Cultural Diversity
advertisement

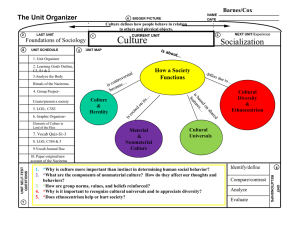
Cultural Diversity Unit 2 Pick up 2 handouts! Warm Up – On a piece of notebook paper, list five items found in your house or apartment that would tell a visitor to which culture you belong and explain how that item is specific to only your culture. Be prepared to defend your choices to the class. Material or Nonmaterial Culture? Material culture – physical objects that people use and create. Material or Nonmaterial Culture? Material culture – physical objects that people use and create. Nonmaterial culture – abstract human creations such as language, religion, beliefs, ideas, skills, government, etc. Material or Nonmaterial Culture? Using the items you wrote down for the warm up, label each one as either material or nonmaterial. If all your items are nonmaterial, think of at least two objects in your home that symbolize your nonmaterial culture. For example, a Bible would symbolize that you are a Christian. (NO! You may not use this one!) Components of Culture Component Technology Symbols Language Values Norms Description Example Components of Culture Component Description Example Technology Objects and rules for using those objects. Fork, computer Symbols An object, gesture, word, sound event, etc; which carries a shared meaning. Language Organization of written or spoken symbols into a standardized system. Values Shared beliefs about what is good or bad, right or wrong, desirable or undesirable. Norms Shared rules of conduct that tell people how to act in specific situations. Folkways Folkways are norms that describe socially acceptable behavior, but do not have great moral significance. A handshake is a folkway. Handshakes U.S. – customary form of greeting especially among men and people in business Japan – handshake imported during American occupation after WWII. Kuwait – only more Westernized men shake hands with other men, NEVER with women. Romania – no matter how many times a Romanian sees another person during the day, there is always a handshake exchanged – used when greeting, meeting leaving and acknowledging. Mrs. Bradley needs a brave volunteer at this point for purposes of a demonstration of cultural folkways. Mores (Pronounced More A) Mores have great moral significance attached to them This relation exists because the violation of such rules endanger society’s well-being and stability. Shoplifting violates the cultural more against theft and dishonesty Laws Societies have established punishments for violating mores in order to protect the social well-being. These serious mores are formalized as laws – written rules of conduct enacted In the United States, laws cover everything from running and enforced by the stop lights to murder. government. Cultural Variation What do we have in common? Some needs are so basic that all societies must develop certain features to ensure these needs are met. Cultural universals – 65 have been identified: music, feasting, housing, cooking, etc. How a society meets its needs is widely varied. Make a list of as many of these cultural universals as you can in 1 minute. Ethnocentrism The tendency to view one’s own group and culture as superior. The cultural traits of your own group is right and good, while those of others are wrong and evil. Cultural Relativism Belief that cultures should be judged by their own standards rather than by applying the standards of another culture. Body Ritual Among The Nacirema The fundamental belief underlying the whole system appears to be that the human body is ugly and that its natural tendency is to . . . disease. Man’s only hope is to avert these characteristics through the use of ritual and ceremony. Every household has one or more shrines devoted to this purpose. The focal point of each shrine is a charm box built into the wall. In this chest are kept the many charms and magical potions without which no native believes he could live. . . Beneath the charm box is a small font. Each day every member of the family . . . enters the shrine room, bows his head before the charm box, mingles different sorts of holy water in the font and proceeds with a brief rite of ablution. A distinctive part of this body ritual is performed only by men, and includes scraping and lacerating (cutting) the surface of the skin with a sharp object. Body Ritual Among The Nacirema Unit 2 Field Study Cultural Scavenger Hunt You and your partner will be given a list of American cultural elements to search for at school and around town. The object is to get digital pictures of as many of these cultural elements as possible in a limited time. The team with pictures of the most elements will be awarded with first prize and a 100 on the vocabulary test for Unit 2. Put your digital photos into a PowerPoint presentation. You may put several pictures – labeled with the cultural element each picture represents – onto one slide. If you cannot obtain a digital camera, there is a journaling option for this assignment. Warm Up: Sociology – Tuesday, January 30, 2007 Define subculture on a piece of paper. Today is a WORK DAY and vocabulary test day. Complete any remaining Unit 2 Cultural Diversity work. Subculture As Americans, we share a common culture with all other Americans. American culture is a collection of traits that are distinct from those of other societies. In addition to these cultural features some groups share values and behaviors that are not shared by the entire population. Counterculture A group rejection of the major values, norms, and practices of the larger society and replaces them with a new set of cultural patterns. Generally, countercultures operate outside the law. Warm Up: Sociology – Thursday, February 1, 2007 Define Counterculture. Today is a WORK DAY and vocabulary test day. Complete any remaining Unit 2 Cultural Diversity work. Complete your PowerPoint presentation for your field study. Presentations will be the last 45 minutes of class.