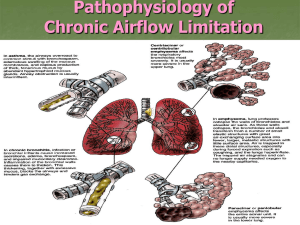
COPD (cont.)
advertisement

Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System Nursing II Valencia Community College The client with CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE COPD Description – Chronic airflow obstruction Irreversible – Chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema Incidence – 13.5 million Americans have bronchitis – 2 million Americans have emphysema – 4th leading cause of death – Death rate still rising – 2nd cause of disability in people > 65 COPD (cont.) Risk Factors – – – – – – – SMOKING Age Male gender Air pollution Occupational exposure Respiratory infections Familial & genetic factors COPD (cont.) Pathophysiology – Slow, progressive – Exacerbations destructive changes – Usually have both chronic bronchitis and emphysema And frequently asthma Emphysema Patho Loss of lung elasticity Hyperinflation of the lungs Alveolar walls and small airways damaged – Airways narrow or collapse – Air trapping – Alveolar damage = poor gas exchange Chronic Bronchitis Patho Inflammation caused by chronic irritation Cause vasodilation → congestion → edema → bronchospasm mucous production Thickened bronchial walls Narrowing of airways = poor gas exchange Diagnostics ABG Sputum C & S CXR CBC Electrolytes Pulmonary function testing Genetic testing Manifestations of COPD Absent or minor early Client usually seeks care after 10 yrs of signs and symptoms – When ADLs affected Manifestations General Appearance – Thin with loss of muscle mass in arms and legs – Stooped posture – Slow moving Manifestations Respiratory – Shallow, rapid respirations – Use of accessory muscles – Crackles, rhonchi, distant breath sounds – Dyspnea – Barrel chested – Bronchitis; Cyanotic, increased mucus, clubbing, cough Manifestations Cardiac – Tachycardia – Irregular pulse – Dependent edema JVD – Clubbing – Emphysema: Cyanosis with advanced disease Pallor Manifestations Psychosocial – Isolation Fatigue Embarrassment Smoking – Negative self image Change in role – Anxiety and fear Collaborative Care Impaired Gas Exchange – Patent airway = pulmonary toilet – Assess frequently – Oxygen Keep O2 sat > 88% – Medications – Energy management – Surgical Lung transplant Lung reduction Collaborative Care Ineffective Breathing Pattern – Teach effective breathing techniques Pursed lip Diaphragmatic/Abdominal – Exercise conditioning Respiratory rehab – Energy Conservation Rest between ADLs Collaborative Care Ineffective Airway Clearance – Effective coughing Controlled coughing – Chest PT – Postural drainage/positioning – Suctioning – Hydration Careful if bronchitis present Collaborative Care Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements – Small, frequent meals – – – – High calorie, high protein, low sodium Pulmocare Oral hygiene Rest before meals Assist with eating No treatments at meal time Collaborative Care Anxiety – Inform patient of all aspects of care – Know what to do if ↑ in signs and symptoms – Support group – Complementary therapy Collaborative Care Activity Intolerance – Pacing activities – Assess during activities for hypoxia – May need supplemental O2 Collaborative Care Potential For Infection (Respiratory) – Flu and Pneumonia vaccines yearly – Avoid large crowds Home Care – Infection prevention – Breathing exercises – ADL assistance – Pulmonary rehab program – Dealing with chronic illness – May need a social worker The Client with Pneumonia Definition Excess fluid in lungs from inflammatory process Types – Infectious → Viral or Bacterial Community acquired Nosocomial – Inhalation of Irritants Incidence 2 – 4 million cases in US yearly 5th leading cause of death incidence – Elderly – LTC residents – Hospitalized clients – On ventilators Incidence Continued More in fall and winter months Community acquired > nosocomial Risk Factors Community Acquired – Older Adult – No pneumococcal or flu vaccines – Chronic illness – Smoking – Alcohol – Exposure to viral or bacterial infections Risk Factors Continued Nosocomial – Older adult – COPD – LOC – Aspiration – Poor nutrition – Immune suppressed – Mechanical ventilation Pathophysiology Organism invades airway Multiples in alveoli Inflammation in interstitial spaces, alveoli, and bronchioles Fluids collect in alveoli gas exchange Patho Continued Fibrin and RBCs move into alveoli – Causes stiffening = compliance Alveoli collapse Consolidation occurs Infection spreads to other lung areas Sites of Pneumonia Lobar pneumonia – Segment or lobe of the lung Bronchopneumonia – In bronchus and bronchioles Diagnostics ABGs CBC, Lytes – May need HIV testing Sputum gram stain and C & S CXR Bronchoscopy Manifestations General Appearance – Flushed fever – Anxious – Muscle weakness – Headache – Chills – Poor appetite Manifestations Respiratory – Productive cough – Tachypnea, orthopneic – Use of accessory muscles – Crackles, wheezing – Pleuritic pain Complications of Pneumonia Hypoxemia Respiratory failure Atelectasis Pleural effusion Pleurisy Empyema Sepsis Collaborative Care Impaired Gas Exchange/Airway Clearance – Oxygen – Pulmonary toilet – Effective cough – Hydration – Medications Collaborative Care Acute Pain – Medicate for effective coughing Splinting – Positioning Collaborative Care Fluid Volume Deficit Disturbed Sleep Patterns Potential for Sepsis – What interventions would you do? Home Care Inquire about medical equipment for home use Activity tolerance