America In WWI
advertisement

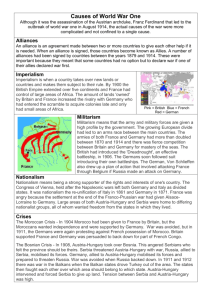
America In WWI Test: 20-November-2014 World War 1 Question : Due 11-Nov-14 Why did World War 1 break out in Europe? Quick Intro • American leaders had successfully followed G.W.’s advice in his Farewell Address to avoid “entanglements” with Europe. • However, during the Spanish-American War, the U.S. acquired an overseas empire and grew to become a major world power. • Another turning point in American foreign policy was reached in 1917, when the U.S. entered WWI Quick Intro • WWI was a GLOBAL war fought with new destructive technologies. • Far More destructive than any previous conflict. The Spark • The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand (by Serb nationalist in 1914) was the immediate cause of the war. • Austria-Hungary : BIG multi-national state • Slavic groups wanted independence (and were willing to commit acts of terrorism to achieve it). • Serbia (neighboring Slavic State) planned the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand (the heir to the throne) The Spark • Austria invaded Serbia to avenge the assassination (encouraged by their ally, Germany) • • • • • Existing alliances quickly brought other major powers into war Russia: Allied to Serbia Germany: Allied to Austria-Hungary Britain and France: Allied to Russia Quickly escalated into a MAJOR European war The Causes • • • • Nationalism Economic Rivalries & Imperialism Militarism & Military Planning The Alliance System Nationalism • Extreme loyalty to a nation and concern for its welfare • Led to rivalries between France, Germany, AustriaHungary, and Russia. Several nationalities in Austria-Hungary wanted to form their own national states. Economic Rivalries & Imperialism • Imperialism: A nation’s attempt to gain control of weaker nations • European nations divided much of Africa into colonies in order to obtain new materials and sell goods. • European powers had competing economic interests. • For example, Russian interests in the Balkans threatened AustriaHungary. • Competing colonial claims added to these tensions. Militarism & Military Planning • A nation’s policy to maintain a strong armed force • Powerful military establishments dominated European life. People were often seen in uniform and extolled the virtues of military discipline and war. • Generals believed it was better to attack than to be attacked because of the time it took to get troops into position The Alliance System • The formation of military agreements among nations • By the 1890s, Europe was divided into 2 alliances • Any dispute involving two of these nations threatened to involve all of them The Alliance System • The Triple Alliance (also known as the Central Powers): • Germany, Austria-Hungary & Italy • The Triple Entente (also known as the Allied Powers): • Great Britain, France & Russia