Discussion Problems
advertisement

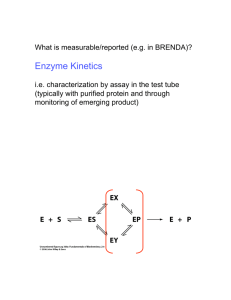
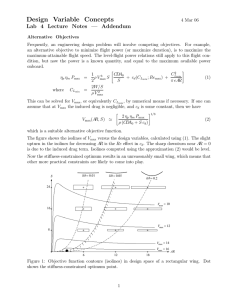
Discussion Problems BT 3016 Protein Structure • How do the amino acids differ from one another structurally? • What properties differ? • What are the kinds of secondary structure? Describe them. • What is quaternary structure? • What causes proteins to fold? Structure - continued • What is a Ramachandran diagram? • What are the four classifications of protein folds? • How can you identify a transmembrane protein? pH, pKa, HH equation • What is the charge on an amino acid in a solution that is 0.1 unit below its pI? • How do you make a buffer of a particular pH and concentration? 50mM glycine buffer, pH 8.8 • What is its ionic strength? Solubility • Describe three ways to cause a protein to precipitate? • Describe three ways to cause an insoluble protein to dissolve? Separations • What techniques separate according to the size of a protein? • What techniques separate according to charge on a protein? • What techniques separate based on a combination of both charge and size? Separation by Size • What fundamental difference is there between determination of molecular weight by SDS PAGE and by Size Exclusion chromatography? Which will separate? Mr (subunit) subunits pI Charge @ pH 8 A 14,200 Monomer 9.5 +14 B 13,900 monomer 5.6 -4 C 67,000 monomer 5.2 -8 D 66,950 dimer 4.9 -20 By the following techniques? Technique gel filtration chromatography ion exchange chromatog. on DEAE cellulose, pH 8.1 ion exchange chromatog. on CM cellulose, pH 6.2 Native Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Isoelectric focusing A from B C from D B from D Activity • • • • • • What is an activity unit? How is it different from a rate? What is total activity? What is specific activity? What is purification fold? What is recovery? Reaction Order • • • • Define the order of the reaction Define the order in a component What does pseudo zero order mean? How could a reaction be pseudo zero order in a component? • What does the order of reaction imply about a mechanism? Determine the order of the reaction • Initial rates – Change one [reactant] – Measure initial rate – See how the rate changes • Integrated Rate Equation – Follow the reaction until significant changes in concentrations occur – See which integrated rate equation describe the data How do you find KM and Vmax [P] vs. time Measure initial rates at several values of [S]0 300 [S]0= 250 [P] (mM) 200 0.005 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.08 150 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 time (s) 40 50 Find Initial Rate for each [S]0 [S]= 5mM 60 50 [P] (mM) 40 30 Slope (convert to mM/min) 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 time (s) 25 30 35 40 45 Make table for all [S]0,V0 [S]0 V0 1/[S]0 1/V0 5 83 200 0.012 10 143 100 0.007 20 222 50 0.0045 40 308 25 0.0033 80 380 12.5 0.0026 Plot 1/V0 vs. 1/[S]0 Double Reciprocal Plot 0.014 1/Vo 0.012 0.01 0.008 -1/KM 0.006 0.004 0.002 1/Vmax 0 -50 0 50 100 1/[S]o 150 200 250 Cooperativity? Vmax .9Vmax [S].9Vmax [S].1Vmax V0 .1Vmax [S].1Vmax [S].9Vmax [S]0 Reversible Inhibition [I] [I] 1/Vo 1/Vo ? competitive Inhibition 1/So 1/Vmax ?competitive Inhibition 1/So -1/KM [I] 1/Vo 1/Vmax ?competitive Inhibition -1/KM 1/So XI = X (1 + [I]/KI) Effect of pH? EH2 + S +H+ EH- + S +H+ E-2 + S EH2S EH2 + P +H+ EHS- EH- + P +H+ ES-2 E-2 + P Effect of T? •Choose a good pH •Measure V0 over a pH range •Plot what? •V0 vs T •ln V0 vs. 1/T •ln (V0/T) vs. 1/T