CARBOHYDRATE REVIEW
advertisement

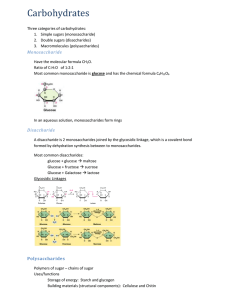
CARBOHYDRATE REVIEW A carbohydrate is: A. An organic compound B. A Biomolecule C. An Inorganic compound D. Ionic compound E. Both a and B Carbohydrates contain the elements: A. Carbon, nitrogen, & oxygen B. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:3:1 ratio C. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio D. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, & nitrogen E. CHNOPS Simplest type of carbohydrates: A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide D. Single sugar E. Both A and D Common examples of monosaccharides are: A. Glucose, fructose & galactose B. Maltose, lactose, & sucrose C. Starch, glycogen, chitin, & cellulose D. Glucose, Fructose, & maltose E. Glucose, Fructose, & lactose Two monosaccharides linked together: A. simple sugar B. polysaccharide C. Disaccharide D. Double sugar E. Both c & D Common examples of disaccharides are: A. Glucose, fructose & galactose B. Maltose, lactose, & sucrose C. Starch, glycogen, chitin, & cellulose D. Glucose, Fructose, & maltose E. Glucose, Fructose, & lactose The largest carbohydrates are: A. Monosaccharides B. Disaccharides C. polysaccharides D. Single sugars E. Double sugars Polysaccharides are made by: A. Linking single sugars together by dehydration synthesis B. Linking single sugars together by dehydration synthesis C. Linking simple sugars together by dehydration synthesis D. . Linking glucose molecules together by dehydration synthesis E. All of the above Common examples of polysaccharides are: A. Glucose, fructose & galactose B. Maltose, lactose, & sucrose C. Starch, glycogen, chitin, & cellulose D. Glucose, Fructose, & maltose E. Glucose, Fructose, & lactose Polysaccharides are A. Polymers B. Monomers C. Macromolecules D. Organic molecules E. Biomolecules F. A, C, D, and E Monosaccharides function as: A. Long term energy storage B. Short term energy storage C. Immediate source of energy D. Serve as monomers for polysaccharides E. Both C and D Carbohydrates can be divided into 2 types based on function: A. Structural & storage polysaccharides B. Structural and Defense polysaccharides C. Storage & insulating polysaccharides D. Storage & cushioning polysaccharides E. Cushioning & insulating polysaccharides STARCH A. Short term energy storage in plants B. Short term energy storage in animals C. Makes up cell wall of plants D. Makes up cell wall of fungi & exoskeleton of insects E. None of the above Glycogen A. Short term energy storage in plants B. Short term energy storage in animals C. Makes up cell wall of plants D. Makes up cell wall of fungi & exoskeleton of insects E. None of the above CELLULOSE A. Short term energy storage in plants B. Short term energy storage in animals C. Makes up cell wall of plants D. Makes up cell wall of fungi & exoskeleton of insects E. None of the above CHITIN A. Short term energy storage in plants B. Short term energy storage in animals C. Makes up cell wall of plants D. Makes up cell wall of fungi & exoskeleton of insects E. None of the above Found in liver & muscle of animals: A. Cellulose B. Chitin C. Glycogen D. Starch Undigestable by us: A. Cellulose B. Chitin C. Glycogen D. Starch FIBER IS: A. Cellulose B. Chitin C. Glycogen D. Starch