Religions of South East Asia
advertisement

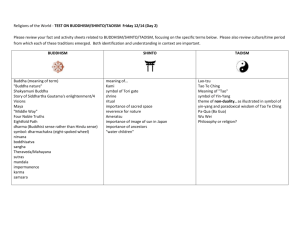
Religions of South East Asia Hinduism- Ethnic • Began: 2000 B.C.E. • Founder: Dravidians • • & Aryans Origin: un-known, but thought to be brought by Aryans Number of members: 838 million Hinduism • Region- SEA: India, Nepal, • Sri Lanka Religious Leaders- priests, gurus- spiritual leaders, swamis- teachers Hinduism • Holy Books: The Bhagavad Gita, Vedas, Upanishads • House of Worship: Temples Hinduism • Holy place: tirthas= pilgrimages (examples: Mt. Kailash, Ganges, and the Himalayas Hinduism • Dietary law: no meat/alcohol • Monotheistic: • NO - over 350 million gods YES – Brahman (pantheism) Holy day of the week: Every day is holy Hinduism • Holidays: • Divali: Festival of lights Dessehra: Rama’s victory over Ravana= victory of good over evil Burial of Dead: cremation burn the dead Hinduism • Name of Diety- 3 main ones (Trimurti) 1. Brahman- judge 2. Vishnu- protector 3. Shiva- destroyer Hinduism Requirements and Main Beliefs • Reincarnation: Karma & Dharma • Caste System 1.Priests 2.Warriors 3.Merchants 4.Laborers 5.Untouchables • Moksha- breaking cycle Hinduism • Diffusion: ethnic religions usually • stay in specific region Symbols: Swastika, Om, Lotus Buddhism Buddhism- Universal • Began: 563 B.C.E. • Founder: Siddhartha • • Gautama Origin: Siddhartha Gautama Number of Members: 500 million to 1.5 billion (due to Chinese Communism) Buddhism • Schools and Regions: Therevada: Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Sri Lanka • Mahayana: China, Korea, Japan, Vietnam Zen: China Tibetan (Mantrayana): Tibet, Nepal Religious leaders: Dalai Lama- reincarnate, Sangha- order of monks Bodhisattva- teacher Buddhism • Holy Book: Tripitaka (3 baskets) - holds Buddha's • sayings & rules for monks they were collected in baskets. House of Worship: Pagodas and Stupas Buddhism • Holy Places- Nepal- birthplace of Buddha Bodh Gaya- Enlightenment Sarnath- sermon & death Buddhism • Dietary Law: Moderation • Monotheistic: More philosophy than religion • Holy day of the week: Every day is holy Buddhism • Holidays: Vassa- meditation from July-October • • Wesak/Vesak- Buddha’s birth Buddha Day – birth, enlightenment, death Burial of the dead: Cremation Name of deities: none Buddhism: Requirements & Main Beliefs • 3 universal truths 1. Nothing is lost in the universe 2. Everything changes 3. Law of cause and effect • Reincarnation • 4 noble truths: 1. 2. 3. 4. all life is suffering suffering comes from desire desire can be eliminated there is a path to eliminate desire • The 8 Fold Path • Nirvana Buddhism • 8 fold path: the right 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. viewpoint values speech actions livelihood effort mindfulness meditation Buddhism • Symbols: Wheel, Bodhi Tree, Footprints, Lotus Flower, Mandalas, Prayer Flags Confucianism Confucianism- Ethnic • • • • • • Began: 520 B.C.E. Founder: Confucius Origin: Confucius Number of Members: 6 million or 350 million Region: SEA – mainly China Religious leaders: Teacher/Sages Confucianism • Holy Books: • • • • 5 classics (Wujing): written by Confucius 4 books (Analects/Shshu): written by his followers House of Worship: None Holy place: None Dietary Law: None I-Ching Monotheistic: Philosophy Confucianism • Holy Day of the Week: • • • • None Holidays: None Burial of Dead: Local Customs Name of Deities: None Diffusion- could be universal but mainly stayed within Chinese culture Confucianism – Requirements and Beliefs • Social code based on morality rather • • • than laws. Established social order within Chinese Society Look to the past for insight to behavior and follow ancestral examples The “Way of Heaven” – natural turn of events The “Mandate of Heaven” - Be a good ruler Confucianism- requirements cont. • Filial Piety: 1.Ruler/Subject 2.Father/Son 3.Older/younger brother 4.Husband/Wife 5.Friend/Friend • Everyone must know their role & live accordingly • Believe the answer to social ills was self-cultivation, starting with education Confucius Sayings: • Study the past if you are to define the future. • Do not dwell on mistakes and thus make them crimes. • Those who do not study are just cattle dressed in men’s clothing Confucius’ comments about women were not as nice……. Taoism • Began: 604 BCE • Founder: Lao Tzu • Origin: Lao Tzu • Number of Members: 20 million • Region: SEA - China Taoism • Religious Leaders: Priests • Holy Book: Tao Te Ching • House of Worship: Temples/Monastaries I-Ching The I Ching is a collection of practical wisdom, pertaining to every conceivable situation. It originates in ancient China and is probably the oldest Chinese classical text. "I Ching" means "Book of Changes." There are 64 different kinds of situations in the I Ching. Each one is indicated by a hexagram, which is a symbol made up by 6 lines, each of which can be broken or unbroken. Taoism • Holy Places: None • Dietary Laws: None • Monotheistic: No – Philosophy/Way of Life. (Taoism has many gods, most of them borrowed from other cultures. These deities are within this universe and are themselves subject to the Tao.) Taoism Holy Day of Week: None Holidays: None Burial of the Dead: Local Customs Deity: The 3 Pure Ones Taoism: Requirements and Main Beliefs • Tao Means “The Way” • Return to Nature • Everything will come out right if you let nature take its course • Live Tranquil rural life in union with nature • Nothing is permanent or absolute, but in a state of flux between two opposites • Yin and Yang: represent opposites (good and evil/light and dark) Diffusion: Mainly in China Shinto (“Way of the Gods”) - Japan Shinto Began: Preliterate times (6th century) Founder: Not known Origin: Japanese indigenous culture Number: Japanese population (ethnic) Shinto Region: SEA - Japan Religious Leaders: Priests Holy Book: Kojiki and Nihon Shoki House of Worship: Shrines Shinto Komainu-Guardians - Buddhist • Holy Place: Family alters, effigies, shrines, or anything marked with a rope or gate (torii) • Dietary Law: Food offerings • Monotheistic: Considered polytheistic or a way of life rather than religion Shinto • Holy Day of the Week: None • Holidays: None • Burial of the Dead: Local customs • Name of Deities: Kami (spirits) and Amaterasu Shinto Beliefs: 1. Most things have a kami (spirit) 2. Prayer and Offerings are used 3. Purity is emphasized 4. Shinto led to the Japanese belief that as sole descendants of the sun, they were uniquely gifted to rule the world. Diffusion: Stays within Japan