element, such as hydrogen, are similar. Elements are the basic substances or building blocks that make other substances. For example, the elements hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. The elements sodium and chlorine combine to form table salt. • The center of an atom is called the nucleus. The nucleus contains smaller particles called protons and neutrons. The electron cloud contains electrons that surround the nucleus. The electrons can be found anywhere in the cloud, but are more likely to be found in some places than in others. The mass of the particles of an atom are recorded in unified atomic mass units (u). The mass of each proton and neutron is very close to 1 u. Electrons have almost no mass. • • Some atoms in an element can have different numbers of neutrons. Because of this, the average atomic mass of the atoms for that element is used to describe atoms. For example, about 99 percent of carbon atoms in nature have a mass of 12 u. About 1 percent of carbon atoms have a mass of about 13 u. To find the average, perform the following calculation: • • 0.99 x 12 u + 0.01 x 13 u = 12.01 u The average mass of a carbon is about 12.01 u. • Protons and electrons have electric charge. Opposite charges attract, whereas like charges repel. The proton has a positive charge, and the electron has a negative charge. The neutron does not have a charge. 8.5 B • Scientists have identified over 100 elements. Each element is made of a characteristic type of atom. All atoms contain a central core called the nucleus. The nucleus contains one or more protons, which are positively charged particles. Most nuclei also contain neutrons, which are uncharged particles. Neutrons help keep the nucleus from breaking apart. Surrounding the nucleus are fast-moving electrons, which are very small, negatively charged particles. • The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons in the atomic nucleus. For example, every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. Every oxygen atom has eight protons. • The number of protons per atom is called the atomic number of the element. Helium has an atomic number of 2. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8. • Atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. Most helium atoms have two neutrons, but some have only one neutron. • Every atom is electrically neutral. Protons carry the positive charge of the atom, and electrons carry the negative charge. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. • Electrons are organized into energy levels. The first energy level is filled with two electrons, and the second energy level is filled with eight electrons. For the first 20 elements, eight electrons also fill the third energy level. The diagram shows the first three elements that have full energy levels: helium, neon, and argon. • The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons. Atoms tend to be most stable when they have filled outermost energy levels. To reach this stability, atoms gain, lose, or share valence electrons by forming chemical bonds with other atoms. Questions? • The atomic number of oxygen is 8. What do all oxygen atoms have in common? • How many possible electrons are in the first and second energy levels? • What are valence electrons? How do valence electrons affect the chemical properties of an element? • Describe the chemical reaction that occurs between sodium, whose atoms have 1 valence electron, and chlorine, whose atoms have 7 valence electrons Petri Dish Elements Element Protons Neutrons Electrons Valence Electrons Metal, NonMetal, Metalloid Period Group Petri Dish Elements Element Protons Neutrons Electrons Valence Electrons Metal, NonMetal, Metalloid Period Group 8.5C • The Periodic Table arranges elements in rows, called periods, and columns, called groups. The order of the elements is determined by atomic number. • The periods grow in size on the table from top to bottom. The first period has only two elements, hydrogen (atomic number 1) and helium (atomic number 2). The second and third periods each contain eight elements, and the next two periods each contain 18 elements. • The last two periods contain 32 elements. To make the table easier to read, some of these elements are placed at the bottom of the table. • The table is organized so that elements with similar configurations of valence electrons are placed in the same column, or group. Atoms of elements in Group 1 (including hydrogen, lithium, and sodium) each have one valence electron. Atoms of elements in Group 17 (including fluorine, chlorine, and bromine) each have seven valence electrons. • Valence electrons help determine the chemical properties of an element. This means that the elements in a group all have similar chemical properties. • The Periodic Table can be used to predict many properties of elements. Metals are located on the left side and in the center of the table, while nonmetals are clustered on the right side. A staircase-like line divides the two groups. Elements called metalloids, which have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals, are located along this line. Teks for Unit 1 and 2 • (5) Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: • • Unit 1 (A) describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud; (B) identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity; (C) interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements; • • • • • • Unit 2 (D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; (E) investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed; and (F) recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. Chemistry Vocabulary, Unit 1, part 1 atom: the smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of that element element: a pure substance, made up of similar atoms, that cannot be broken down by chemical means nucleus: the center of an atom, which contains protons and neutrons proton: the subatomic particle in the nucleus that has a positive electric charge neutron: the subatomic particle in the nucleus that has no electric charge electron cloud: the region around the nucleus where electrons are found electron: the negatively charged subatomic particle that exists in a cloud surrounding the nucleus unified atomic mass unit (u): the unit for measuring the mass of atoms electric charge: a property of matter that causes it to experience a force near other charged matter valence electrons: the outermost electrons of an atom, which help determine an element’s chemical properties ion: an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons chemical bond: an attractive force between atoms or ions, formed by the sharing or transfer of valence electrons Periodic Table: a logical arrangement of the elements into rows and columns; an element’s position in the Periodic Table can be used to predict its properties The Periodic Table: A meeting of the elements The Periodic Table: A meeting of the elements Draw two elements from the element bag on the teachers desk. Write a minimum of 8 sentences of a discussion that might occur between the two elements. Draw two elements from the element bag on the teachers desk. Write a minimum of 8 sentences of a discussion that might occur between the two elements. ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________