11 Project Management in Action

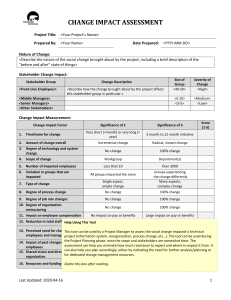
The University of California
Berkeley Extension
1
X470 Project Management
Lisa Bausell
X470 Project Management
1 Project Management
Introduction
Project Initiation
2 Project Planning
Scope
Workflow
3 Project Planning
Resources
Finalization
4 Project
Baseline
Monitor & Control
5 Project
Reporting & Communication
Closure
6 Project Management
Review
Presentations
2
Official Roster and Grade Option
1. DO NOT fill in your final grade, I’ll do that!
2. Double check your name on the roster and note any needed changes after your name
3. Write in the Grade Option you have selected
CLG – Credit Letter Grade
CP/NP - Credit Pass/Not Pass
NC - Not for Credit
4. Sign (Student Signature)
3
4
• Name on paper
Final
• Complete final and turn it in
• Ask me questions if you don’t understand something
• We will finish when everyone is done
5
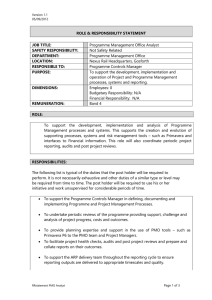
Project Closure
• Close Project
• Verify Scope
• Assess Lessons Learned
• Present Final Projects
Close Project (or Phase)
Finalize all activities across all the project management process groups to formally complete the project or phase. (PMBOK 4.6)
• Verify scope and obtain project sign-off.
• Recognize accomplishments.
• Send a final project report to communicate that the project is done.
• Assess Lessons Learned.
• Archive project data.
6
Verify Scope
Formalize acceptance of the completed project deliverables. (PMBOK 5.4)
Although scope verification is done at the end of a project (or phase/iteration), success depends on earlier work. As you approach completion, validate:
• Requirements for each project deliverable
• Tests and acceptance criteria
• Who will be responsible for evaluating results and formally accepting project deliverables
7
Obtain Project Sign-off
Within your team, verify that all project deliverables at least meet all agreed-upon acceptance criteria.
Present your project results to the individual stakeholders who will evaluate them, and request formal sign-off.
If there are issues, work to resolve them promptly, through:
• Fixing the problems
• Negotiating scope changes consistent with delivered results
(If issues persist, propose project baseline changes for additional effort or budget needed to obtain sign-off.)
8
Recognize Accomplishments
• Thank project team members in person, or at least in writing, for their contributions to the project’s success.
• Praise people publicly (as culturally appropriate).
• Reward people using available recognition programs.
• Celebrate success. Schedule similar events for global teams
9
Send a Final Project Report
A final project report is similar to a typical status report, with particular attention to:
• Project completion and success.
• Significant results.
• Recognition for the work done by specific contributors.
• Final project statistics and other metrics.
Let people know you are done!
10
11
Project Management in
Action
• PMO
• Project Charter
• Project Scope
• Project Estimates
• Project Risks
12
PMO
Successes and Failures
13
What problems are we trying to solve?
• Each business unit doing “their” projects
• Project selection by loudest voice
• Project failure rate too high
• Lack of consistency
• Resources not coordinated
• Project rollout not well planned
14
Services of a PMO
• Data for project selection
• Standards and metrics
• Policies
• Resource Management
• Software
• Time tracking
• Cost tracking
• TRANSPARENCY
15
PMO Involvement
16
• PSO
• PMO
• EPMO
Definition
Projects and Programs
“A program is defined as a group of related projects managed in a coordinated way… A project may or may not be part of a program, but a program will always have projects.”
Project
Program
Project
Project
Project Project
17
18
Portfolio
Program
Project
19
Who are the customers of the
PMO
• Project Managers
• Stakeholders
• Sponsors
• Executives
• Department Managers
20
PMO – Keeper of the stats
• Lessons learned
• Trending
• Find projects in trouble early
• Executive decision making support
• Resource planning (past, current, future)
Link to corporate strategy
21
Help to do the right projects and not just do projects right
Strategic planning/project committees
– Finance
– IT
– Business
– HR
– Link to CEO
22
PMO in action
• Who do the PMs work for?
• Who makes decisions of what projects to do?
• Delivery of updates and news
(PMO? PM’s?)
23
PMO Road to Failure
24
Problems
• Perception ? Reality?
– No buy-in
– Bad for cowboys and cowgirls
– Too much time needed to track
– Cumbersome process holds up work
– Neutralizes power
24
25
Case study
How not to start a PMO
• Do too much at once
• Bring in consultants to do all the planning
• Plan for MONTHS and then implement everything
• Don’t get participation from all levels
• Go too slow or too fast
25
26
Success tips for PMO’s
• Executive support
• User support
• PM’s need to see the benefit
• Scope in line with organization
• Show value immediately
• Deliver news to different audiences in different ways
• Continuous improvement!
27
PMO Maturity
28
Project Management in
Action
• PMO
• Project Charter
• Project Scope
• Project Estimates
• Project Risks
Project Charter
Project charters include information such as:
• Project purpose or justification
• Project leader/manager
• Project sponsor authorizing the work
• Measurable objectives and initial requirements
• Milestone schedule
• Initial budget
• Completion criteria
• High-level risks
29
Project Scope
“Developing a detailed description of the project and product.” (PMBOK 5.2)
Scope definitions may be called (or be part of):
• Project Charter
• Project Data Sheet
• Proposal
• Reference Specifications
• Statement of Work
• Plan of Record
• …
Whatever you call it, write it down .
30
• Accuracy
Project Estimates
• Getting input
• “Budget” estimates
• Creating a baseline
• Measuring results
• Making changes
31
Project Risks
• Identify specifics, not just general risks.
• List the “Top 10”—Keep risks visible.
• Document contingency plans.
• Assign triggers and owners.
• Plan responses to all big risks and document all risks.
• Assess project size (effort months).
• Establish project contingency reserves, based on risk
(time and/or budget).
32
Risk Responses
Brainstorm responses to risks, considering:
• Avoidance (Replan project to remove the risk)
• Mitigation (Revise plans to lower risk probability and/or impact)
• Transfer (Shift all or part of risk impact to others)
• Acceptance (Leave plans unchanged, but monitor the risk, and where appropriate, establish contingency plans for recovery.)
33
34
Present Final Projects
Your turn!
Course Evaluations
Course Title: Project Management
Instructor: Lisa Bausell
Term Fall Year: 2013
Today’s Date: 11/01/2013
EDP
35