Properties of Earth_s Atmosphere 2014
advertisement

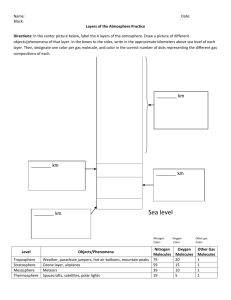
Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere ESRT p1, 14 All information regarding the earth’s composition Is found on p 1 ESRT atmosphere Earth’s Atmosphere is • A thin layer of gases that surrounds the Earth • A protective layer from the Sun’s ultraviolet radiation due to Ozone in the stratosphere • Divided in layers based upon temperature variations Selected Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere p14 Earth Science References Tables (2011ed): Selected Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere • Do Now: Take out ESRT and open to page 14. In your notebook, summarize what you learned by graphing the various atmospheric layers vs. their temperature. After you complete this see the directions that follow. Directions: Check off as you complete! • 1._____Using a highlighter, highlight the 4 layers of the atmosphere 2._____Highlight the x-axis and the y-axis 3._____Circle the three headings- Temperature zones, Atmospheric pressure, and Water vapor • Answer the following: 1. State the temperature ranges for the Troposphere_______to____________ • Stratosphere_______to___________ • Mesosphere_______to____________ • Thermosphere______to____________ 2.. List the boundaries (or interfaces!):____________________ ______________ 3. What is the atm pressure 10km up?___________________ 4. What is the water vapor concentration at sea level?_________________ Why?_________________________ ________________________ 5.What is the temperature at the interface between the troposphere and the stratosphere?__________________ 6.Which layer do we live in?_________________________ 7. Which layer do airplanes fly in?______________________ State one conclusion below based on the information in this chart: • Think about (It Says…I Say…And So…) • 1. What does the chart say? • 2. What do I know or say? • 3. Combine the information in the chart and what you know to come up with your inference…and so Make a chart in your notes…if it helps o The Ozone Hole is recreated every Spring at the South Pole as the winds die down. http://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/ o It formed due to chlorofluorocarbons or CFC’s o The Montreal Protocol was an international treaty signed to protect the Ozone layer in 1981 The Northern Lights or the Aurora Borealis Wrap up: Knowing what you know now about the earth’s atmosphere, infer how the sun pillar formed in the picture below: From EPOD:


![Earth's Atmosphere Earths Atmosphere [Autosaved]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010123574_1-f1783c71f4d74c47566894d317b29466-300x300.png)