Glenco-chapter-7
advertisement

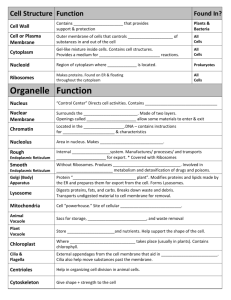
Glenco chapter 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL Cell: The basic unit of living matter separated from it’s environment by a plasma membrane. CELL THEORY All living organisms are composed of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure Cells came from previously existing cells THE STUFF INSIDE Cytoplasm: Everything inside the cell between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. Organelle: (small organ) A cellular structure with a specialized function. PROKARYOTIC CELLS Prokaryotic cells: (pro: before + karyon: kernel) lacks true nucleus. DNA is coiled into a nucleoid region. Very small; averaging about 1/10 the size of eukaryotic cells. Mainly bacteria PROKARYOTES DNA is in direct contact with cytoplasm. Plasma membrane encloses cytoplasm. Most bacteria have a chemically complex bacterial cell wall surrounding the plasma membrane EUKARYOTIC CELLS Eukaryotic cells: (eu: true + karyon: kernel) Have a true membrane-bound nucleus. All eukaryotic cells are fundamentally similar. Membranes portion the cytoplasm into compartments (membranous organelles) Cell Membrane Phospholipid bilayer hydrophilic head (Polar) hydrophobic tail (nonpolar) Lipid Bilayer Main component of cell membranes Gives membrane its fluid properties Fatty acid tails sandwiched between hydrophilic heads Fluid Mosaic Model Membrane is a mosaic of Phospholipids Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Most phospholipids and some proteins can drift through membrane Membrane Proteins Functions: Enzyme activity Cell-to-cell recognition Cell-to-cell signaling Transport of materials Membranes & Movement Equilibrium: Equal concentrations of solute on both sides of the membrane Selectively permeable: Allows some substances to pass through the membranes and stopping others Transport Across Cell Membrane Passive transport: The diffusion of a substance across the cell membrane. No energy needed! Diffusion: The tendency for particles to spread out from where they are more concentrated to less concentrated. Driven by Entropy. Concentration Gradient The concentration gradient is when one side of the membrane has a greater concentration and the substance diffuses across the membrane until it reaches equilibrium. Facilitated Diffusion The diffusion of a substance across the cell membrane through a transport protein. Still passive transport because no energy is used. Osmosis The diffusion of water Hypertonic: Solution with a higher solute concentration Hypotonic: Solution with a lower solute concentration Isotonic: Solutions with equal solute concentrations Active Transport The movement of molecules across the cell membrane using energy to pump the substance through a transport protein. ATP is usually the source of energy. ATP Adenosine triphosphate: Almost all energy for cellular work comes from ATP. Transporting Large Molecules Extocytosis: The export of large material out of the cell. Endocytosis: The import of large molecules into a cell. Nucleus Stores genetic material DNA In the form of chromatin Nucleolus Where ribosomes are made Ribosomes Found on the rough ER and in the cytoplasm, Where proteins are produced, Rough & Smooth ER Rough ER: Has ribosomes on it, Where proteins are made Smooth ER: No ribosomes Where lipids are produced Golgi Apparatus Stores and/or modifies products of the endomembrane system, Named after Camillo Golgi Lysosomes Greek meaning “breakdown body”, Breaks down waste products using hydrolytic enzymes Endomembrane System The compartmentalization of the cells organelles using membranes Transfer of material in membranous sacs called vesicles Smooth & rough ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are found in plants and some protists Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy in sugars, Site of photosynthesis Mitochondria Cells energy factory, ATP synthesis Mitochondrial matrix Inner compartment Cristae Folds in the inner membrane Cytoskeleton Network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm Support Motility Regulation of biochemical activities Microtubules, microfilaments, intermediated filaments Movement Flagella: Long, thin, whip-like structure with a core of microtubules used for movement Cilia: Shorter and more numerous bundles of microtubules used for movement