Chapter 5.2 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

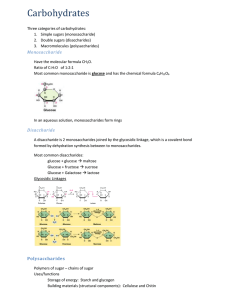
AP Biology Dr. Solis Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building material Carbohydrates Polymers of Sugars Disaccharides (double sugars) Polysaccharides (macromolecules) Sugars Monosaccharides (simple sugars) Carbohydrates Monosaccharides – simple sugars Carbohydrates Disaccharides – double sugars Carbohydrates Polysaccharides – polymers composed of many sugar building blocks Remember: Sugars are Carbs! Sugars are carbs Most names for sugars end in ose Glucose, fructose, Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas that are some multiple of the unit CH2O Sugars? Nutritious? Glucose is a monosaccharide Is a major nutrient to the cell Important for: Cellular respiration Cellular respiration: Cells extract energy in a series of reactions made possible by glucose The carbon skeleton of glucose lays a foundation for other the synthesis of other molecules (amino acids, fatty acids) Disaccharide Disaccharide consists of two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage. Glycosidic linkage: simply – the dehydration reaction formed by the molecules forming a covalent bond. Lactose is a disaccharide in milk. Maltose is a sugar in beer. Sucrose is table sugar. Polysaccharides Polysaccharides – macromolecules (a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. Serve as structures and building material for cells and organisms Polysaccharides Some are stored for later use These are things like ‘starch’ in plants Stockpiling of surplus glucose Sugar can be withdrawn later through hydrolysis Potatoes, grains, corn, rice – starch in the human diet 5.2 – Part 2 Important Polysaccharides Review: Plants store sugar in the form of starch. Starch is a polysaccharide Human diets are made up mostly of starch. Important Polysaccharides Glycogen – A polymer of glucose Animals (including humans and other vertebrates) store glycogen in liver and muscle cells Hydrolysis in these cells release glucose when the demand for sugar increases Glycogen is stored; but not for long In humans, glycogen is depleted in about a day unless it is replenished. Gives the animal much needed fuel when none other is available. How would this be a concern for people on a low-carb diet? Glycogen has 30,000 glucose units Structural Polysaccharides Polysaccharides are also important because: Organisms can build strong materials from them Cellulose is a polysaccharide Structural polysaccharides Cellulose is important because: A major component of the cell walls that enclose plant cells Globally, plants produce almost 100 billion tons of cellulose per year. It is the most abundant organic compound on Earth Cellulose Structure Cellulose is also a polymer of glucose (like starch) But it differs in its structure In starch - all monomers are in the same orientation But in cellulose, every other beta glucose monomer is upside down Cellulose In plant cell walls, cellulose molecules held together in a parallel way are grouped into units called microfibrils Cable like structures – that are very strong Cellulose Cellulose is the major component of paper and the only component of cotton Cellulose Normal enzymes are unable to hydrolyze the linkages in cellulose Most organisms cannot digest cellulose Humans cannot digest cellulose – so it passes through our body without being broken down. What animals can you name that can digest cellulose?