Reflection and Plane Mirrors
advertisement

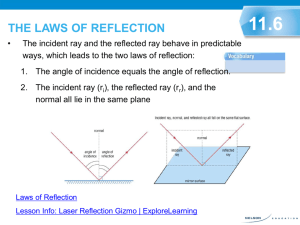
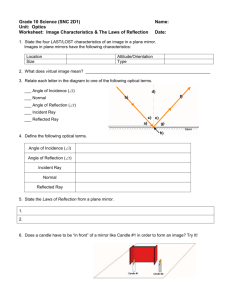
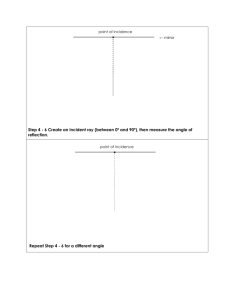
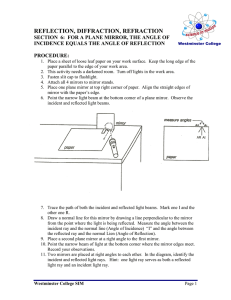
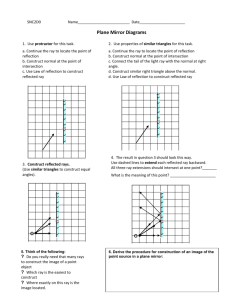
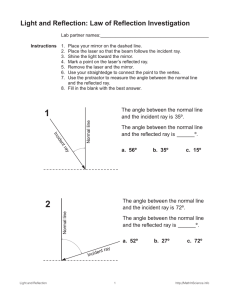
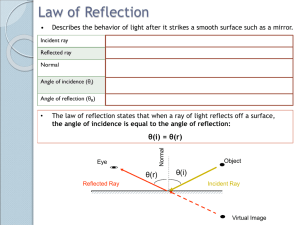
Reflection and Mirrors A plane mirror is one that is flat Light hits the mirrors and reflects back to our eyes. We see an image "in" the mirror Reflection can occur in still water too! Read Only! Dyslexia is a condition that many people have – its where people have difficulty reading print Examples: Read Only! One problem with people who have dyslexia is the glare from the light reflecting off white paper Sometimes using coloured filters helps! Characteristics of an Image An image can have 4 characteristics when comparing to the object Location: closer, farther or same distance Orientation: upright or inverted (upside down) Size : larger or smaller Type: virtual (imaginary rays cross) or real (light rays cross) Remember L.O.S.T Writing Reflectively Looking ONLY at the mirror, write your name so that it appears right side up! Mini Lab In grps of 4 collect the following materials: white paper, plane mirror, protractor, ray box Draw a capital T Place the mirror along the top of the T Aim the ray of light at the mirror as seen above Trace the light in the and reflected light Use the protractor to measure the angle of each line – measure from the centre line Fill out the LOST for the image you see in the mirror Characteristics of Images in Plane Mirrors L: same distance behind mirror O: Right side up and left-right switch S: Same size T: Virtual (there are no light rays where the image is) Reflection Terms Normal – the line drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface Incident Ray – a ray traveling towards the reflecting surface The angle of Incidence (Θi) – the angle between the incident ray and the normal The point of incidence –the spot where the incident ray hits the reflecting surface Reflected Ray – a ray of light that bounces off a reflected surface Angle of Reflection (Θr) – the angle between the reflected ray and the normal Laws of Reflection 1.) The angle of incidence equals the angle of relfection (Θi = Θr) 2.) The incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie in the same plane (all flat) Reflection can occur on 2 types of surfaces: Reflection Specular Reflection 1. Shiny, smooth surfaces. Diffuse Reflection 2. Rough surfaces READ ONLY Worksheet How do you draw the image you see in a mirror? Complete the worksheet after seeing the teacher complete an example