blood - Andrus alta anatomy
advertisement

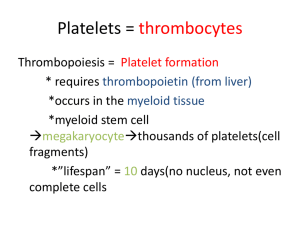
BLOOD Functions of Blood Transportation – oxygen and carbon dioxide – nutrients, hormones, metabolic wastes – heat Regulation – pH through buffer systems – body temperature – osmotic pressure within cells Protection – clot blood – Fight disease Components of Blood Plasma = straw colored liquid portion – Water = 92% – Solutes – electrolytes, hormones, gases, etc. = 8% Formed Elements = Blood Cells – Erythrocytes – Leukocytes – Thrombocytes Plasma and Serum Plasmapheresis: separates plasma from blood cells Serum --when blood clotting factors are removed Hematopoiesis Production of blood cells occurs in red bone marrow From stem cells called Hemocytoblasts Erythropoietin produced in the kidneys starts new RBCs (see pg 372) Erythrocytes (RBC’s) Carry Hemoglobin -gives whole blood it’s red color Have no nucleus Live about 120 days Hemoglobin Heme = iron – contains 4 per globin –gives blood it’s color Globin = protein ( carries some CO2) Leukocytes (WBC’s) main function protection from foreign particles Two Main Types: Granulocytes Agranulocytes Granulocytes Neutrophils – Phagocytes – most numerous Eosinophils – Removes allergens, reduces inflammation, increase with virus Basophils – promotes inflammation by secreting histamines – Heparin to prevent blood clotting Agranulocytes Lymphocytes – produce antibodies T and B cells) Monocytes – become Macrophages – Large “large eaters” Thrombocytes (Platelets) Clot blood (hemostasis) and repair damaged blood vessels life span of about 5 to 9 days Hemostasis mechanism by which bleeding is stopped Three Basic Mechanisms – Vascular Spasms – Platelet Plug Formation – Coagulation (Clotting) Vascular Spasm contraction of the smooth muscles in the vascular walls of a damaged blood vessel reflexes from pain receptors Platelet Plug Formation Platelet Adhesion = platelets contact and stick to walls of damaged vessels Platelet Release Reaction = platelets extend projections and release content of their granules Platelet Aggregation = platelets gather in area of wound or injury forms a Platelet Plug to stop bleeding Coagulation (Clotting) Several steps needed for process to work Intrinsic (within blood) Extrinsic (within tissues) forms a Clot = a network of fibrinogen(protein fibers) changes to fibrin Coagulation Fibrinogen changed to fibrin Thrombus and Embolus Thrombus: stationary clot Embolus: traveling clot – effects 4 organs – heart, lungs, brain and kidneys Clot may be blood, gas, fat, wastes, etc. ABO Blood Typing each parent contributes antigens (agglutinogens), or lack of antigens to their offspring O + O = O blood type A + O and A + A = A blood type B + O and B + B = B blood type A + B = AB blood type Rh Factor Presence or absence of Protein D on erythrocyte May effect – mother’s 2nd pregnancy May cause Hemolytic disease of the newborn. THE END OF BLOOD