Ancient Civilizations
advertisement

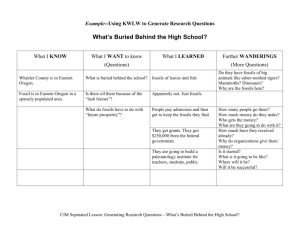
Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1: Section 1 Standards • H-SS 6.1: Students describe what is known through archeological studies of the early physical and cultural development of humankind from the Paleolithic era to the agricultural revolution. • (Link) ELA Reading 6.2.1: Identify the structural features of popular media and use the features to obtain information. Objective •To learn about the physical and social development of early humankind through archeological discoveries. Language of the Discipline •Prehistory •Archeology •Artifact •Fossil •Mary and Louis Leakey •Donald Johanson •Michael Brunet Anticipatory Set Studies of Early Humans (Input) •About 6,000 years ago humans had no way to write down things. •The time before this is called Prehistoric. •Archeology- is the study of human life in the past through the examination of the things that people left behind. Artifacts (Input) • They look for places where people used to live a long time ago. They are covered by layers of dirt. • They dig up artifacts. Artifacts are objects made and used by humans. • Teaches them how those people hunted for food or what types of plants they ate. • They have found animal bones with carvings on them, however, they cannot explain the thoughts and ideas of the people who created them. Fossils (Input) • For the people who lived thousands of years ago, archeologist rely on fossils. • Fossils are the remains or imprints of living things that existed millions of years ago. • Plants, feathers, bones, footprints Fossils (Input) • One a living thing dies, it becomes covered by mud. The soft parts of an animal decay. The hard parts last longer. The minerals from the soil replace the soft parts and leave a rocklike copy of the original animal. • Dating Fossils and Artifacts • Comparing objects found in similar layers of rock or soil • Comparing an objecting with similar fossil or artifact whose age is already known. Fossils (Input) • Radioactive dating. • Living things and rocks contain radioactive materials • These elements day over time • Measure the amount of radioactive material that is left. It can tell when the object was formed. • Other Methods • Physical tests • Chemical tests • All to determine the age of something Hunting for Fossils • Where did people first appear on the Earth? • 1959- Mary and Louis Leakey discovered human fossils in Olduvai Gorge in East Africa. • They found a piece of a skull with large molars (rear teeth). • They figured this person must of eaten a lot of plants. Donald Johnson (Input) • He has been searching for human remains in Ethiopia, a country in East Africa. • It had become too hot to continue looking. On his way back to camp he saw a piece of bone sticking out of the ground. • He began to uncover what he found and eventually found hundreds of bones that belonged to a 3.5 foot woman. • He named her Lucy. Michael Brunet (Input) • “Oldest One” • Many scientists believe humankind began in East Africa. • Michael Brunet • He found a brown humanlike skull in Chad (located in Africa). They say it was 7 million years old. • This was the oldest skull that had ever been found. • Many believed that the skull looked like an ape, not like a human skull. • Scientists still don’t have an answer Review (Input) • You studied what an archeologist does • You studied what a fossil it and how it is made • You also studied where human remains where first founded Check for Understanding • Please determine the BEST answer for the following question. • Please write your answer on your white boards and wait for the teacher’s signal. • On the teacher’s signal, hold up your white boards. Checking for Understanding •What did Mary and Louise Leakey find in Olduvai Gorge in 1951? •Mary and Louise Leakey found human fossils Checking for Understanding •How did the Leakey find impact the search for the origins of human kind? • The Leakey find impacted the seaach for the origins of human kind because from that point on, searches were centered in Africa. Checking for Understanding •What was the search for the “oldest one?” • Michael Brunet found a skull that was 7 million years old. This led scientists to more questions. Guided Practice/Independent Practice • Guided Practice • Complete questions 1 - 2 on the reading comprehension worksheet. • Raise your hand and wait to get stamped. • If you received an “R” go to the back table with Ms. Graham. • Independent Practice • Once you have been stamped moved to independent practice and complete numbers 3 and 4 on the reading comprehension worksheet. • Homework • Note-taking guide on the reverse side.