reflection. - Pasti Skor
advertisement

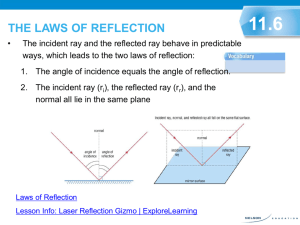
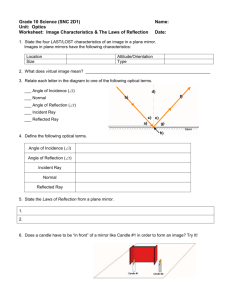
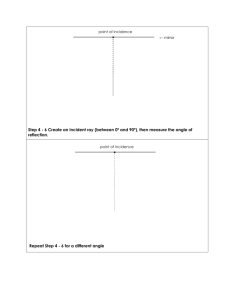
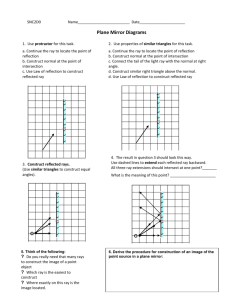
OBJECTIVE • At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: – Describe the characteristic of the image formed by reflection of light. – Solve problem involving reflection of light. WHAT IS MEANT BY LIGHT? • Light is a form of energy. • It travels in straight line and high speed about 3 x 108 ms-1. • It can be reflected, refracted and dispersed. • Rays are the path and direction which light energy flows. • When the light rays fall on the surface of an object, they are either: – Reflected • When it hits a smooth surface. – Refracted • When it passes through a transparent object. – Absorbed • When it strikes a black or dark body. REFLECTION OF LIGHT • Reflection of light occurs when light rays falling on a surface and bounce off the surface. • Light striking different surface will be reflected differently: – Regular reflection is the reflection of parallel light rays in a certain direction from a smooth surface such as plane mirror. – Diffused reflection is the reflection of parallel light rays in all directions from a rough surface such as white paper. Types of reflection Regular reflection Diffused reflection Why do you see an image in the mirror? • Light is reflected off your body as an image and you are then able to see the image that is reflected. You will see the image as if it is inside the mirror! When light bounces off a surface, it is called reflection. TYPE OF MIRROR • Plane mirror • Curve mirror CURVED MIRRORS • Is actually a spherical mirror. • Has the same shape as a section of a large sphere. • Type of curved mirrors: i. concave mirrors ii. convex mirrors CONVEX MIRRORS • Curves outwards. • Parallel light rays the hit the convex surface are reflected outwards. • Also known as a diverging mirror. • Only produce a virtual image. CONCAVE MIRRORS • Curves inward. • Parallel light rays that hit the concave surface are reflected inwards. • Also known as a converging mirror. CHARACTERISTIC OF THE IMAGE FORMED IN A PLANE MIRROR. • • • • Upright Same size as the object Laterally inverted Distance between image and mirror same as distance between object and mirror. • Virtual - image cannot captured on the screen. • Why the word AMBULANCE is written in reverse letter at in front of the body? • The word ambulance is written in reverse letter because the lettering will appear normal when the viewed through the rearview mirror of car in front of the driver seat. PROBLEM SOLVING PROBLEM SOLVING Solution no 1 • Initially, the distance between Jacelyn and her image =5+5 = 10m • After Jacelyn and the mirror moved, the distance between Jacelyn and the mirror =5+1–3 = 3 m. • So, distance between Jacelyn and the new position of the image =2x3 =6m • The reduction in distance between Jacelyn and her image = 10 – 6 =4m# PROBLEM SOLVING Solution no 2 • The distance between Helmi and the plane mirror 12 /2 = 6 m • i) The new distance between Helmi and the plane mirror 6m – 2m = 4 m • ii) The new distance between Helmi and his image 4m + 4m = 8m PROBLEM SOLVING • Answer no 3 = 4m •What is meant by light? •Light is a form of energy. •How it travels? •It travels in straight line and high speed about 3 x 108 ms-1. •When the light ray strike on the surface of an object, what happen to the light ray? •It can be reflected, refracted and absorbed. •How the reflection of light occurs? •Reflection of light occurs when light rays strike on a surface and bounce off the surface. •Give me 2 types of reflection? •Regular reflection •Diffused reflection OBJECTIVE • At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: – State the law of reflection of light. – Solve problem involving reflection of light. How does light behave during reflection? • How can we investigate? LAWS OF REFLECTION 1. • FIRST LAW state that: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane. 2. • SECOND LAW state that: The angle of incidence, i is equal to the angle of reflection, r. Angle of incident, i is angle between incident ray and the normal. Angle of reflection, r is angle between reflected ray and the normal. Example PROBLEM SOLVING Question 1 • Figure 1 show of light ray is directed to a plane mirror. Incident ray 30° Plane mirror What is the angle of reflection? Question 2 • Figure 2 show a ray of light reflected on a plane mirror. The angle between the incident ray and reflected ray is 100°. The mirror is then turned to 10° in the anticlockwise direction as shown Incident ray Reflected ray 100° 10° • What is the new angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray? Answer • Angle of incident = 90° - 30° = 60° • Angle of reflection = Angle of incident Incident ray Reflected ray 60° 60° 30° Answer • Before the mirror turns, the angle of incidence is 50°. When the mirror has turned to an angle of 10° , the normal also turn to 10° . The new angle of incidence is now 40° (50° - 10°). Therefore, the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray has become 80°