David Snow Glycolysis Krebs Cycle
advertisement
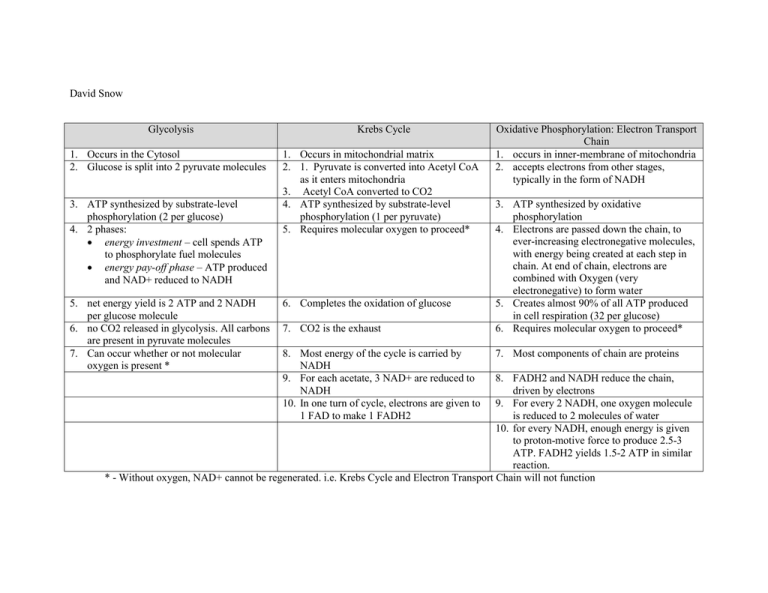
David Snow Glycolysis Krebs Cycle 1. Occurs in the Cytosol 2. Glucose is split into 2 pyruvate molecules 1. Occurs in mitochondrial matrix 2. 1. Pyruvate is converted into Acetyl CoA as it enters mitochondria 3. Acetyl CoA converted to CO2 4. ATP synthesized by substrate-level phosphorylation (1 per pyruvate) 5. Requires molecular oxygen to proceed* 3. ATP synthesized by substrate-level phosphorylation (2 per glucose) 4. 2 phases: energy investment – cell spends ATP to phosphorylate fuel molecules energy pay-off phase – ATP produced and NAD+ reduced to NADH 5. net energy yield is 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule 6. no CO2 released in glycolysis. All carbons are present in pyruvate molecules 7. Can occur whether or not molecular oxygen is present * 6. Completes the oxidation of glucose 7. CO2 is the exhaust 8. Most energy of the cycle is carried by NADH 9. For each acetate, 3 NAD+ are reduced to NADH 10. In one turn of cycle, electrons are given to 1 FAD to make 1 FADH2 Oxidative Phosphorylation: Electron Transport Chain 1. occurs in inner-membrane of mitochondria 2. accepts electrons from other stages, typically in the form of NADH 3. ATP synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation 4. Electrons are passed down the chain, to ever-increasing electronegative molecules, with energy being created at each step in chain. At end of chain, electrons are combined with Oxygen (very electronegative) to form water 5. Creates almost 90% of all ATP produced in cell respiration (32 per glucose) 6. Requires molecular oxygen to proceed* 7. Most components of chain are proteins 8. FADH2 and NADH reduce the chain, driven by electrons 9. For every 2 NADH, one oxygen molecule is reduced to 2 molecules of water 10. for every NADH, enough energy is given to proton-motive force to produce 2.5-3 ATP. FADH2 yields 1.5-2 ATP in similar reaction. * - Without oxygen, NAD+ cannot be regenerated. i.e. Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain will not function