Organizer
advertisement
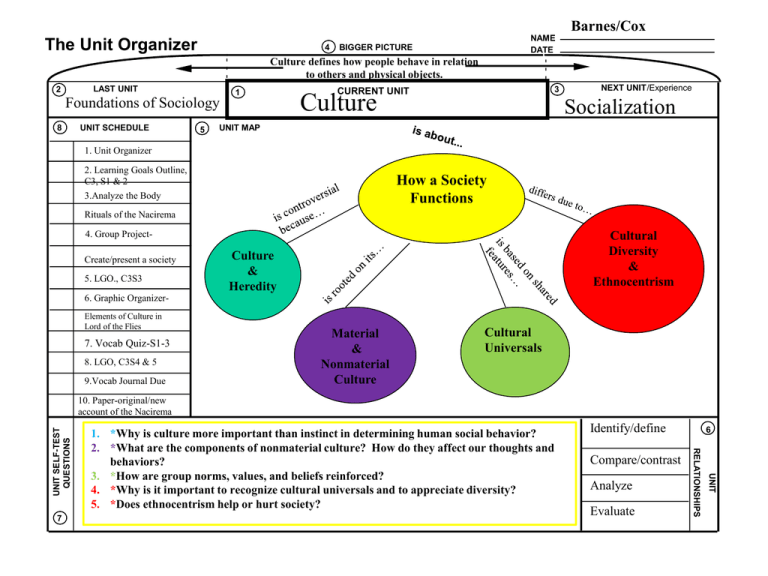
Barnes/Cox The Unit Organizer 4 NAME DATE BIGGER PICTURE Culture defines how people behave in relation to others and physical objects. LAST UNIT 2 Foundations of Sociology 8 UNIT SCHEDULE 5 1 3 CURRENT CURRENT UNIT UNIT Culture NEXT UNIT/Experience Socialization UNIT MAP 1. Unit Organizer 2. Learning Goals Outline, C3, S1 & 2 3.Analyze the Body How a Society Functions Rituals of the Nacirema Cultural Diversity & Ethnocentrism 4. Group ProjectCreate/present a society 5. LGO., C3S3 6. Graphic OrganizerElements of Culture in Lord of the Flies 7. Vocab Quiz-S1-3 8. LGO, C3S4 & 5 9.Vocab Journal Due Culture & Heredity Material & Nonmaterial Culture Cultural Universals Identify/define Compare/contrast Analyze Evaluate 6 UNIT 7 1. *Why is culture more important than instinct in determining human social behavior? 2. *What are the components of nonmaterial culture? How do they affect our thoughts and behaviors? 3. *How are group norms, values, and beliefs reinforced? 4. *Why is it important to recognize cultural universals and to appreciate diversity? 5. *Does ethnocentrism help or hurt society? RELATIONSHIPS UNIT SELF-TEST QUESTIONS 10. Paper-original/new account of the Nacirema Culture The Unit Organizer 9 NAME DATE Barnes/Cox Expanded Unit Map How a Society Functions Cultural Diversity & Ethnocentrism Culture & Heredity Nature vs. Nurture Debate-p73 Culture-blueprint for behavior-p. 72 Instincts, Reflexes & Drives-p. 73 Twin Studies-p.73 NEW UNIT SELF-TEST QUESTIONS 10 Cultural Universals Material & Nonmaterial Culture Material Culture-p. 92-93 Concrete, Tangible objects (cars, etc..) Nonmaterial Culture: Symbols-p. 77 Language-p.77-79 Norms Values-p. 89 Sanctions Beliefs-p. 92 General traits that exist in all cultures-p.. 102 (70+ traits) Cultural changesp.95 Social categoriesp.98 Subculture-p. 98 Counterculture-p. 98 Ethnocentrism-p. 98 pros and cons Folkways, Mores, Laws, Taboos-p. 81-85 Formal vs. Informal, Positive vs. Negative-p. 87-88








