Subsurface Processes Presentation
advertisement
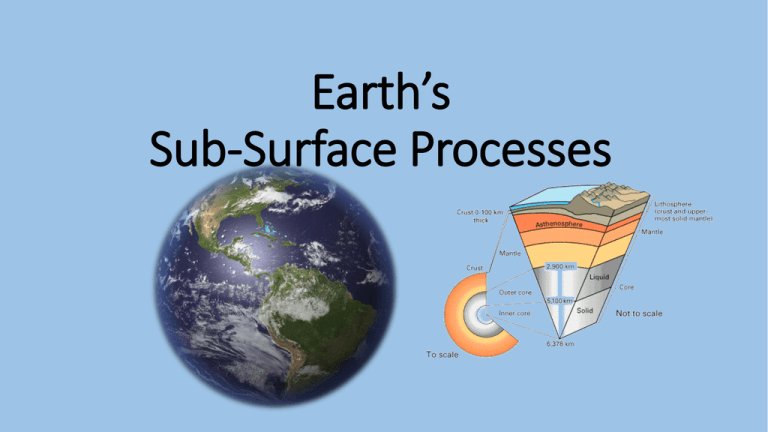
Earth’s Sub-Surface Processes CONTINENTAL DRIFT The process by which the continents move slowly across Earth’s surface. PLATE TECTONICS The theory that pieces of the Earth’s lithosphere, called plates, move about slowly on top of the asthenosphere. ALFRED WEGENER German scientist who first introduced the theory Kontinentalverschiebung... AKA CONTINETAL DRIFT Recognized that South America and Africa fit together like a puzzle What’s the evidence???? • Similarities of coastlines of continents (fit together like a puzzle) • Discoveries and correlations of worldwide distribution of plant and animal fossils • Records of Earth’s ancient magnetism captured in lava flows What’s the evidence???? • Observations of the flow of heat from Earth’s interior • Studies of the nature and exploration of the ocean floor • Locations of volcanoes and records of earthquakes The evidence Wegener needed… Seafloor Spreading: The movement of the ocean floor away from either side of a mid-ocean ridge Creates NEW CRUST!!! Mid-Ocean Ridges: A system of undersea mountain ranges that wind around the earth Subduction: When one plate moves under another plate at a plate boundary. Why does this happen?? Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust, so it is forced under the less dense material Zone of Subduction Oceanic-oceanic crust Oceanic-continental crust Forms: Volcanic Island Arcs & Deep trenches Understanding the Theory of Plate Tectonics • The theory not only describes continental movement, but also proposes an explanation of WHY and HOW continents move. • Tectonics is the study of the formation of features in the Earth’s crust. • The theory that pieces of the Earth’s lithosphere, called plates, move about slowly on top of the asthenosphere. Lithosphere Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core CRUST: outer surface; can be oceanic or continental LITHOSPHERE: rigid interior of crust ASTHENOSPHERE: plastic upper mantle MANTLE: molten rock OUTER CORE: liquid iron nickel INNER CORE: solid iron nickel Solid rock that slowly flows (Like putty) PLATE BOUNDARIES Divergent Pull away from each other Convergent Crash into each other Transform Fault Slide past each other National Geographic video Stress: Folding & Faults Compression Tension Shearing Tension Rocks are pulled apart Occurs at divergent boundaries Rocks become thinner Compression Crustal rocks are pressed together Occurs at convergent boundaries Pushes rock higher up or deeper down in the crust Shearing This stress pushes rocks in opposite direction Sheared rock bends, breaks, and twists as they slide past each other Occurs at transform faults Result of Stress ANTICLINE: up-curved folds in layers of rock SYNCLINE: down-curved folds in layers of rock MONOCLINE: gently dipping bends in horizontal rock layers Anticline Syncline Monocline Result of Stress If there is no movement on either side of break…this is a fracture. When there is movement, this is a fault Normal fault Occur along divergent boundaries and the hanging wall moves downward, relative to the footwall Reverse fault Occurs along convergent boundaries and the hanging wall moves upward, relative to the footwall Strike-slip fault Occurs along transform fault boundaries and the rock on either side of fault slides horizontally Thrust fault special reverse fault where fault plane is nearly horizontal (common in steep mountains) This Type of Creates this type of PLATE BOUNDARY STRESS Place where two plates meet Force acting on a rock to change its shape or volume. CONVERGENT BOUNDARY Two Plates Move Towards Each Other That Stress, creates this type of FAULT Break in the crust, where rocks slip past each o REVERSE FAULT Hanging Wall forced UP the Footwal COMPRESSION STRESS Rock is Squeezed Together DIVERGENT BOUNDARY Two Plates Move Away From Each Other NORMAL FAULT Hanging Wall Slides DOWN the Footw TENSION STRESS Rock is Stretched Out STRIKE ‘N’ SLIP FAULT Hanging Wall Moves PARALLEL (Left or Right) to the Footwall. TRANSFORM BOUNDARY Two Plates Move Parallel To Each Other SHEARING STRESS Rock is Pushed in Two Opposite Directions http://youtu.be/ryrXAGY1dmE Hawaii Hotspot Seafloor spreading and Megathrust