Chapter 8 Ionic Compounds
advertisement

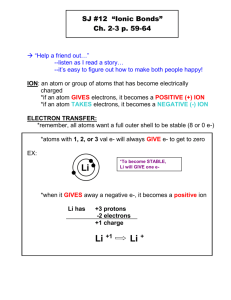
Chapter 8 Ionic Compounds Formation of Ions ► Which type of elements are the most stable (least willing to undergo change)? ► How many valence electrons do they have? ► What would you expect of the other elements to increase their stability? Octet Rule ► Octet Rule- atoms gain, lose, or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of 8 valence electrons. Ex. sodium ►A sodium ion is more stable than the neutral sodium atom because it now has 8 valence electrons. Ions ► Cation: A positively charged ion formed when an atom loses an electron ► Anion- A negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains an electron Chemical Bonds ► Chemical bond- an attraction (force) between atoms that holds them together 3 Types of Bonds 1. Nonpolar covalent bond- Valence electrons are shared equally between bonded atoms 2. Polar covalent bond- Valence electrons are shared unequally between the bonded atoms. 3. Ionic bond- Valence electrons are transferred from one atom to another, forming ions. These oppositely charged ions attract holding ionic compounds together. Ionic Bonds ► Ionic compound – compound made up of positive and negative ions that combine to be neutral consists of a metal and a nonmetal OR a metal and a polyatomic ion Formation of Ionic Cmpds. ► Formation of ionic compounds-compounds form to get 8 valence electrons Using Electron Configurations: ► Ex. Na and Cl to Na+ and Cl- = NaCl Using electron-dot notation Ex. Na and Cl to Na+ and Cl- = NaCl Ions ► Formula unit-Simplest ratio of the ions represented in an ionic compound Ex. MgCl2 ► Oxidation number (charge) –Equals the number of electrons transferred from or to an atom in order to form an ion (the charge of a monatomic ion) Written as superscripts-number to the upper right of symbol Positive oxidation number-electrons are transferred from Negative oxidation number-electrons are transferred to Binary Ionic Compounds Binary ionic compounds are composed of a metal cation and a nonmetal anion. Writing Ionic Chemical Formulas: 1. Cation symbol first; followed by the anion symbol 2. Subscripts (numbers to the lower right of a symbol that represent the number of ions of each element) are used to get an overall neutral compound. Write the chemical formulas for the following compounds: 1. sodium chloride 5. manganese (II) nitride 2. aluminum sulfide 6. lead (IV) phosphide 3. magnesium nitride 4. zinc oxide Binary Ionic Cmpds. Naming binary ionic compounds: 1. Name the cation first and the anion second 2. Use the element name for the cation 3. For the anion, take the root of the element name plus the suffix –ide. Examples: 1. CaCl2 3. Na2O 2. Ba3N2 Using Roman Numerals Ions with multiple charges: Transition metals and metals in group 4A of the periodic table often have more than one charge. (Exception zinc, silver, cadmium) Examples: 1. PbO2 3. MnCl3 5. GaI2 2. MnN 4. FeF3 Polyatomic Ions ► Polyatomic one element ions-an ion made up of more than ► Oxyanion-polyatomic ion composed of an element, usually a nonmetal, bonded to one or more oxygen atoms. Ex. -the ion with more oxygen atoms use the suffix –ate -the ion with less oxygen atoms use the suffix –ite Polyatomic Ions Ionic compounds with polyatomic ions: ► Charge applies to entire group of atoms ► Polyatomic ions act as individual ions so you can write chemical formulas the same way as binary compounds. Examples: 1. Ammonium chloride 2. Aluminum carbonate 3. Calcium phosphate 4. Iron(III) perchlorate Polyatomic Ions Naming ionic compounds with polyatomic ions 1. Name the cation first, followed by the anion. 2. If the compound contains a polyatomic ion, simply name the ion. Examples: 1. CaCO3 3. Al(ClO3)3 2. NH4Cl 4. CoCO3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. nickel (II) phosphide copper (III) chromate potassium sulfite silver nitrate Fe2(SO4)3 CaI2 PbO Properties of Ionic Cmpds. Properties of Ionic Compounds: ► Crystal lattice-3-D geometric arrangement of particles that is formed because of a strong attraction of positive ions and negative ions in an ionic compound ► High melting points and boiling points, and high degree of hardness-Because the bond is very strong, it takes a lot of energy to break apart the bond Properties of Ionic Cmpds. ► Ionic compounds are brittle ► Electrolyte-Ionic compounds dissolved in liquids are good conductors of electricity because the ions are free to move ► Energy changes occur when ionic compounds form A positive ion to a negative ion is always exothermic. Lattice energy-energy needed to separate the ions of the ionic compound. (Strength of holding ions). The more negative the number, the stronger the bond. Naming Binary Acids Acid-A compound that produces hydrogen ions in solution (hydrogen in front). 2 types of acids: binary acids and oxyacids Naming binary acids (Hydrogen and one other element) 1. The prefix hydro- is used to name the hydrogen part of the compound. 2. Add the root of the second element and the suffix -ic, and finally the word acid. Naming Acids Examples: 1. HCl 4. H2S 2. HBr 3. H3P Formulas for Binary Acids Examples: 1. Hydrosulfuric acid 2. Hydrofluoric acid 3. Hydronitric acid Oxyacids Naming oxyacids (An acid that contains H and an oxyanion) 1. Identify anion 2. Use a form of the anion + a suffix + the word acid. 3. If the anion ends in: -ate, replace it with the suffix –ic -ite, replace it with the suffix –ous Oxyacids Examples: 1. H2SO4 3. HClO3 Examples: 1. perchloric acid 3. Chromic acid 2. H2SO3 2. nitric acid 4. hydronitric acid Metallic Bonding Metallic bonding-bonding due to attraction between metal atoms and a sea of electrons. Explain these properties with bonding concept. ► Malleability-metals can be hammered in sheets. ► Ductility-metals can be drawn into wires ► Boiling points- atoms must be separated from the group of cations and electrons ► Good conductors-movement of mobile electrons around positive cations Alloys Alloys-mixture of elements that has metallic properties 2 types of alloys 1. Substitutional Alloy- Atoms of the original metallic solid replaced by other metal atoms of similar size. 2. Interstitial Alloy -The small holes in a metallic crystal are filled with smaller atoms