World History Cold War PPT - Reading Community Schools
advertisement

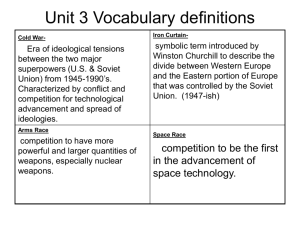
World History Cold War PPT Cody Reardon Battle of Ideologies • Communism vs. Capitalism • The Cold War (1945-91) was one of perception where neither side fully understood the intentions and ambitions of the other. This led to mistrust and military build-ups. • United States – U.S. thought that Soviet expansion would continue and spread throughout the world. – They saw the Soviet Union as a threat to their way of life; especially after the Soviet Union gained control of Eastern Europe. Battle of Ideologies • Soviet Union – They felt that they had won World War II. They had sacrificed the most (25 million vs. 300,000 total dead) and deserved the “spoils of war.” They had lost land after WWI because they left the winning side; now they wanted to gain land because they had won. – They wanted to economically raid Eastern Europe to recoup their expenses during the war. – They saw the U.S. as a threat to their way of life; especially after the U.S. development of atomic weapons. The “Iron Curtain” • Alarmed Americans viewed the Soviet occupation of eastern European countries as part of a communist expansion, which threatened to extend to the rest of the world. • In 1946, Winston Churchill gave a speech at Fulton College in Missouri in which he proclaimed that an “Iron Curtain” had fallen across Europe. • In March 1947, U.S. president Harry Truman proclaimed the Truman Doctrine. Policy of Containment • Definition: – By applying firm diplomatic, economic, and military counter-pressure, the United States could block Soviet aggression. • Formulated by George F. Kennan as a way to stop Soviet expansion without having to go to war. – HOW IS THIS POSSIBLE????? • Ironically, the Soviets were looking for insulation from the Capitalist West. The Marshall Plan • War damage and dislocation in Europe invited Communist influence • Economic aid to all European countries offered in the European Recovery Program • $17 billion to western Europe • Soviets refused – The blame for dividing Europe fell on the Soviet union, not the United States. And the Marshall Plan proved crucial to Western Europe’s economic recovery. Berlin Crisis • U.S., Britain, and France merged their zones in 1948 to create an independent West German state. • The Soviets responded by blockading land access to Berlin. The U.S. began a massive airlift of supplies that lasted almost a year. (7,000 tons a day) In May 1949 Stalin lifted the blockade, conceding that he could not prevent the creation of West Germany. • Thus, the creation of East and West Germany The Creation of NATO • Stalin’s aggressive actions accelerated the American effort to use military means to contain Soviet ambitions. • The U.S. joined with Canada, Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg to establish NATO, a mutual defense pact in 1949. • Pledged signers to treat an attack against one as an attack against all. • When West Germany joined NATO in 1955 Counter: The Warsaw Pact Treaties that didn't’t help • • • • • Paris Peace Treaty 1947 Yalta Conference Tehran Conference NATO Warsaw Treaty Problems of the Atomic Age • The most frightening aspect of the Cold War was the constant threat of nuclear war. – Russia detonated its first atom bomb in 1949. – Truman ordered construction of the hydrogen bomb. • Call for buildup of conventional forces to provide alternative to nuclear war Nuclear Confrontation • The Soviet army had at its command over 260 divisions. • The United States, in contrast, had reduced its forces by 1947 to little more than a single division. – American military planners were forced to adopt a nuclear strategy in face of the overwhelmingly superiority of Soviet forces. – They would deter any Soviet attack by setting in place a devastating atomic counterattack. • For the next quarter century, the U.S. and the USSR would engage in a nuclear arms race that constantly increased the destructive capability of both sides The Fall of China 100,000 people walked 6,000 miles to escape from the Nationalist Party. During The Long March Mao Zedong became the official leader of the party – The Nationalist republic maintained control through 1949. They improved transportation, provided a better education to more people, and encouraged industry. – However, peasants and workers lives were not improved The Fall of China (contd.) • In 1949 the Communist Party wins the civil war. • Mao declares China a communist state called The People’s Republic of China. • Chiang Kai-shek and the Nationalist Party flee to the island of Taiwan and establish The Republic of China. First Stage of Communism 1. Land was seized from the wealthy and given to the peasants. 2. A five year plan brought all industry under the government’s control. 3. Peasants combined their land to form collective farms. The Great Leap Forward 1. Collective Farms became huge communes— 25,000 peasants living together! 2. Poor production, droughts, and floods caused one of the worst famines in history. 3. In two years 20 million people starved to death Cultural Revolution (Removing the Competition) 1. To maintain control Chairman Mao launched the Cultural Revolution to remove opposition to the Communist Party. 2. The Cultural Revolution punished people who spoke against communism or the government. Artist were forced to create propaganda supporting communism. Korean War 1950-1953 • After WWII, Korea divided at 38th parallel: North was communist, South was not • Cause: 1950, North Korea invaded South Korea (supported by Soviet resources) • UN (led by US & Gen. Douglas MacArthur) sent forces to push back communists • Soviets boycotting UN for U.S. refusal to allow "Red China" into UN Security Council • China sends hundreds of thousands of troops to push back UN • Result: cease-fire and border at 38th parallel restored; still in existence today Arab Nationalism • Arab nationalists loosely united by opposition to colonialism and migration of Jews to Palestine • Balfour Declaration in 1917 indicated Britain favored creation of Jewish “national home” in Palestine—opposed by Saudi Arabia • Great Britain announced its withdrawal from Palestine in 1948. • United Nations voted for creation of two states, one Arab and one Jewish • Palestinians vowed to fight on until state of Israel destroyed or until they established own independent Palestinian state; led to several wars and numerous conflicts in late 20th century The Space Race • I am better than you nana boo boo! • Look up the following source and form an argument to who won the space race • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/moon/timeli ne/index.html Cuban Missile Crisis • Simulation of the Cuban Missile Crisis • I will place you into teams after you read the scenario for your nation • Why is this a momentous event in the Cold War. Vietnam • The Geneva Peace Accords, signed by France and Vietnam in the summer of 1954, provided for the temporary partition of Vietnam at the 17th parallel, with national elections in 1956 to reunify the country. • In the North, a communist regime, supported by the Soviet Union and the People's Republic of China, set up its headquarters in Hanoi under the leadership of Ho Chi Minh. Vietnam • The United States prevented the elections that were promised under the Geneva conference because it knew that the Communists would win. • The North Vietnamese used classic Maoist guerrilla tactics. “Guerrillas must move through the peasants like fish through sea,” i.e., the peasants will support them as much as they can with shelter, food, weapons, storage, intelligence, recruits. Vietnam • In early January 1973, the Nixon White House convinced Saigon that they would not abandon the South Vietnamese army if they signed the peace accord. • On January 23, therefore, the final draft was initialed, ending open hostilities between the United States and North Vietnam. • The Paris Peace Agreement did not end the conflict in Vietnam, however, as Saigon continued to battle Communist forces. German Reunifucation • German nationalism slowly began to show in the early 1800’s. Germany was divided into a number of small states and desired a unification within them. There goal was to become completely independent out of the control of all other nations as they had been in the past. Factors of Reunification • National factors: 1. Dissatisfaction with socialism 2. The economic situation in the GDR 3. The majority of West-Germans wanted to be reunited with the East Germans. Detante • Reasons A split between the USSR and China • China and the USSR became enemies since the mid-1960s •Both of them feared being isolated and were keen to create better relations with the US The changes of American policy •The defeat in the Vietnam War drove the US to adopt the non-commitment policy in the 1970s Detente • Reasons (contd) The fear of a nuclear war • Both knew that war meant global destruction • Led to arms limitations talks The burden of military expenditure •High costs of the arms race affected the development of the country •Both the US and USSR wanted to use its own resources to develop its home economy and to solve the problems of home poverty