Properties of Matter
advertisement

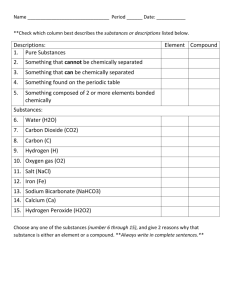
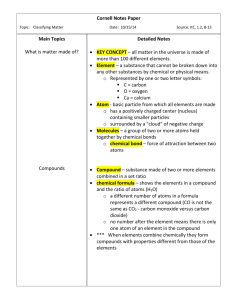
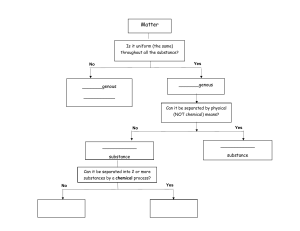
Properties of Matter Classifying Matter • • Matter- anything that has mass and takes up space 2 categories 1. Mixtures- contain more than one kind of matter that can be separated out 2. Substances • • Some are made up of only one kind of matter elements Some are made of more than one kind of matter but cannot be separated without changing the substance Mixtures • Homogeneous mixture- contains more than one type of matter and is the same throughout(soda pop, air, chocolate ice cream) • Heterogeneous mixture- contains more than one type of matter and is not the same throughout (chicken noodle soup) Substances • All substances are either elements or compounds • Elements • Compounds- substances that are made of 2 or more elements that cannot be separated by physical means Measuring Matter • Mass- the amount of matter an object has • Volume- the amount of space an object takes up • Density Volume • Rectangular solid or cube – Length x width x height • Cylinder – pi x radius2 x height • Cone – 1/3 x pi x radius2 x height • Sphere – 4/3 x pi x radius3 Volume • Irregular shapes? – Displacement method • Use graduated cylinder • Object displaces water • Read water level at the bottom of the meniscus Mass • Use a scale- measures the gravitational force between an object and Earth, calculates mass from weight • Use a balance- measures mass of unknown object by comparing it with objects whose masses are known Mass • Measuring very large and very small amounts – Use indirect measurement (pg 282) States of Matter • Molecule- smallest particle of a compound that retains the properties of the compound • Atom- smallest particle of an element Water • Compound • Each molecule has one atom of oxygen ad 3 atoms of hydrogen Mixtures The Building Blocks • Atoms • Molecules The Atom • Building blocks of matter – Subatomic particles • Electrons • Protons • Neutrons