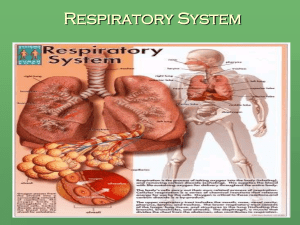
The Respiratory System
advertisement

The Respiratory System Lesson 3: Standard 9a. Students know how the complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide What have we learned so far? • The definitions of specialized cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems • The body is kept in homeostasis (balance) by the actions of different organ systems working together • Feedback inhibition is the mechanism for maintaining homeostasis in the body What have we learned so far? • The major parts of and the types of blood vessels in the circulatory system and The veins, arteries, valves, and chambers of the heart • The direction of blood flow through the heart • Pulmonary and systemic circulation The Human Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring about the ________ of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the ___, the ______, and the ________. The Human Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring about the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the ___, the ______, and the ________. The Human Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring about the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air, the the ______, and the ________. The Human Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring about the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air, the blood, and the ________. The Human Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to bring about the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air, the blood, and the tissues. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be _______ and _________ before it reaches the lungs. ______ in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any _________ you inhale and helps _______ the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be cleaned and _________ before it reaches the lungs. ______ in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any _________ you inhale and helps _______ the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be cleaned and moistened before it reaches the lungs. ______ in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any _________ you inhale and helps _______ the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be cleaned and moistened before it reaches the lungs. Mucus in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any _________ you inhale and helps _______ the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be cleaned and moistened before it reaches the lungs. Mucus in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any particles you inhale and helps _______ the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. Cilia and Mucus The tissues of the lungs are very delicate. Air must be cleaned and moistened before it reaches the lungs. Mucus in the cells that line the respiratory system helps trap any particles you inhale and helps moisten the air that travels to the lungs. Cilia are hair-like parts of cells. The respiratory passageways are lined with cilia. These cilia help move trapped particles that were inhaled back up and out of the body. The Lungs Your left lung is a little bit ______ than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the __________. When you breathe in, the diaphragm ________ to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, you breathe ____. The Lungs Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the __________. When you breathe in, the diaphragm ________ to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, you breathe ____. The Lungs Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the diaphragm. When you breathe in, the diaphragm ________ to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, you breathe ____. The Lungs Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the diaphragm. When you breathe in, the diaphragm contracts to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, you breathe ____. The Lungs Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the diaphragm. When you breathe in, the diaphragm contracts to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, you breathe out. How Breathing is Controlled • Breathing is not completely voluntary or involuntary • You can change your breathing rate almost any time you want, but you do not have to think about it. Your brain will make sure that you keep breathing. • There are cells in a part of the brain called the ________ __________ that monitor the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood are high, the medulla oblongata sends signals through ______ that cause your diaphragm to contract, making you breathe in. How Breathing is Controlled • Breathing is not completely voluntary or involuntary • You can change your breathing rate almost any time you want, but you do not have to think about it. Your brain will make sure that you keep breathing. • There are cells in a part of the brain called the medulla oblongata that monitor the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood are high, the medulla oblongata sends signals through ______ that cause your diaphragm to contract, making you breathe in. How Breathing is Controlled • Breathing is not completely voluntary or involuntary • You can change your breathing rate almost any time you want, but you do not have to think about it. Your brain will make sure that you keep breathing. • There are cells in a part of the brain called the medulla oblongata that monitor the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood are high, the medulla oblongata sends signals through nerves that cause your diaphragm to contract, making you breathe in. Alveoli and Gas Exchange The _______ are tiny air sacs in the lungs. They increase the ______ ____ of the lungs to maximize gas exchange. Alveoli and Gas Exchange The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs. They increase the ______ ____ of the lungs to maximize gas exchange. Alveoli and Gas Exchange The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs. They increase the surface area of the lungs to maximize gas exchange. RIGHT NOW • Pick a partner. THIS MUST BE SOMEONE SITTING NEAR YOU. • Point to your partner. This is the person you will make a lung model with • Start coloring in the diagrams of the respiratory system while Mrs. Campbell distributes the lung model materials • DO NOT TOUCH THE LUNG MODEL MATERIALS YET