Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
advertisement

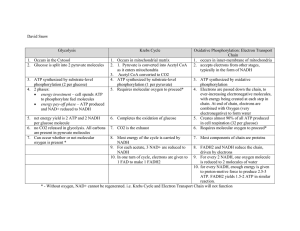
• Living cells require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform tasks • Energy flows into ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat • Chemical elements essential to life are recycled • Cellular respiration breaks down fuel to generate ATP, and the waste products become the reactants for Photosynthesis Organic compounds store energy in their arrangement of atoms - enzymes help break down products to simpler waste products with less energy One catabolic process, fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without the use of oxygen Cellular Respiration- oxygen is consumed as a reactant with organic fuel - 2 of 3 processes take place in mitochondria - similar to combustion of gasoline - CHO’s, proteins, and fats can combust and consume fuel Redox Reactions or Oxidation-reduction reactions deal with the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another. • Oxidation-the loss of electrons from one substance • Reduction- the addition of electrons to another substance • Reducing Agent-the electron donor • Oxidizing agent- electron acceptor Reactions do not occur all at once, but it steps to properly harness energy - gas tank explosion doesn’t drive car Glucose broken in a series of catalyzed steps by an enzyme NAD+ - a oxidizing agent or coenzyme that will strip electrons along with a proton (hydrogen) NADH is reduced form that is potential energy and can make ATP Glycolysis-breaks glucose into two molecules of a compound pyruvate - cytosol of cell - does not require oxygen - catabolic Citric Acid Cycle- Completes the breakdown of glucose by oxidizing a derivative of pyruvate to carbon dioxide - mitochondrial matrix - redox reaction transfers electrons and forms NADH - Also referred to as the Krebs cycle Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and chemiosmosis - inner membrane of mitochondria -accounts for 90% of ATP generated by respiration ATP synthesis that occurs when an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from the substrate to ADP - generates a smaller amount of ATP - substrate is generated from catabolism of glucose Glycolysis- (splitting of sugar) breaks a six-carbon sugar into two three-carbon sugars 3 carbon sugars are oxidized and remaining atoms form 2 molecules of pyruvate 10 steps in the reaction Energy investment phase – 2 ATP are spent in the initial break down of glucose to its first 5 intermediates Energy Payoff phase – ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation and NAD+ is reduced to NADH by electrons released from oxidation of food - produces 4 ATP molecules Net production is 2 ATP molecules