Notes
advertisement

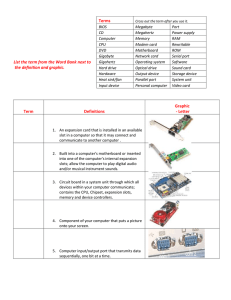
Computer Architecture Notes 1. Input Devices Keyboards: Notes: This is the primary input device for a computer. It is used to manually enter information into the computer. Keyboards are available in both standard and natural (curved) styles and come in many different varieties. Mouse Notes: Used with graphical interface environments to point and select objects on the system's monitor. Can be purchased in a variety of sizes, shapes, and configurations. Scanner Notes Converts printed or photographic information to digital information that can be used by the computer. Works similarly to the scanning process of a photocopy machine. Microphone Notes: Works like the microphone on a tape recorder. Allows input of voice or music to be converted to digital (binary) information and saved to a file. CD-ROM / DVD-ROM Notes CD-ROM stands for Compact Disc-Read Only Memory. It stores large amounts of data (650 MB) on a compact disc that can be read by a computer. DVD-ROM stands for Digital Video Disc: stores larger amounts of data (4.7 GB, or approximately 4700 MB) that can be read by a computer. 2. Processing Devices Motherboard Notes: The large circuit board found inside the computer. Without it, a computer is just a metal box. The motherboard contains all the remaining items in this section; for all practical purposes, it is the computer. Chip set Notes: A group of computer chips or integrated circuits (ICs) that, when working together, manage and control the computer system. This set includes the CPU and other chips that control the flow of data throughout the system. Data Bus Notes: A group of parallel conductors (circuit traces) found on the motherboard and used by the CPU to send and receive data from all the devices in the computer. Expansion Slots Notes: Specialized sockets that allow additional devices called expansion cards or, less commonly, circuit boards to be attached to the motherboard. Used to expand or customize a computer, they are extensions of the computer's bus system. There are four different types of expansion slots. The most commonly used one is called the PCI (Peripheral Connection Interface) and is usually white in color. Normally, sound cards, modems, and network cards are designed to fit into PCI slots. Another important expansion slot is called AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) and is used only for video cards. The newest type of video card expansion slot is called PCI Express. It allows for data to be transferred twice as fast as AGP slots, so they give better video performance. The fourth type of expansion slot is called ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) and is black in color. This slot is commonly found on older computers and is seldom used anymore, because of its slow data transfer rate. Processor Chip Notes: The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of your computer. It handles all the instructions you give your computer, and the faster it does this, the better. Battery Notes: Protects unique information about the setup of the computer against loss when electrical power fails or is turned off. Also maintains the external date and time. Memory (RAM) Notes: Stores temporary information (in the form of data bits) that the CPU and software need to keep running. Most new computers contain anywhere from four gigabytes to sixteen gigabytes (4-16 GB) of RAM. The more RAM the computer has, the more programs it can run at the same time. 3. Output Devices Printer Notes: Generates a "hard copy" of information. Most common types of printers are color inkjet and laser (most commonly grayscale, although more expensive color laser printers are available). Monitor Notes: The primary output device. Visually displays text and graphics. Older monitors are CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and newer ones are flat-screen LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). Monitor quality is measured in D.P.I (dots per inch)—the more dots (pixels), the greater the resolution of the monitor and the better picture it will produce! Most monitor sizes range between 17 to 21 inches, measured diagonally across the screen. Plotter Notes: Similar to a printer, but uses pens to draw an image. Most often used with graphics or drawing programs. Architects commonly use plotters to create building blueprints. Speakers Notes: Reproduce sound. Optional high-quality speakers can be added to provide improved output from games and multimedia software. Higher-quality speakers often include a third speaker, called a sub-woofer, to add a deeper bass sound. 4. Input and Output (I/O) Devices Hard Drive Notes: The hard drive is a high-capacity internal (and sometimes external) magnetic disk for storing data and program files. Also called a fixed disk. Modem Notes: Converts computer data to information that can be transmitted over telephone wires and cable lines. This allows communication between computers over long and short distances. Modems are primarily used to allow computers to connect to the Internet. Modem stands for Modulate/Demodulate. Network Card Notes: An expansion card that allows several computers to connect to each other and share information and programs. Also called network interface card (NIC) or a local area network (LAN) card. CD and DVD-Recorder (burner) Notes: Also called CD/R or DVD/R. You can create CDs or DVDs with these devices, but you can only write to a section of the disc once. Variations on this type of device include CD-RW (CD Read/Write) or DVD-RW drives. These products allow you to read, write, and overwrite special CD-ROM or DVD-ROM type discs. Flash Drive Notes: Flash drives are currently the most commonly used method of easily transporting information from one computer to another. Flash drives are inserted into USB ports and currently have storage capacities from 1 GB to 128 GB.