Layers of the Earth
advertisement

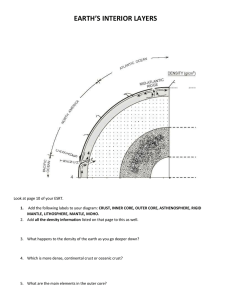
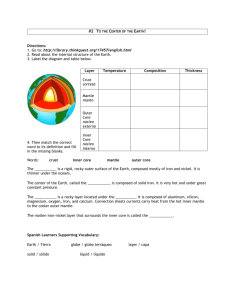
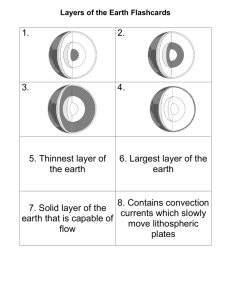
Ms. Wood 4 layers Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core Inner Core Solid Dense ball of solid metal (definition) Made of iron and nickel 2,000 – 5,000 degrees Celsius (as hot as the surface of the sun) Between 5150 km and 6371 km below surface of the Earth Outer Core Liquid Molten metal that surrounds inner core (definition) Made of iron and nickel 2,000 – 5,000 degrees Celsius (as hot as the surface of the sun) 2,900 km to 5150 km below the surface of the Earth Mantle Solid layer of hot rock (definition) Lithosphere – uppermost part of the mantle; 109 km thick Asthenosphere- layer of mantle below lithosphere that is soft and flows slowly Solid mantle below asthenosphere Mantle cont. Composed of silicon, oxygen, iron, and magnesium Starts at 5 -40 km below surface; extends to 2,900 km 2,200 degrees Celsius Crust Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin (definition) Thinnest under the ocean and thickest under mountains Two types: Continental Oceanic Crust continued Between 5 km and 4 km Potassium thick/deep (avg 32km) Composed of: Magnesium Oxygen Silicon Aluminum Calcium Iron Sodium Earth’s Layers Info As you get deeper into the Earth, the pressure and temperature increase Geologists – scientists who study the forces that make and shape Earth Magnetic field – Currents in liquid outer core force inner core to spin This creates a bar magnet Magnetic poles are near geographic poles, but aren’t the same This is how a compass works