unit 3: creation of the united states
advertisement

UNIT 3:
CREATION OF THE UNITED
STATES
•
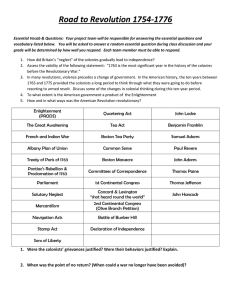
SSUSH3 The student will explain the primary causes of the American
Revolution.
•
a. Explain how the end of Anglo-French imperial competition as seen in the
French and Indian War and the 1763 Treaty of Paris laid the groundwork for
the American Revolution.
•
b. Explain colonial response to such British actions as the Proclamation of
1763, the Stamp Act, and the Intolerable Acts as seen in Sons and
Daughters of Liberty and Committees of Correspondence.
•
c. Explain the importance of Thomas Paine’s Common Sense to the
movement for independence.
CREATION OF THE UNITED
STATES
• UNIT FOCUS
This unit examines the conflict and
change associated with the American
Revolution, including the ideological
background of the Declaration of
Independence. Through the conceptual
lens of beliefs and ideals, the unit also
focuses on early American documents
including the Articles of Confederation,
Constitution, and the U. S. Bill of Rights.
The unit ends with the Presidencies of
George Washington and John Adams,
which along with the contributions of early
American leaders such as Thomas
Jefferson, James Madison, and Alexander
Hamilton, show how individuals, groups,
and institutions affect societal change.
CREATION OF THE UNITED STATES
NORTH AMERICA, EARLY 1700S
CREATION OF THE UNITED STATES
CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN
REVOLUTION
• 1. FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR (AKA 7 YEARS
WAR) (1754–1763)
• 1)the North American chapter of the Seven
Years' War, known in Canada as the War of the
Conquest. The name refers to the two main
enemies of the British: the royal French forces
and the various American Indian forces allied
with them. The war resulted in the British
conquest of Canada.
CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN
REVOLUTION
• 2)CAUSES
• a. Both New France and New England wanted to expand
their territories with respect to fur trading and other
pursuits that matched their economic interests. Using
trading posts and forts, both the British and the French
claimed the vast territory between the Appalachian
Mountains and the Mississippi River, from the Great
Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico
• b. both European powers took advantage of Native
American factions to protect their territories and to keep
each other from growing too strong.
• c. The English colonists also feared France’s Roman
Catholic influence. English law provided religious and
other freedoms.
FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR
• 3)NATIVE AMERICANS TENDED TO
SUPPORT FRENCH. AS FUR
TRADERS, FRENCH BUILT FORTS
RATHER THAN PERMANENT
SETTLEMENTS.
• 4)GREAT BRITAIN (ENGLAND) WON.
• 5)TREATY OF PARIS, 1763, SIGNED TO
END WAR.
PROVISIONS OF TREATY OF
PARIS, 1763
• 1.FR LOST CANADA TO ENG.
• 2.FR LOST ALL LAND EAST OF
MISSISSIPPI RIVER EXCEPT CITY OF
NEW ORLEANS.
• 3.ENG. GAINED COMPLETE, OFFICIAL
CONTROL OF ALL AMERICAN
COLONIES.
NORTH AMERICA AFTER TREATY OF
PARIS, 1763
CAUSES: AMERICAN
REVOLUTION
• 2.ENG. PARLIAMENT PASSED LAWS TO TAX
COLONIES TO HELP PAY FOR COST OF
MILITARY PRESENCE TO PREVENT ATTACKS
AND PROTECT FROM NATIVES.
• 3.PROCLAMATION OF 1763, STOPPED
AMERICANS FROM MOVING WEST BEYOND
APPALACHIAN MOUNTAINS (TO TRY AND
STOP CONFLICT WITH NATIVES)
• 4.IDEAS OF THE ENLIGHTENMENT
(FREEDOM, NATURAL RIGHTS,
DEMOCRACY, 1ST AMEND. RIGHTS (RAPPS)
RESISTANCE BY AMERICAN
COLONIES
• 1.AMERICAN COLONISTS FELT RIGHTS AS
ENGLISHMEN WERE BEING
VIOLATED…SUCH AS:
• 1) TAXATION WITHOUT REPRESENTATION
• 2)TRIAL BY JURY
• 3)PROTECTION FROM SEARCHES WITHOUT
WARRANTS
• 4)PROTECTION FROM HAVING TROOPS
QUARTERED ON PROPERTY
ACTIONS OF PARLIAMENT
• 1.SUGAR ACT, 1764 (TAX ON IMPORTS, BRITISH RATHER THAN
COLONY CTS.)
• 2.STAMP ACT, 1765 (TAX ON ALL PRINTED MATERIAL, {PAPER
WITH SPECIAL STAMPS}, BUYING PAPER, PAYING TAX
•
1)RESULT/REACTION: A. FORMATION OF SONS OF LIBERTY (SAMUEL ADAMS)
B. STAMP ACT CONGRESS-FORMAL PROTEST TO KING
• 3.TOWNSHEND ACT, 1767, (IMPORT TAX ON GLASS, LEAD,
PAINT, PAPER)
•
1)RESULT/REACTON: BOYCOTTS OF BRITISH GOODS
• 4.INTOLERABLE ACTS, 1774, (CLOSED PORT OF BOSTON DUE
TO BOSTON TEA PARTY, BRITISH TRIED IN ENGLAND,
COLONISTS HAD TO QUARTER TROOPS)
• 1)RESULT/REACTION: FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS TO
PROTEST
AMERICAN COLONISTS REACT
TO PARLIAMENT’S ACTIONS
• 1.BOSTON MASSACRE, 1770 (CRISPUS ATTUCKS)
• 2.BOSTON TEA PARTY, 1773 (RESULT WAS INTOLERABLE
ACTS)
• 3.COMMITTEES OF CORRESPONDENCE (SECRET
COMMUNICATIONS)
• 1)PLANNED 1ST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS,
• 2)1ST ORG. LINKING COLONIES TO OPPOSE ENG
• 3)LOYALISTS (KING) V. PATRIOTS (AMERICANS)
•
•
•
•
4.THOMAS PAINE PUBLISHED COMMON SENSE
1)ATLANTIC TO WIDE FOR ENG. TO RULE
2)ISLAND COULD NOT RULE CONTINENT
3)IF ENG WAS “MOTHER COUNTRY” “NO MOTHER WOULD
TREAT CHILD SO BADLY…”
SAMUEL ADAMS, BOSTON
MASSACRE
THOMAS PAINE
“THE SHOT HEARD ROUND THE
WORLD…”
• REMEMBER THE INTOLERABLE ACTS…
• 1.COLONIAL REACTION:
• 1)1ST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS, SEPT.,
OCT., 1774
• 2)NEW ENGLAND TOWNS PREPARED
MILITARY
a.FORMATION OF MINUTEMAN REGIMENTS,
CIVILIAN SOLDIERS
b.STOCKPILE WEAPONS
“THE SHOT HEARD ROUND THE
WORLD…
• 2. BRITISH GENERAL GAGE ENGAGES
AMERICAN COLONISTS AT LEXINGTON AND
CONCORD, MASSACHUSSETS, THE FIRST
SHOTS OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION.
• 3.SEE CLIP.
• 4.THE MIDNIGHT RIDE OF PAUL
REVERE…AND SAMUEL PRESCOTT AND
WILLIAM DAWES TO WARN, “THE REGULARS
(BRITISH) ARE COMING!!!!”
PAUL REVERE