Homo erectus
advertisement
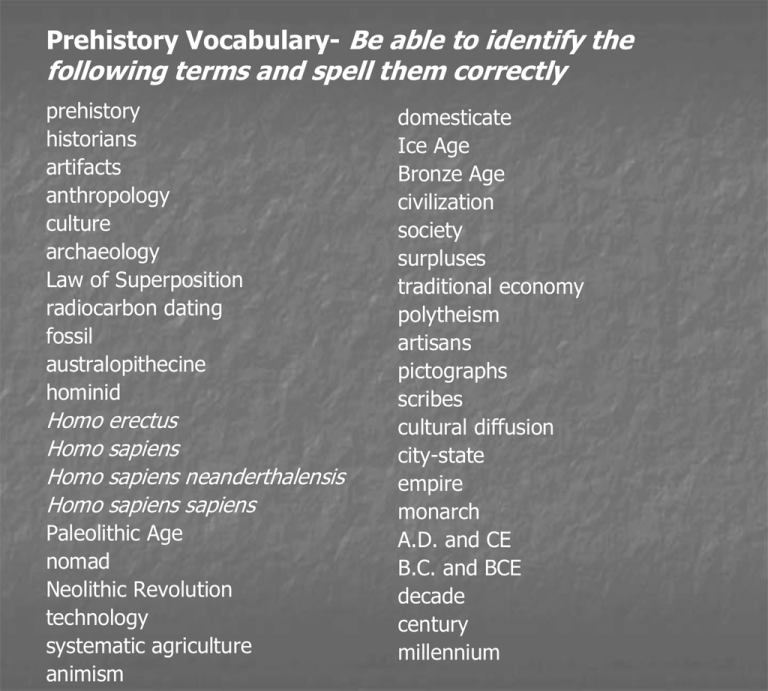
Prehistory Vocabulary- Be able to identify the following terms and spell them correctly prehistory historians artifacts anthropology culture archaeology Law of Superposition radiocarbon dating fossil australopithecine hominid Homo erectus Homo sapiens Homo sapiens neanderthalensis Homo sapiens sapiens Paleolithic Age nomad Neolithic Revolution technology systematic agriculture animism domesticate Ice Age Bronze Age civilization society surpluses traditional economy polytheism artisans pictographs scribes cultural diffusion city-state empire monarch A.D. and CE B.C. and BCE decade century millennium Basic World Geography Label the seven continents and four oceans. Be able to spell the names correctly and always capitalize proper nouns. History v. Prehistory Historians primarily study written documents, using archaeological and anthropological evidence to aid in creating an accurate picture of past human actions. The only way that researchers are able to learn about humankind before the invention of writing (prehistory) is by studying artifacts and fossil remains. Prehistory Anthropology is a discipline that encompasses the study of humankind in relation to its origin, distribution, classification, physical character, environmental and social relationships, and culture. Anthropology Anthropology is the study of the origins and development of people and their societies. (root word anthropos- Greek for human being) society- a network of people who interact with one another. There are two ways to study Anthropology: 1. 2. Academic record Applied research 4 subdisciplines of Anthropology: Physical Anthropology Cultural Anthropology Linguistics Archaeology Physical Anthropology Cultural Anthropology Linguistics Linguistics is the study of language. Languages distinguish humans from all other animals. Archaeology Archaeology is the study of human and material remains. Different kinds of archaeology Archaeology Archaeology Fieldwork Why study archaeology? 1. 2. It is the sole means by which the early record of man can be understood. It serves as a cross-reference to the historical past. Archaeological Dating Methods Relative Dating Stratigraphy Law of Superposition Absolute Dating Radiocarbon Dating Thurmoluminesence Dating Amino Acid Racemization Dating ____________ Study Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Explain how historians might use evidence acquired through archaeological research. What is the crucial factor that distinguishes prehistory from history? What is a theory, and how do theories relate to anthropology and archaeology? Review the two methods of archaeological dating described on p. 5 of your textbook. What is the difference between the two methods? Provide an example of each method. List the hominids discussed on pp. 9-10 in your textbook and explain when and where they are thought to have existed. For what purposes might Homo erectus have used fire? Describe the technology of Homo habilis and Homo erectus. All humans today belong to which species and subspecies of the genus Homo? Early Humans Australopithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapiens Homo sapiens Neanderthalensis Homo sapiens sapiens Archaeology: Shifts in Human Technology Stone Age Paleolithic Age Mesolithic Age Neolithic Age Chalcolithic Bronze Age Age Iron Age Industrial Age Information Age Last Ice Age c.100 kya – 10 kya Study Questions 9. What evidence suggests to some anthropologists that late Paleolithic people believed in life after death? 10. Summarize the roles of men and women during the Paleolithic Age. 11. What was the most significant development of the Neolithic Age? 12. List some of the plants and animals that were domesticated during the Neolithic Age. Why were they domesticated? When and where were they domesticated (provide specific examples)? 13. How did the social structure and material wealth of societies change as people began to transition from a nomadic lifestyle to living in settled communities? 14. What geographic feature did all of the earliest civilizations have in common? 15. According to your textbook, what are the seven basic features that define civilization? Refer to the chart on p.20 of your textbook. 16. By whom and for what purposes was writing used in the earliest civilizations? 17. As you read pp.22-23 think about how civilizations change over time. What are some of the factors behind this change? Describe two of these factors. 18. Explain the difference between a city-state and an empire. Neolithic Revolution c. 8000 B.C. Nomadic Hunting and Gathering to the Domestication of Plants and Animals. Plants? Animals? The emergence of systematic agriculture. Characteristics of the Neolithic Revolution: Was the quality of life better for everyone in the early Neolithic farming villages? What real impact did the Neolithic Revolution have on humankind? What did it mean for humans? Systematic Agriculture in different regions of the world: Southwest Asia (Near East) Southeast Asia and China Central Africa Mesoamerica (Mexico, and Central and South America) Early Neolithic Farming Villages Jericho (8000 B.C., Palestine)- perhaps the oldest continually occupied city on Earth. Catal Huyuk (6700-5700 B.C., southern Turkey) Obsidian Points from Catal Huyuk Consequences of the Neolithic Revolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Technological Change The introduction of metals to create tools Copper (4000 B.C.) Bronze (copper + tin) Bronze Age (c.3000 B.C. – 700 B.C.) Iron Age (c. 1200 B.C.) Which of the metals listed above is the strongest? By c. 4000 B.C., as a result of agricultural surpluses, populations began to increase significantly along the major river valleys Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, China The effects of agriculture on population? Year 10,000 B.C. 5,000 B.C. 3,000 B.C. 2,000 B.C. 1,000 B.C. 500 B.C. Human Population 4 million 5 million 14 million 27 million 50 million 100 million Civilization 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Civilization- a complex, highly organized social order Culture- the way of life of a society, which is handed down from one generation to the next by learning and experience Seven Basic Features of Civilization organized governments complex religions job specialization social classes art and architecture cities writing (earliest form- keeping records) Timeline Read pp. 1146-1147 in textbook B.C. (Before Christ) or B.C.E. (Before the Common Era) A.D. anno Domini “In the Year of Our Lord” or C.E. (Common Era) 476 A.D. 1066 A.D. 632 A.D. 510 B.C. 326 B.C. 970 B.C. Know the difference between the terms decade, century, and millennium.








