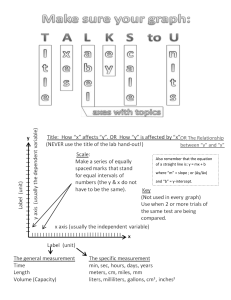
Enzyme Inhibition Modes and Linearization Table Mode of Inhibition → Effect of inhibition on vmax Effect of inhibition on K M Competitive No change vmax vmax Increases KM Noncompetitive Uncompetitive [I ] KI KM 1 Plot depicting uninhibited enzyme and increasing concentrations of inhibitor slope = Lineweaver-Burk Linearization How does inhibitor alter slope? Reason? How does inhibitor alter y-intercept? Reason? Eadie-Hofstee Linearization Hanes-Woolf Linearization KM vmax Inhibition causes slope to increase (since it increases K M and leaves vmax unchanged 1 y-intercept = vmax Inhibition leaves yintercept unchanged since vmax is unchanged by inhibition Plot depicting uninhibited enzyme and increasing concentrations of inhibitor How does inhibitor alter slope? Reason? How does inhibitor alter y-intercept? Reason? Plot depicting uninhibited enzyme and increasing concentrations of inhibitor Ganesh Sriram, BIOE120 Biology for Engineers, Spring 2022 1 Copyrighted Material; Only for Registered Students Enzyme Inhibition Modes and Linearization Table How does inhibitor alter slope? Reason? How does inhibitor alter y-intercept? Reason? Ganesh Sriram, BIOE120 Biology for Engineers, Spring 2022 2 Copyrighted Material; Only for Registered Students