Electric Fields
advertisement

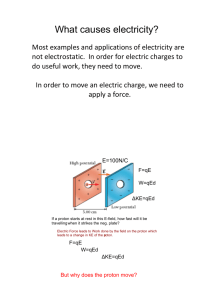
Electrostatics Electric Charge • The source of negative charge is the electron • The source of positive charge is the proton • The smallest possible amount of charge, the elementary charge, is 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs • Electron charge = - 1.6 x 10-19 C • Proton charge = + 1.6 x 10-19 C – All other amounts of charge are multiples of these • Electric Charge is a conserved quantity What is an Electric Field? • One charged object can influence another charged object without any direct contact. • We say a charged object is surrounded by an electric field, a region of influence. Any other charged object in that space will interact with that field and experience an electrical force. Electric Field Strength • The electric field strength at a given location is defined as the amount of force per unit of charge at that location. E=F/q (units of E: N/C) This is analogous to the way we described gravitational field strength earlier in the year: g = Fg/m Field around a positive charge • A positive charge placed in this field will feel a force directed away from the source of the field…repulsion • A negative charge placed in this field will feel a force directed towards the source of the field…attraction Field around a negative charge • A positive charge placed in this field will feel a force directed toward the source of the field…attraction • A negative charge placed in this field will feel a force directed away from the source of the field…repulsion Field around two opposite charges (same amount) Any charge placed in the field will feel a force in a direction tangent to the field lines Field around two like charges (same amount) Electric Field Lines • When drawing, or interpreting, electric field lines keep in mind the following… – Filed lines originate at + charge or infinity – Field lines terminate at – charge or infinity – Filed lines are always perpendicular to the surface of a charged object – Line density is an indicator of field strength – The number of lines leaving a + and terminating at a – is proportional to the magnitude of charge – Field lines NEVER cross each other (Why?) Electric Force – how strong is it? • The magnitude of force between two charges is described by Coulomb’s Law: 𝑘𝑄1 𝑄2 𝐹= 𝑟2 𝑘 – constant = 9.0 x109 Nm2/C2 𝑄 – amount of charge 𝑟– distance between charged objects Determine the electrostatic force on the electron in a hydrogen atom from the proton in the nucleus • Q1 = • Q2 = • r= For comparison purposes, determine the gravitational force between them as well…