Reflection and Refraction Lab: Snell's Law & Optics
advertisement

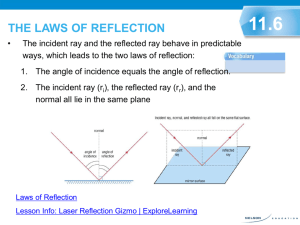
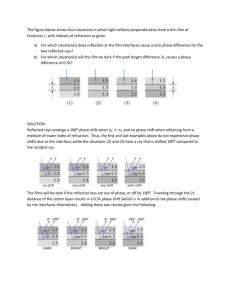
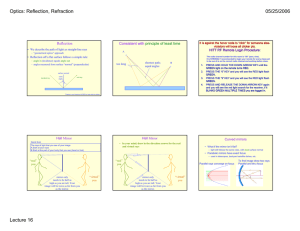
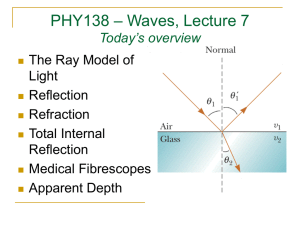
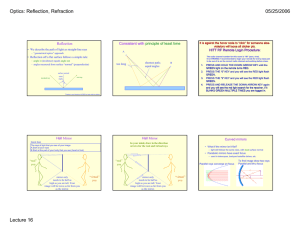
Lab 9: Reflection and Refraction – – Law of Reflection Law of Refraction (Snell’s Law) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Index of Refraction The Critical Angle Total Internal Reflection Dispersion Light Passing through a Window Pane or Prism How Large does a Mirror Need to be? Location of Mirror Image Rainbows Corner Reflectors Fiber Optics Polarization by Reflection • Light ray – Originates at a point source – Travels straight – Changes direction at interface • Reflection & refraction in this lab • Object – Point source of light rays • Image – Apparent convergence point of light rays from object • Draw diagrams involving – Light rays – Interface – Angles • Estimate angles to the tenth of a degree – Take several measurements and then average them Light Rays • indicated as arrows • from object extend outward Light Rays white light light unit: a ray of light made by a slit Interface normal : direction perpendicular to interface interface : boundary between different media Cross-sectional View air medium Reflection (Specular) angles measured from normal angle of incidence (qi ) qi qr angle of reflection (qr ) air mirror Cross-sectional View air Top view Experiment #1 ray of light qM ray of light qA Component Line qA qM Experiment #2 Aim light ray at the center of semicircle. Reflection qi qr qr – qi (degree) (degree) (degree) 0 10 85 Refraction #1 qA qM (degree) (degree) sinqA sinqM sinqA/sinqM (= nglass) 0 N/A 10 85 Use the “degree” mode on your calculator