THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM C16L1
advertisement

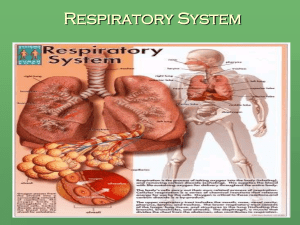
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM C16L1 Part 2 glottis the space between the folds epiglottis a thin, flexible flap in front of the larynx; folds over and blocks the glottis during swallowing It keeps food and liquids from entering the rest of the respiratory system. Trachea (windpipe) the tube that carries air between the pharynx and the bronchi trachea It is held open by C-shaped rings of cartilage. lined by the ciliated mucous membrane which traps matter such as dust, pollen, and smoke ends behind the heart, where it divides into 2 bronchi bronchi (singular, bronchus) the 2 branches off of the trachea leading into the lungs bronchi function: carrying air to and from the lungs lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Inside the lungs, the bronchi continue to branch into smaller and narrower tubes called bronchioles. bronchi bronchi branch and rebranch to form bronchioles bronchioles carries air to and from the alveoli within the lungs alveoli (singular, alveolus) the microscopic sacs in which the exchange of gases takes place in the lungs alveoli walls only 1 cell thick surrounded by capillaries How does this gas exchange take place? by diffusion breathing the process of inhaling and exhaling air diaphragm Below the lungs is a large muscle called the diaphragm that contracts and relaxes and moves air in and out of your lungs. breathing diaphragm: main muscle used in breathing Secondary muscles are the intercostals Breathing and air pressure The movement of your diaphragm causes changes in the air pressure inside your chest. Air rushes into and out of the lungs to equalize the air pressure inside and outside the body. Breathing and air pressure During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves down, enlarging the space around the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and moves up, reducing the space around the lungs. Breathing and air pressure