Topic 4-6 Review
advertisement

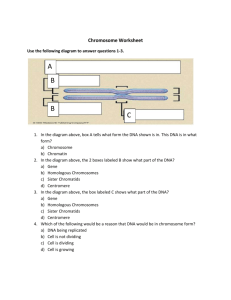
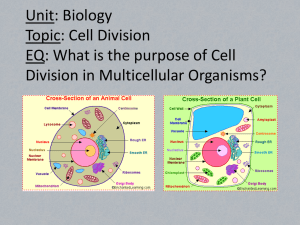
Topic 4-6 Review - Biodiversity Be able to define the following: a. Allele: One of two or more alternative forms of a gene that are found at the same place on a chromosome. One allele is from the Mother, one allele is from the Father. b. Gene: A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. (ex: blue eyes) c. Genetics: The study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics. DNA is the shortened form of this:__Deoxyribonucleic Acid_________ What is this structure called? _____Chromosome_______ Chromosomes are made of what? _____DNA___________ In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA. The structure is a ____double helix____, which is like a twisted ladder. The sides of the DNA ladder (backbone) are made of alternating __sugars___ and ___phosphates____ molecules. The bases in DNA are known by these letters: Check your notes These bases always bond in a certain way. Adenine will only bond to Check your notes Guanine will only bond with Check your notes Write the complimentary DNA sequence: ATGCACATAGTCAATCGGCTAA TACGTGTATCAGTTAGCCGATT CELL DIVISION Asexual: Word Bank: CHROMOSOMES, MITOSIS, Reproduction involves only __ONE__ parent. All of the offspring are genetically __IDENTICAL____ to the parent. In single cell organisms, ___BINARY FISSION_______ enables the parent cell to split its contents __EQUALLY_____ between the two new cells. Prior to division, parent cells must ___DUPLICATE____ their DNA and when the split takes place each new cell receives a complete and exact copy of the DNA from the parent. In multi-cellular organisms the process that produces two new cells with the same number of ___CHROMOSOMES______ is called _________MITOSIS_______. STAGES OF MITOSIS Please draw in and label each of the following stages of Mitosis (2 chromosomes) Interphase Sexual: Word Bank: Sexual reproduction usually involves ___TWO___ individual organisms. The offspring that are produced from this union have genetically ___DIFFERENT____ characteristics, half from one __PARENT____ and the other half from the other parent - making a ___UNIQUE____ offspring. During sexual reproduction, the specialized sex cells (_GAMETES___) unite to form a ___ZYGOTE____, which develops into the new organism. Male gametes are called ___SPERM_____ and female gametes are called ____EGG_____ . ___MEIOSIS___is a type of cell division that produces cells with only ___HALF__ the DNA of a normal cell. This process involves two ____CELL DIVISION_____, not one. Please draw in and label each of the following stages of Meiosis (2 chromosomes) Interphase I Interphase II Word Bank: All human cells contain __46___ chromosomes. In order to have a complete human organism, all of the chromosomes must be present. Not all organisms have the same number of chromosomes (Dogs have 78, cats have 38). Every cell of a human contains __23___ pairs of chromosomes (dogs 39, cats 19). Not all of the chromosomes from species to species are the same, which accounts for the different characteristics between the species. Genes are located in the ____CHROMOSOMES_____ and come in pairs. Each chromosome has numerous ___GENE_____ locations. Both genes in a pair carry DNA instructions for the same thing. Specific characteristic genes occupy matching locations on the two chromosomes. These variations in forms are called ___ALLELES_____. The ultimate combination of the chromosome pair is what makes the variation possible combining the different variations of different characteristics to create a ____UNIQUE______ variation. INHERITED/NON-INHERITED & CONTINUOUS/ DISCRETE VARIATIONS List 3 examples of inherited (heritable) characteristics 1 Eye colour 2 Skin colour 3 Check your notes Not all characteristics are inherited. Some depend entirely on the environment. Non-inherited characteristics are acquired and not necessarily passed on from generation to generation. List 4 examples of non-inherited characteristics 1 Tattoos 2 Scars 3 Check your notes List 3 examples of Continuous variations 1 Weigh 2 Height 3 Check your notes List 3 examples of Discrete variations 1 Attached/unattached earlobes 2 Blood Type 3 Check your notes Changing Our Genetic Information Factors in the environment, or random events can change genetic information contained in DNA. These changes are called mutations, and can cause changes in the structure of organisms, including people. What is the word we used to describe these MUTATIONS What are 3 examples of Mutagens? 1 UV LIGHT 2 CHEMICALS 3 CHECK YOUR NOTES Some mutations can cause a very serious disease called ___CANCER_____, which promote rapid cell division and impair full normal cell development. The cancerous cells can interfere with other cells and prevent certain processes from occurring as they should. If mutations occur in the DNA of reproductive cells, the changes can be passed on from the ___PARENT____ to the ______OFFSPRING______ Explain the drawbacks of the process of Artificial Selection. ** Please refer to your notes and/or textbook for this answer Explain what occurs during the process of each type of artificial selection technique below. Cloning To make an identical copy of the organism artificial insemination The injection of semen into the uterus other than by sexual intercourse in vitro fertilization A process by which egg cells are fertilized by sperm outside the womb Genetic engineering (Genetically Modified Organisms) the deliberate modification of the characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genetic material. Darwin explained his theory of natural selection, which could be summed up in four statements: Variation. Organisms (within populations) exhibit individual variation in appearance and behavior. These variations may involve body size, hair color, facial markings, voice properties, or number of offspring. On the other hand, some traits show little to no variation among individuals—for example, number of eyes in vertebrates. Inheritance. Some traits are consistently passed on from parent to offspring. Such traits are heritable, whereas other traits are strongly influenced by environmental conditions and show weak heritability. High rate of population growth. Most populations have more offspring each year than local resources can support leading to a struggle for resources. Each generation experiences substantial mortality. Differential survival and reproduction. Individuals possessing traits well suited for the struggle for local resources will contribute more offspring to the next generation. Why do scientists use Punnett Squares to predict heredity? They want to know the different combinations of genotypes that one of their offspring might have. So, we draw a Punnett square In hamsters, black coat color (B) is dominant to white coat color (b). A homozygous black hamster (BB) is mated with a heterozygous black (Bb)hamster. What will be the genotype and phenotype percentages be of their offspring? B b B BB Bb B BB Bb GENOTYPE: 50% BB, 50% Bb PHENOTYPE: 100% Black coat offspring In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue (b)*. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed. Draw the Punnett square that illustrates this marriage. What is the man’s genotype? What are the genotypes of the children? ** Please refer to your notes and/or textbook for this answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Across 3. DNA is arranged in the cell in compact packages, called _______________ 7. This process ensures each cell ends up with a complete set of chromosomes, identical to each other and identical to the original cell. 8. Examples of these variations include: height, shoe size, hand span, skin color, hair color 9. Examples of these variations include: tongue rolling ability, blood groups, earlobe attachment 10. those characteristics which are passed on to offspring directly from their parents. These traits are passed on by way of the genetic material 13. The base found in DNA that begins with the letter "G" 14. This is a type of cell division that produces cells with only half the DNA of a normal cell. This process involves two cell divisions, not one Down 1. This molecule (full name) is the inherited material responsible for variation (two words, no space between) 2. The base found in DNA that begins with the letter "T" 4. The base found in DNA that begins with the letter "A" 5. The base found in DNA that begins with the letter "C" 6. Examples of these includes: X-rays, ultraviolet rays, cosmic rays and some chemicals can cause mutations 11. This disease promotes rapid cell division and can impair normal cell development. 12. These are located on the chromosomes and come in pairs. Each chromosome has numerous locations for these.