Nuclear Chemistry - Duluth High School
advertisement

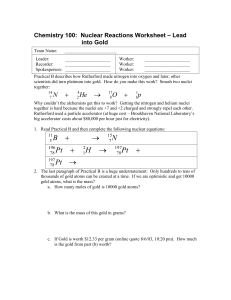
Nuclear Chemistry September 21, 2009 Trianna McCall Nuclear Reactions • Nuclear chemistry is the study of changes in an atoms nucleus. • Reactions that involve a change in the nucleus of an atom are called nuclear reactions. Characteristics of Nuclear Reactions • Occur when nuclei emit particles and/or rays • Atoms are often converted into atoms of another element • May involve protons, neutrons, and electrons • Associated with large energy changes • Reaction rates aren’t normally affected by temperature, pressure, or catalyst Table 25-1 (p805 of textbook) What Causes Nuclear Reactions? • The nuclei of some atoms are unstable and may undergo several changes. • Unstable systems gain stability by losing energy. • Certain atoms lose energy by emitting rays and particles called radiation. Related Terms • This spontaneous emission of radiation is a process called radioactivity. • The process by which unstable nuclei emit radiation to lose energy is called radioactive decay. • Radioisotopes, isotopes of atoms with unstable nuclei, undergo nuclear decay. Types of Radiation • Alpha -Composed of alpha particles -Contains 2p+ and 2n⁰ -42He • Beta -Composed of beta particles -Fast moving e- 0-1β or 0-1e Types of Radiation (cont) • Gamma -Not deflected by electric or magnetic fields -No charge -00γ • http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/ess entialchemistry/flash/radioa7.swf Types of Radiation Summary Type of Radiation Symbol Charge Penetration Ability Mass alpha 4 2He 2+ blocked by paper heaviest (4 amu) beta 0 -1β 1- blocked by metal foil lightest (1/1840 amu) gamma 0 0γ 0 not completely none blocked by lead or concrete Nuclear Equations • Used to express nuclear reactions • Both sides of the equation must have an equal sum of atomic mass and atomic numbers • Examples: - 23592U ______________ + 23190Th - 37K 0e + ______________ - 41Ca Ca + 0 _________________ Half-Life • The time required for one half of a radioisotope’s nuclei to decay into its products is called a half-life. • Amt Remaining=(Initial Amt)(1/2)n -n = # half lives passed • Amt Remaining=(Initial Amt)(1/2)t/T -t=elapsed time -T=duration of half life Half-Life (cont) • Example half-life problems: - How much of a 100.0g sample of 198Au is left after 8.10 days if its half-life is 2.70 days? -A 50.0g sample of 16N decays to 12.5g in 14.4 seconds. What is its half-life? -The half-life of 42K is 12.4hours. How much of a 750g sample is left after 62.0hours? -What is the half-life of 99Tc if a 500g sample decays to 62.5 g in 639,000 years? Fission and Fusion • The splitting of an atoms nucleus into fragments is called fission. -Provides energy for nuclear power plants • http://www.visionlearning.com/library/flash_ viewer.php?oid=2391&mid=59 • The combining of atomic nuclei is called fusion. -Fuels the sun • http://www.visionlearning.com/library/flash_ viewer.php?oid=2747&mid=59