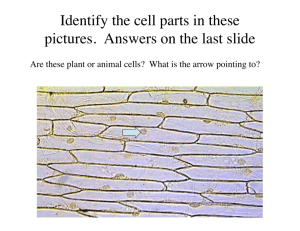
human body tissues
advertisement
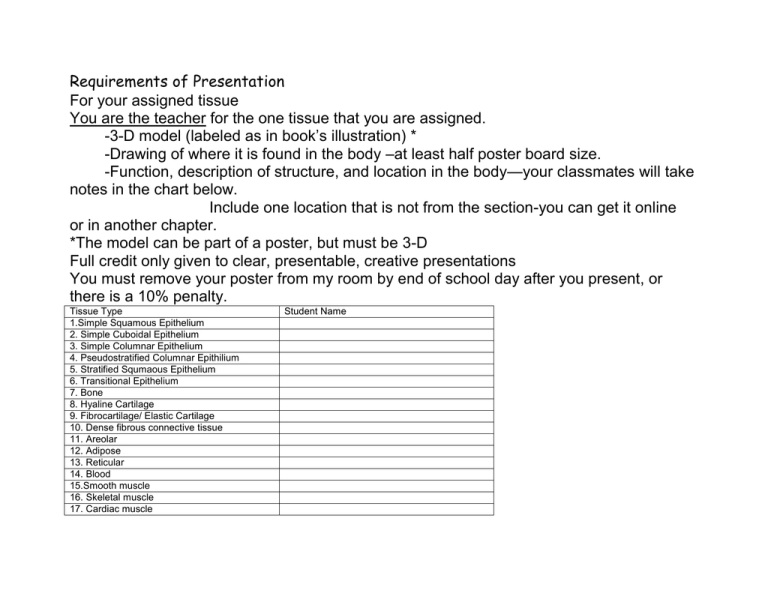
Requirements of Presentation For your assigned tissue You are the teacher for the one tissue that you are assigned. -3-D model (labeled as in book’s illustration) * -Drawing of where it is found in the body –at least half poster board size. -Function, description of structure, and location in the body—your classmates will take notes in the chart below. Include one location that is not from the section-you can get it online or in another chapter. *The model can be part of a poster, but must be 3-D Full credit only given to clear, presentable, creative presentations You must remove your poster from my room by end of school day after you present, or there is a 10% penalty. Tissue Type 1.Simple Squamous Epithelium 2. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium 3. Simple Columnar Epithelium 4. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithilium 5. Stratified Squmaous Epithelium 6. Transitional Epithelium 7. Bone 8. Hyaline Cartilage 9. Fibrocartilage/ Elastic Cartilage 10. Dense fibrous connective tissue 11. Areolar 12. Adipose 13. Reticular 14. Blood 15.Smooth muscle 16. Skeletal muscle 17. Cardiac muscle Student Name 18. Nervous tissue 19 Glands (page 81) Endocrine and exocrine Serous membranes (page 97) 20. Peritonium 21. Pericardiuim 22. Pleura 23, 24 Synovial joints pg 98 25.26 Cell Types 27 Cytoskeleton (pg 63) 28 Mucus Membrane (pg 96) 2 students present together to teach this page Can be a team HUMAN BODY TISSUES TISSUE TYPE EPITHELIAL Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple Columnar Epithelium Pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar FUNCTION With key terms underlined NAME ________________ DESCRIPTION Of STRUCTURE LOCATION Epithelium Stratified Squamous Epithelium Transitional Epithelium FUNCTION DESCRIPTION CONNECTIVE TISSUE—All connective tissue is composed of living cells in a non-living matrix. Bone Hyaline Cartilage Fibrocartilage Elastic cartilage Dense fibrous Areolar LOCATION Adipose Reticular Blood FUNCTION DESCRIPTION LOCATION Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Nervous tissue Serous membranes All have same basic function Peritonium Pericardium Pleura Synovial membranes Glands . HUMAN BODY TISSUES TISSUE TYPE FUNCTION With key terms underlined Allows passage of materials by diffusion DESCRIPTION LOCATION Single layer of flattened cells Delicate Air sacs of lungs, blood vessels Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Secretion and absorption Single layer of cubelike cells Kidney tubules, ovary surface Simple Columnar Epithelium Absorption, secretion of mucous May contain mucous secreting goblet cells. Ciliated type propels mucous Single layer of tall cells, some with cilia Lines digestive tract from stomach to anus Simple Squamous Epithilium Ciliated type lines bronchi and uterine tubes. Pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar Epithelium Mainly secretion and propulsion of mucous. (also contains goblet cells.) Single layer of cells of different heights, some w/ cilia Ducts of large glands, ciliated in trachea Stratified Squamous Epithelium Protect underlying tissue from friction Thick w several cell layers Esophagus, mouth, vagina Epidermis of skin Transitional Epithilium Readily stretches to allow distension of bladder Several layers of various shape that slide past one another and thin when stretched Urinary tract including bladder Osteocytes (bone cells) in lacunae (cavities in the matrix) Bones Rubbery matrix with glassy appearance Ends of long bones, attaches ribs to sternum, Embryonic skeleton Connective Tissue -- Always constists of living cells in a non-living matrix Bone Protects and supports other organs Provides levers for muscles to act on Calcium storage Blood cell production Hyaline Cartilage Support structures and cushioning “Gristle” Fibrocartilage Strong support and withstands heavy pressure Similar to hyaline but slightly softer Intervertebral discs Discs of knee joints Allows great flexibility while maintaining shape Also similar to hyaline, but most elastic External ear Epiglottis Attaches muscles to bones, or bones to bones. Parallel collagen fibers Tendons and ligaments Elastic cartilage Dense fibrous Areolar Wraps, cushions, protects organs. Holds tissue fluids. During inflammation, holds fluid like a sponge-edema. Contains hungry phagocytes that look for debris Soft, pliable, “cobwebby “ tissue Lamina propria, underlies of all mucous membranes Adipose Insulation, protects organs, fuel reserves Contains large droplet of oil “Signet ring cells” (like a class ring) Under skin (sub Q “fat”) Around kidney and eyeballs, breasts. Reticular Forms a soft internal skeleton called stroma,, which supports white blood cells and other cell types. Interwoven fibers with reticular cells Lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow Blood Transport of nutrients, gases, wastes Liquid tissue Matrix is the proteins in plasma Within blood vessels Smooth muscle Propels materials along a passageway (peristalsis), involuntary control Walls of hollow organs: stomach, bladder, uterus, blood vessels Skeletal muscle Voluntary control of muscles, and facial expression Spindle shaped (fusiform) pointed at both ends, with no striations, uninucleate Long, cylindrical, multinucleate, with straitions Cardiac muscle Contractions of the heart by involuntary control Walls of the hear Nervous tissue Transmit electrical signals in body coordination Display irritability and conductivity Branching, striated, uninucleate, cells connected by intercalated discs Branching cells with processes (extensions) that can Attached to bone or occasionally to skin. Brain, spinal cord, nerves be quite long Serous membranes Protects internal organs by reducing friction Simple squamous epithilium on thin layer of areolar tissue Synovial membranes Provide a smooth surface and lubricate joints to reduce friction Soft areolar connective tissue Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium Parietal peritonioum Visceral peritonium Parietal and visceral pleura Line the joints Describe the 3 steps of tissue repair and discuss which tissues regenerate well and which regenerate poorly.