Salwa-3 - King Saud University Repository
advertisement
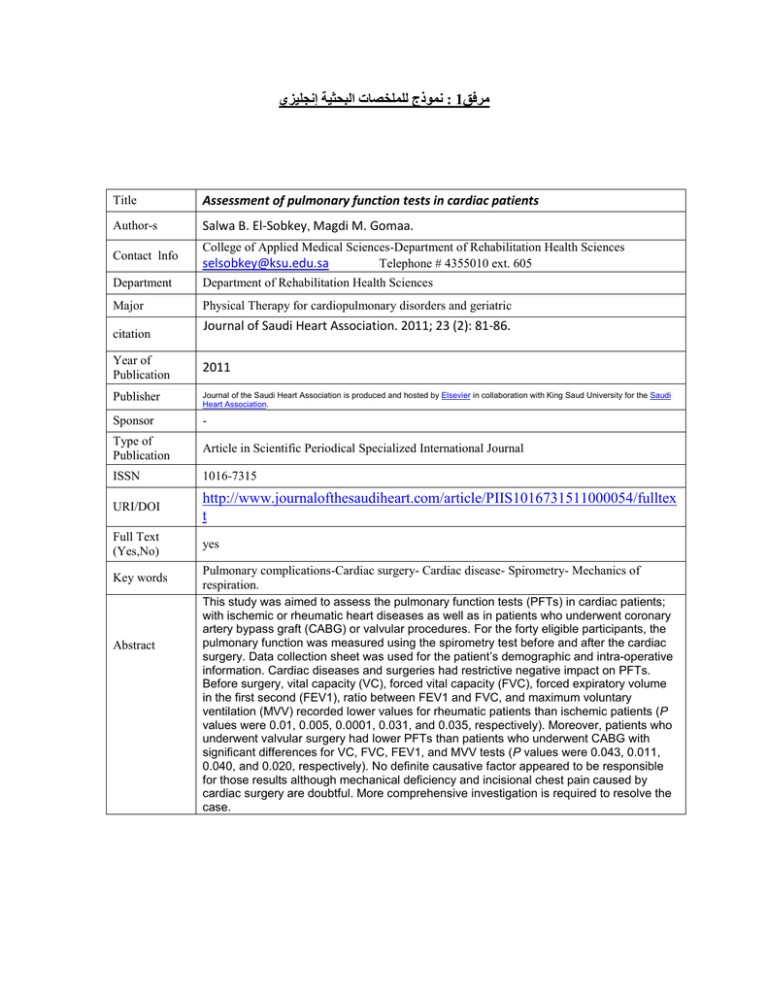
نموذج للملخصات البحثية إنجليزي: 1مرفق Title Assessment of pulmonary function tests in cardiac patients Author-s Salwa B. El-Sobkey, Magdi M. Gomaa. Contact lnfo College of Applied Medical Sciences-Department of Rehabilitation Health Sciences selsobkey@ksu.edu.sa Telephone # 4355010 ext. 605 Department Department of Rehabilitation Health Sciences Major Physical Therapy for cardiopulmonary disorders and geriatric citation Journal of Saudi Heart Association. 2011; 23 (2): 81-86. Year of Publication 2011 Publisher Journal of the Saudi Heart Association is produced and hosted by Elsevier in collaboration with King Saud University for the Saudi Heart Association. Sponsor - Type of Publication Article in Scientific Periodical Specialized International Journal ISSN 1016-7315 URI/DOI http://www.journalofthesaudiheart.com/article/PIIS1016731511000054/fulltex t Full Text (Yes,No) yes Key words Abstract Pulmonary complications-Cardiac surgery- Cardiac disease- Spirometry- Mechanics of respiration. This study was aimed to assess the pulmonary function tests (PFTs) in cardiac patients; with ischemic or rheumatic heart diseases as well as in patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) or valvular procedures. For the forty eligible participants, the pulmonary function was measured using the spirometry test before and after the cardiac surgery. Data collection sheet was used for the patient’s demographic and intra-operative information. Cardiac diseases and surgeries had restrictive negative impact on PFTs. Before surgery, vital capacity (VC), forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), ratio between FEV1 and FVC, and maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) recorded lower values for rheumatic patients than ischemic patients (P values were 0.01, 0.005, 0.0001, 0.031, and 0.035, respectively). Moreover, patients who underwent valvular surgery had lower PFTs than patients who underwent CABG with significant differences for VC, FVC, FEV1, and MVV tests (P values were 0.043, 0.011, 0.040, and 0.020, respectively). No definite causative factor appeared to be responsible for those results although mechanical deficiency and incisional chest pain caused by cardiac surgery are doubtful. More comprehensive investigation is required to resolve the case.