DNA Replication Sv
advertisement

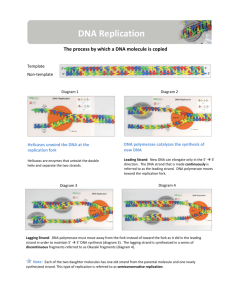
SBI 4U DATE: ____________________ DNA REPLICATION Recall: Before a cell can divide, it must first make a copy of each of its _________________________ DNA Replication Two DNA molecules are made from __________________ Each new DNA molecule (double helix) will have one strand of DNA from the ______________ molecule and one ___________ strand. o i.e. it is ______________________________ Parent DNA molecule and two daughter molecules are ________________ (same nucleotides in same order) Recall: Chargaff’s Rule o Adenine binds with Thymine o Cytosine binds with Guanine o Therefore, if you know the order of one strand, you know the order of the other SEPARATING THE DNA STRANDS 1. Replication begins when proteins bind at a specific site on DNA – _______________________ 2. DNA ____________ “unzips” or “unwinds” the DNA helix by breaking the Hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases that holds the two strands together. 3. ___________________________________ (SSBs) prevent the complementary strands from _______________ (pairing together) o This allows the strands to remain as _________________ for new DNA synthesis 4. DNA _______________ (in prokaryotes) and similar enzymes in Eukaryotes helps relieve tension on the unwinding DNA DIRECTIONALITY Replication begins in two directions from the origin as a region of the DNA is unwound DNA can’t be completely unwound due to size, so replication begins as soon as an opening is available Replication fork________________________________________________________________ o Replication goes ______________ the direction of the fork in one strand, and ___________ from it in another strand (leading vs. lagging strand…stay tuned ) o Can be more than one in eukaryotes due to size Replication bubble ____________________________________________________________ SBI 4U DATE: ____________________ BUILDING THE COMPLEMENTARY STRANDS Important: DNA is synthesized in the ___________ direction ONLY!! o i.e. _______________________ can only travel in the direction of 5’-3’; o Free bases are added via the ________ of a growing DNA strand via ________________ Step One: Priming Replication using RNA primase _______________ binds at the initiation point of the __________________ DNA polymerase cannot initiate a polynucleotide strand; it can only add to the 3’ end of an ______________________ strand o Thus __________________ helps to lay down an _________________ (a series of complementary RNA nucleotides) o the primer _______ be laid down _________ o They are “____________;” can be removed later _____________________________ can start elongation of the new strand by adding free ________________________________ from cytoplasm to the elongating strand DNA Polymerase III uses the ___________ from breaking the bond b/w the first and second ________________ to drive the condensation rxn that adds a nucleotide to the growing strand Step Two: Elongation The elongation process is different for the 5'-3' and 3'-5' template Leading 5'-3' Template: The daughter strand that uses the 5'-3' template is called _____________________ because DNA Polymerase III can "read" the template and ________________________ adds nucleotides o i.e. DNA polymerase is traveling continuously in the _______ direction of the new strand Lagging 3'-5'Template: The 3'-5' template ___________ be "read" by DNA Polymerase III (***DNA polymerase only travels in the 5’-3’ direction) Strand is synthesized ___________________ in short fragments in the opposite direction to the replication fork called _________________________ As a replication bubble opens, a polymerase molecule can work its way from the ____________ __________________________________________ As the bubble _____________ another segment can be made Therefore, the lagging strand is synthesized in a series of segments o Called __________________________ SBI 4U DATE: ____________________ Leading vs. Lagging Strand Step 3: Cleanup ___________________________ removes RNA __________ from both leading and lagging strands and replaces them with appropriate _______________________________ Since lagging strand is built in short segments, _____________ (enzyme) joins Okazaki fragments into one strand by _______________________________ Two ______ double-stranded molecules each twist into two ___________________ SBI 4U OVERVIEW OF REPLICATION RE-EMPHASIZING THE SEMI-CONSERVATIVE MODEL One strand acts as a ______________ to make a new strand. Process is ________________________ because each daughter strand is paired with a parent strand. One old and one new. DATE: ____________________