Respiratory System

Respiratory System
Function of the Lungs
Supplies oxygen to the blood by inhaling. This oxygen is then carried to all the cells of the body.
Removes carbon dioxide (a waste gas) from the cells and release it outside the body. This is done when you exhale.
Facts about the lungs
In the cells the oxygen being delivered combines with nutrients to provide energy that the cells can use.
The carbon dioxide that you breathe out is absorbed by the plants and converted back into oxygen.
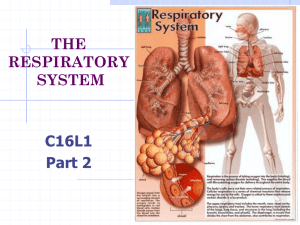
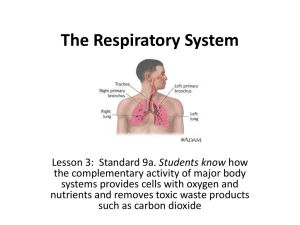
What makes up the respiratory system?
Trachea: Windpipe that directs air to the lungs
Bronchi: passages through which air enters the lungs
Alveoli: microscopic air sacs in the lungs which allow the exchange of
O2 and Co2
Diaphragm: muscle that contracts and relaxes to allow the lungs to breathe.
Common Problems
Bronchitis: swelling of the bronchi caused by a virus or bacteria causing coughing, fever, and chest tightness.
Asthma: an inflammatory disease that causes the bronchi to become blocked or narrowed.
Pneumonia: is a lung infection caused by viruses or bacteria.
Common Cancers
Emphysema: a disease in which the alveoli are damaged or destroyed.
Lung Cancer: a disease in which tissues of the lung are destroyed by the growth of a tumor.
Caring for your lungs
Stay Active: regular activity strengthens your lungs and helps keep parts of the respiratory clear. It also strengthens your diaphragm.
Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke: All types of tobacco increase your risk of respiratory diseases.