Unit 7 Review - Static Electricity ANSWER KEY
advertisement
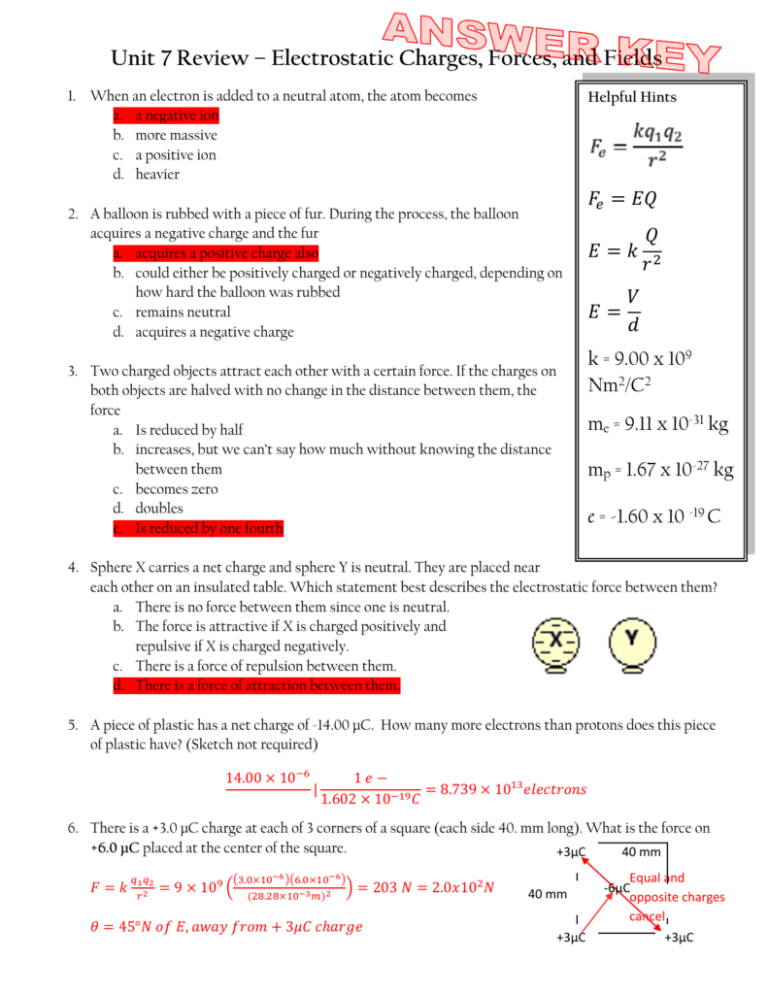
Unit 7 Review – Electrostatic Charges, Forces, and Fields 1. When an electron is added to a neutral atom, the atom becomes a. a negative ion b. more massive c. a positive ion d. heavier Helpful Hints 2. A balloon is rubbed with a piece of fur. During the process, the balloon acquires a negative charge and the fur a. acquires a positive charge also b. could either be positively charged or negatively charged, depending on how hard the balloon was rubbed c. remains neutral d. acquires a negative charge 𝐹𝑒 = 𝐸𝑄 𝐸=𝑘 𝐸= 𝑄 𝑟2 𝑉 𝑑 k = 9.00 x 109 Nm2/C2 3. Two charged objects attract each other with a certain force. If the charges on both objects are halved with no change in the distance between them, the force a. Is reduced by half b. increases, but we can’t say how much without knowing the distance between them c. becomes zero d. doubles e. Is reduced by one fourth me = 9.11 x 10-31 kg mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg e = -1.60 x 10 -19 C 4. Sphere X carries a net charge and sphere Y is neutral. They are placed near each other on an insulated table. Which statement best describes the electrostatic force between them? a. There is no force between them since one is neutral. b. The force is attractive if X is charged positively and repulsive if X is charged negatively. c. There is a force of repulsion between them. d. There is a force of attraction between them. 5. A piece of plastic has a net charge of -14.00 μC. How many more electrons than protons does this piece of plastic have? (Sketch not required) 14.00 × 10−6 | 1𝑒− = 8.739 × 1013 𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑟𝑜𝑛𝑠 1.602 × 10−19 𝐶 6. There is a +3.0 μC charge at each of 3 corners of a square (each side 40. mm long). What is the force on +6.0 μC placed at the center of the square. +3μC 40 mm 𝐹=𝑘 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝑟2 (3.0×10−6 )(6.0×10−6 ) = 9 × 109 ( (28.28×10−3 𝑚)2 ) = 203 𝑁 = 2.0𝑥102 𝑁 𝜃 = 45°𝑁 𝑜𝑓 𝐸, 𝑎𝑤𝑎𝑦 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 + 3𝜇𝐶 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 40 mm +3μC Equal and -6μC opposite charges cancel +3μC 7. Consider a container of 1.0 grams of hydrogen atoms (one gram mole). Suppose you removed all the electrons and moved them to the other side of the Earth (Earth diameter 12740. km). (a) How much charge is left behind? 1.0𝑔𝐻 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐻 6.02×1023 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑠 1 𝑒− −1.60×10−19 𝐶 | 1.0𝑔𝐻 | |1𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝐻| 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐻 1 𝑒− (b) = 9.6 × 104 𝐶 What is the attractive force between the protons here and the electrons at the other side of the Earth? (96320𝐶)(−96320𝐶) 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝐹 = 𝑘 2 = 9 × 109 ( ) = 5.1 × 105 𝑁 (12740 × 103 𝑚)2 𝑟 8. In a lithium atom, ,the valence electron and 3-proton nucleus are separated by 0.20 nm. a. What is the magnitude of the force on the electron? (−1.60 × 10−19 𝐶)(3 × 1.60 × 10−19 𝐶) 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝐹 = 𝑘 2 = 9 × 109 ( ) = 1.7 × 10−8 𝑁 (0.20 × 10−9 𝑚)2 𝑟 b. What is the net force on the system? Fnet = 0N because the electron and the nucleus pull on one another with equal but opposite force. 9. Which of the arrows shown in the figure at right represents the correct direction that a negative charge would accelerate in the electric field between the two metal plates? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. None of the above 10. Electric field lines a. are closer together the stronger the field. b. start on positive charges and end on negative charges. c. are perpendicular to the surface of the object. d. all of the above 11. In the diagram to the right, each of the charges shown are ±1.0 C. a. What is the magnitude and direction of the electrical force on the negatively-charged particle? 𝐹𝑥 = 𝑘 𝐹𝑦 = 𝑘 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝑟2 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝑟2 (−1.0𝐶)(+1.0𝐶) = 2 × 9 × 109 ((132×10−2 𝑚)2 ) = 1.03𝑥1010 𝑁 (−1.0𝐶)(+1.0𝐶) = 9 × 109 ((225×10−2 𝑚)2 ) = 1.78𝑥109 𝑁 225cm 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 = √𝐹𝑥2 + 𝐹𝑦2 = 1.0𝑥1010 𝑁 𝜃= 𝐹 tan−1 𝑦 𝐹𝑥 132cm ° = 80 N of E b. 90o If the negatively-charged particle has a mass of 25 grams, what is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration it will experience within this electrical field? 𝑎= 𝐹 1.0𝑥1010 𝑁 = = 4.2𝑥1011 𝑚⁄𝑠 2 𝑚 . 025𝑘𝑔 12. A test charge of -2.5 C in a field of strength 8.8 N/C would feel what force? 𝑁 𝐹𝑒 = 𝐸𝑄 = (8.8 ) (−2.5𝐶) = −22𝑁 𝐶 13. What is the value of the electric field when a +8.6 V potential is found 0.9 mm from its center? 𝐸= 𝑉 8.6𝑉 = = 9.6𝑥103 𝑉/𝑚 𝑑 0.9𝑥10−3 𝑚 14. What is the electrostatic potential found 0.83m from the center of a 9.2 V/m field? 𝑉 𝑉 = 𝐸𝑑 = (9.2 𝑚) (0.83𝑚) = 7.6𝑉 Ftens Fgrav Felec 20cm=.20m 15. A balloon, D is electrostatically charged with 4.35 μC of charge. A second balloon, C, 20 cm away is charged with -3.90 μC of charge. If you consider the balloons to be point charges, what is the force between them? 𝐹=𝑘 (4.35𝑥10−6 𝐶)(−3.90𝑥10−6 𝐶) 𝑞1 𝑞2 9 = 9 × 10 ( ) = −3.82 𝑁 (20𝑥10−2 𝑚)2 𝑟2 16. If one of the balloons has a mass of 0.0620 kg, with what acceleration does it move toward or away from the other balloon? 𝑎= 𝐹 −3.82 𝑁 = = −61.6 𝑚⁄ 2 𝑠 𝑚 . 0620𝑘𝑔 17. Calculate the tension force on one of the strings holding up the balloons. 2 2 𝐹𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠 = √𝐹𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 + 𝐹𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑣 = 3.77𝑁 0.6076𝑁 𝜃 = tan−1 ( ) = 9.04° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓 𝐸 −3.82𝑁











