carbohydrate notes
advertisement

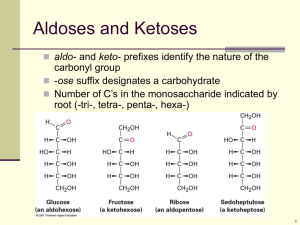
Carbohydrates Three categories of carbohydrates: 1. Simple sugars (monosaccharide) 2. Double sugars (disaccharides) 3. Macromolecules (polysaccharides) Monosaccharide Have the molecular formula CH2O. Ratio of C:H:O of 1:2:1 Most common monosaccharide is glucose and has the chemical formula C6H12O6 In an aqueous solution, monosaccharides form rings Disaccharide A disaccharide is 2 monosaccharides joined by the glycosidic linkage, which is a covalent bond formed by dehydration synthesis between to monosaccharides. Most common disaccharides: glucose + glucose maltose Glucose + fructose sucrose Glucose + Galactose lactose Glycosidic Linkages Polysaccharides Polymers of sugar – chains of sugar Uses/functions Storage of energy: Starch and glycogen Building materials (structural components): Cellulose and Chitin Polysaccharides for storage Starch Glycogen Found only in plants. Found only in animals linkages are 1,4 and 1,6 various linkages Helical in shape Helical in shape Some branching Many branches More on Starch and Glycogen Starch will provide long-term storage of sugars. It is stored in plastids in plant cells. Hydrolysis will release individual sugars as needed by the plant. We release sugars from starch with an enzyme in our saliva called amylase. Glycogen is stored in the liver and muscle cells and is only temporary. It is either used for energy or transferred to fat cells within 24 hours. glucose and glucose glucose and glucose are 2 isomers of glucose. Storage polysaccharides are made of glucose. Structural polysaccharides are made of -glucose. Structural polysaccharides Cellulose and chitin (pronounce “kite-in”) are both polysaccharides that are used in structure. Cellulose is a strong fiber that is used by plants as part of their cell walls. Chitin is used by fungi in their cell walls and in arthropods as their exoskeletons. Made of glucose in straight chains (not helical and never branched) The hydroxyl groups free to hydrogen bond Parallel lines of cellulose molecules are held together into units called microfibrils Who can digest cellulose? The enzymes that hydrolyze starch cannot hydrolyze cellulose. Many animals cannot digest cellulose, however, cows, horses, etc. have bacteria in their gut that can hydrolyze cellulose. Who can digest cellulose? Termites have microbes living in their gut that can hydrolyze cellulose. Chitin Chitin is cellulose with a nitrogen-containing appendage. Leathery in texture in fungus (like a mushroom). Encrusted with calcium carbonate chitin becomes hard and makes up the outer shell of arthropods (insects, lobsters, shrimp).