Econometric Analysis of Panel Data
advertisement

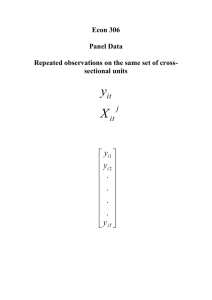
Econometric Analysis of Panel Data • Panel Data Analysis – Random Effects • • • • Assumptions GLS Estimator Panel-Robust Variance-Covariance Matrix ML Estimator – Hypothesis Testing • Test for Random Effects • Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects Panel Data Analysis • Random Effects Model yit xit' β ui eit (t 1, 2,..., Ti ) y i Xi β ui iTi ei (i 1, 2,..., N ) – ui is random, independent of eit and xit. – Define eit = ui + eit the error components. Random Effects Model • Assumptions – Strict Exogeneity E (eit | X) 0, E (ui | X) 0 E (e it | X) 0 • X includes a constant term, otherwise E(ui|X)=u. – Homoschedasticity Var (eit | X) e2 , Var (ui | X) u2 , Cov(ui , eit ) 0 Var (e it | X) e2 e2 u2 – Constant Auto-covariance (within panels) Var (εi | X) e2ITi u2iTi iT' i Random Effects Model • Assumptions – Cross Section Independence Var (ε i | X) i e2 ITi u2 iTi iT' i 1 0 0 2 Var (ε | X) Ω 0 0 0 0 N Random Effects Model • Extensions – Weak Exogeneity E (e it | xi1 , xi 2 ,..., xiTi ) E (e it | Xi ) 0 E (e it | xi1 , xi 2 ,..., xit ) 0 E (e it | xit ) 0 – Heteroscedasticity 2 eit 2 2 Var (e it | Xi ) ui Var (eit | Xi ) ui 2 ei Random Effects Model • Extensions – Serial Correlation eit 1 vit yit x β ui eit , eit i eit 1 vit ' it – Spatial Correlation yit xit' β e it , e it wije jt eit , eit ui vit j Model Estimation: GLS • Model Representation y i Xi β εi , εi ui iTi ei E (εi | Xi ) 0 Var (εi | Xi ) i e2 ITi u2 iTi iT' i 2 2 T 2 e i u e Qi ITi Qi 2 e 1 where Qi ITi iTi iT' i Ti Model Estimation: GLS • GLS ˆβ ( XΩ 1X) 1 XΩ 1y N X 1X GLS i 1 i i i 1 1 N 1 1 ˆ Var (βGLS ) ( XΩ X) i 1 Xi i1Xi 2 1 1 e where i 2 Qi 2 ITi Qi 2 e e Ti u and 1/2 i e2 1 ITi Qi Qi 2 2 e e Ti u 1 X i 1 i i y i N Model Estimation: RE-OLS • Partial Group Mean Deviations yit xit' β e it xit' β (ui eit ) yi xi' β (ui ei ) i 1 e2 e2 Ti u2 yit i yi (xit' i xi' )β [(1 i )ui (eit i ei )] yit xit' β e it Model Estimation: RE-OLS • Model Assumptions E (e it | xi' ) 0 Var (e it | xi' ) (1 i ) 2 u2 (1 2i / Ti i 2 / Ti ) e2 e2 Cov(e it , e is | xi' ) (1 i ) 2 u2 (2i / Ti i 2 / Ti ) e2 0, t s Note : i 1 • OLS e2 e2 Ti u2 N βˆ OLS ( X' X)1 X' y i 1 Xi' Xi 1 N i 1 Xi y i ˆ (βˆ ) ˆ 2 ( X' X) 1 ˆ 2 N X' X Var OLS e e i 1 i i ˆ 2 εˆ ' εˆ / ( NT K ), εˆ y Xβˆ e 1 Model Estimation: RE-OLS • Need a consistent estimator of : ˆi 1 ˆ e2 ˆ e2 Tiˆ u2 – Estimate the fixed effects model to obtain ˆ e – Estimate the between model to obtain T ˆ u2 ˆ v2 – Or, estimate the pooled model to obtain ˆ e2 ˆ u2 – Based on the estimated large sample variances, it is safe to obtain 0 ˆ 1 2 Model Estimation: RE-OLS • Panel-Robust Variance-Covariance Matrix – Consistent statistical inference for general heteroscedasticity, time series and cross section correlation. ˆ (βˆ ) E[(βˆ β)(βˆ β) '] Var 1 N i 1 X Xi i 1 X εˆ εˆ Xi i 1 Xi' Xi N ' i N 1 ' ' i i i 1 N Ti N Ti Ti N Ti ' ' ˆ ˆ ' i 1 t 1 xit xit x x e e x x i 1 t 1 s 1 it is it is i 1 t 1 it it εˆ i y i Xi βˆ , eˆit yit xit' βˆ 1 Model Estimation: ML • Log-Likelihood Function yit xit' β (ui eit ) xit' β e it y i Xi β ε i (t 1, 2,..., Ti ) (i 1, 2,..., N ) εi ~ iidn(0, i ), i e2ITi u2iTi iT' i Ti 1 1 lli (β, , | y i , Xi ) ln 2 ln i εi i1εi 2 2 2 2 e 2 u Model Estimation: ML • ML Estimator N 2 2 ˆ ˆ ˆ (β, e , u ) ML arg max i 1 lli (β, e2 , u2 | y i , Xi ) where Ti 1 1 ln 2 ln i εi i1εi 2 2 2 Ti 1 e2 T u2 2 ln 2 e ln 2 2 e2 2 2 1 Ti Ti ' 2 ' u ( yit xit β) 2 t 1 ( yit xit β) 2 e Ti u2 t 1 2 e lli (β, e2 , u2 | y i , Xi ) Hypothesis Testing To Pool or Not To Pool, Continued • Test for Var(ui) = 0, that is Cov(e it ,e is ) Cov(ui eit ,ui eis ) Cov(eit ,eis ) – If Ti=T for all i, the Lagrange-multiplier test statistic (Breusch-Pagan, 1980) is: 2 2 N T 2 ' ˆ e NT eˆ ( I N J T )eˆ NT i 1 t 1 it 2 LM 1 1 ~ (1) N T ' 2 2 T 1 eˆ eˆ 2 T 1 eˆit i 1 t 1 βˆ ' where eˆit yit xit 1 , J T iT iT' uˆ Pooled Hypothesis Testing To Pool or Not To Pool, Continued – For unbalanced panels, the modified BreuschPagan LM test for random effects (Baltagi-Li, 1990) is: 2 2 Ti N ˆ T e i1 i i 1 t 1 it 2 LM 1 ~ (1) N Ti N 2 2 i 1 Ti (Ti 1) i 1 t 1 eˆit N 2 – Alternative one-side test: LM ~ N (0,1) under H 0 P Value : Prn ( z LM ) Hypothesis Testing To Pool or Not To Pool, Continued • References – Baltagi, B. H., and Q. Li, A Langrange Multiplier Test for the Error Components Model with Incomplete Panels, Econometric Review, 9, 1990, 103-107. – Breusch, T. and A. Pagan, “The LM Test and Its Applications to Model Specification in Econometrics,” Review of Economic Studies, 47, 1980, 239-254. Hypothesis Testing Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects H 0 : Cov(ui , xit' ) 0 (random effects) H1 : Cov(ui , xit' ) 0 ( fixed effects) Estimator Random Effects E(ui|Xi) = 0 Fixed Effects E(ui|Xi) =/= 0 GLS or RE-OLS (Random Effects) Consistent and Efficient Inconsistent LSDV or FE-OLS (Fixed Effects) Consistent Inefficient Consistent Possibly Efficient Hypothesis Testing Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects • Fixed effects estimator is consistent under H0 and H1; Random effects estimator is efficient under H0, but it is inconsistent under H1. • Hausman Test Statistic ' 1 H βˆ RE βˆ FE Var (βˆ RE ) Var (βˆ FE ) βˆ RE βˆ FE ~ 2 (# βˆ FE ), provided # βˆ FE # βˆ RE (no intercept ) Hypothesis Testing Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects • Alternative (Asym. Eq.) Hausman Test – Estimate any of the random effects models ( yit yi ) (xit' xi' )β (xit' xi' ) γ eit (or , random effects model : yit xit' β ( xit' xi' ) γ eit ) ( yit yi ) (xit' xi' )β xi' γ eit ( yit yi ) (xit' xi' )β xit' γ eit – F Test that g = 0 H0 : γ 0 H 0 : Cov(ui , xit ) 0 Hypothesis Testing Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects • Ahn-Low Test (1996) – Based on the estimated errors (GLS residuals) of the random effects model, estimate the following regression: eˆ ( X ˆ X )β X γ e it it i NTR ~ (# γ ) 2 2 i it Hypothesis Testing Fixed Effects vs. Random Effects • References – Ahn, S.C., and S. Low, A Reformulation of the Hausman Test for Regression Models with Pooled Cross-Section Time-Series Data, Journal of Econometrics, 71, 1996, 309-319. – Baltagi, B.H., and L. Liu, Alternative Ways of Obtaining Hausman’s Test Using Artificial Regressions, Statistics and Probability Letters, 77, 2007, 1413-1417. – Hausman, J.A., Specification Tests in Econometrics, Econometrica, 46, 1978, 1251-1271. – Hausman, J.A. and W.E. Taylor, Panel Data and Unobservable Individual Effects, Econometrics, 49, 1981, 1377-1398. – Mundlak, Y., On the Pooling of Time Series and Cross-Section Data, Econometrica, 46, 1978, 69-85. Example: Investment Demand • Grunfeld and Griliches [1960] I it i Fit g Cit e it – i = 10 firms: GM, CH, GE, WE, US, AF, DM, GY, UN, IBM; t = 20 years: 1935-1954 – Iit = Gross investment – Fit = Market value – Cit = Value of the stock of plant and equipment