Biochemistry 6/e - Personal Webspace for QMUL
advertisement

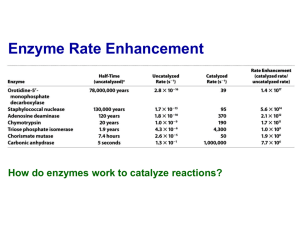
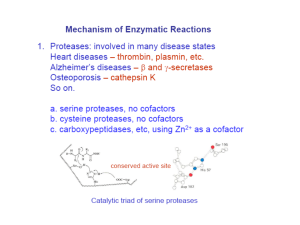
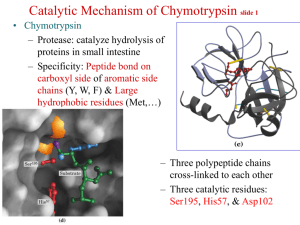
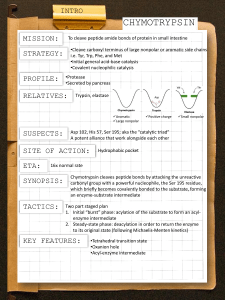
Chymotrypsin Lecture Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin What’s so great about enzymes? • They accomplish large rate accelerations (1010-1023 fold) in an aqueous environment using amino acid side chains and cofactors with limited intrinsic reactivity, relative to catalysts in organic synthesis. • They are exquisitely specific Chymotrypsin • Digestive enzyme secreted by the pancreas • Serine protease, specific for the peptide carbonyl supplied by an aromatic residue (eg Tyr) of a large hydrophobic (eg Met) Common catalytic strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. Covalent catalysis General acid-base catalysis Metal-ion catalysis Catalysis by approximation And enzymes often combine these strategies eg an example of use of 1 & 2 is chymotrypsin Proteases Catalyse a Fundamentally Difficult Reaction They cleave proteins by hydrolysis – the addition of water to a peptide bond Half life for hydrolysis of typical peptide is 300600 years. Chymotrypsin accelerates the rate of cleavage to 100 s-1 (>1012 enhancement). The carbon-nitrogen bond is strengthened by its double-bond character, and the carbonyl carbon atom is less electrophilic and is less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than are the carbonyl carbon atoms in carboxylate esters. Identification of the reactive serine • Around 1949 the nerve gas di-isopropyl-fluorophosphate was shown to inactivate chymotrypsin • 32P-labelled DIPF covalently attached to the enzyme • When labelled enzyme was acid hydrolysed the phosphorus stuck tightly; the radioactive fragment was Ophosphoserine • Sequencing established the serine to be Ser195 • Among 28 serines, Ser195 is highly reactive, why? Probing enzyme mechanism S1-subsite Subtilisin Fig. 1. The isomerization reaction catalyzed by triosephosphate isomerase Jogl, Gerwald et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 50-55 Copyright ©2003 by the National Academy of Sciences Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 9: Catalytic Strategies Copyright © 2007 by W. H. Freeman and Company