3.2 Costs and Costing Methods KGL
advertisement

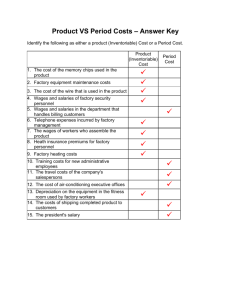
IB Business and Management 3.2 – Costs and Revenues LEARNING OUTCOMES • Define, explain and give examples of each different type of cost (AO2): – Fixed – Variable – Semi-variable – Direct – Indirect/Overheads • Total Revenue and revenue streams, using examples (AO2) COST CLASSIFICATIONS Why are costs important? If businesses do not keep a record of costs then they will be unable to take effective and profitable decisions. Keeping cost records allow comparisons to be made with past periods of time. Past cost data can help to set budgets for the future. Costs we need to know about… – – – – – Fixed Variable Semi-variable Direct Indirect In Pairs…… Can you define each of these? (Imagine you are writing a 2 mark definition answer) Fixed Costs A Fixed Cost is a cost which does not change as the level of output changes in the short run. What are some examples? What will fixed costs look like on a graph What will happen to the Fixed Cost per unit as output increases? Costs Costs are constant (the same) at all levels of production Output Variable Costs A Variable Cost is a cost which tends to change directly as the level of output changes What are some examples? What will fixed costs look like on a graph What will happen to the Fixed Cost per unit as output increases Costs Variable Costs $1500 $1000 400 600 Output Semi-variable Costs Costs with both a fixed and a variable element. Often the cost is fixed up to a certain level of output and then becomes variable after that level is exceeded Examples? -Telephone Bill -Electricity Bills -Some Labour costs Can you explain why these costs are semi-variable? Direct Costs A direct cost is a cost that can be completely attributed to the production of specific goods or services. Direct costs refer to materials, labor and expenses related to the production of a product. What would be the direct costs of producing a big mac? Indirect Costs Indirect Costs are costs which cannot be accurately attributed to specific cost objects. They typically benefit multiple cost objects and it is not possible to accurately trace them to individual products, activities or departments. Indirect costs are often referred to as overheads or expenses Task The following costs are incurred by a factory on the production of cupboards: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Laborers' wages Synthetic wood Power consumption Glass Nails and screws Factory insurance Handles, locks and hinges Wood Supervisors' salaries Factory depreciation Varnish, glue, paints Factory manager's salary TYPICAL OVERHEADS Production Overheads Factory rent, rates, power, depreciation of equipment. Administrative Overheads Office rent and rates, clerical and executive salaries Selling and Distribution Overheads Warehouse, salaries of sales staff Finance Overheads Interest on bank loans and debentures Identify the costs….. Fixed Costs Variable Costs Semi Variable Costs Direct Costs Indirect Costs What is meant by revenue? REVENUE Revenue Revenue or turnover is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. So what types of income does revenue NOT include? Calculating Revenue Revenue = Selling Price X Quantity Revenue Streams • A revenue stream is a form of revenue. Revenue streams refer specifically to the individual methods by which money comes into a company What are the revenue streams? Increasing Revenue Revenue = Selling Price x Quantity • How can Revenue be increased?? • Increasing quantity will increase revenues • Increasing the price will sometimes increase revenue • This depends on the price elasticity of the product PROFIT Calculating Profit Profit = Total Revenue Total Costs Question A gnome manufacturing firm has the following costs: Loan Repayments: Salaries: Electricity: Materials: Packaging: £100 per month £2000 per month £150 per month £5 per unit £1 per unit The Gnomes sell for £15 What would their monthly profit be if they make and sell 500 gnomes? What would the monthly profit be if they make and sell 1,000 gnomes? Profit = Revenue – Total Costs • • • • How can profit be increased?? Profit can be increased by: Increasing Revenues Reducing Costs • If costs are reduced this must be done in a way that does not affect the quality of the product or consumer demand