Punnett Square Practice PowerPoint
advertisement

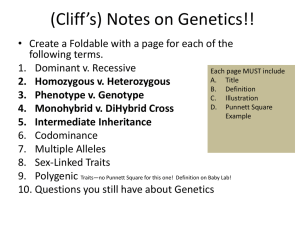
HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Copy ONLY the UNDERLINED WORDS and ANSWER the questions. Tongue Rolling (T) is dominant to Non-Tongue Rollers (t). 1. What are the possible GENOTYPES for the tongue-rolling trait? 2. What are the possible PHENOTYPES for the tongue-rolling trait? 3. If an individual was HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE for tongue-rolling, what would their PHENOTYPE look like? Their GENOTYPE? Tongue Rolling (T) is dominant to Non-Tongue Rollers (t). 1. What are the possible GENOTYPES for the tongue-rolling trait? TT, Tt, tt 2. What are the possible PHENOTYPES for the tongue-rolling trait? Tongue Rolling and Non-Tongue Rolling 3. If an individual was HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE for tongue-rolling, what would their PHENOTYPE look like? Their GENOTYPE? Phenotype = Non-Tongue Roller Genotype = tt Collect Today NOTHING!!! Assigned Page 75 – Wizard Genetics (TOMORROW) M.K.M.S. MAKE-UP Quiz (TOMORROW) Page 70 – Notecard Definitions (Thursday) Page 74 – Family Tree Project Part 1 (Friday) IBB MAKE-UP Quiz (Next Monday) Late Page 71 - Family Tree Project Research (-30%) Unit 5 – Genetics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. PG 70 Definitions Due Thursday (12/3/15) All Parts Due Thursday (12/10/15) Allele 10.Hybrid 18.Purebred Co-Dominance 11.Incomplete 19.Recessive Dominance Dihybrid Cross 20.Sex-linked Traits 12.Monohybrid Dominant 13.Multiple Alleles Gene 14.Pedigree Genotype 15.Phenotype Gregor Mendel 16.Polygenic Heterozygous 17.Punnett Square Homozygous Essential Question PG 73 How do I model the predicted inheritance of a single trait? Standard B6F - Predict possible outcomes of genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses. Mendel’s assumptions about segregation predicted a phenotypic ratio of 3:1. Mendel’s assumptions about segregation predicted a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1. The fact that genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance is known as independent assortment. The principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. Independent assortment helps account for the many genetic variations observed in many organisms. Punnett Square Steps 1st Step = Identify what letter is being used What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? “P” and “p” Punnett Square Steps 2nd Step = Assign the trait for each letter. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? P= PINK p = WHITE Punnett Square Steps 3RD Step = Match what letters are being used for each parent/gender. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? = PP DAD = pp MOM Let’s sum it up….. 1st = Identify what letters are being used. 2nd = Assign the trait for each letter. 3rd = Match what letters are being used for each parent/gender. 4th = Now fill in your Punnett Square. Punnett Square practice… 1. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? p p P P Pp Pp Pp Pp P = Pink p = White DAD = PP MOM = pp **When using the letters like “P and p” OR “C and c”, draw the lowercase letter in cursive or just make sure you make them look different. Otherwise, you might confuse the dominant for the recessive ** Phenotype: 4 Pink Flowers 0 White Flowers Genotype: 4 Pp 2. Long fingers are dominant (F) to short fingers (f). Complete the Punnett square for a homozygous recessive mom and a heterozygous dominant dad. f f F f Ff ff F = Long f = Short ff DAD = Ff MOM = ff Ff Is the Punnett Square Correct? 3. In a plant, long stems are dominant (L) to short stems (l). If a homozygous dominant flower and a homozygous recessive plant are crossed, what would be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? l l L L Ll Ll L = Long l = Short Ll DAD = LL MOM = ll Ll Genotypic Ratio: 0 LL : 4 Ll : 0 ll Phenotypic Ratio: 4 long: 0 short 4. Straight hair (C) is dominant to curly hair (c). What would be the probability that a child would have curly hair if both parents are heterozygous dominant? C c C c CC Cc Cc cc C = Straight c = Curly DAD = Cc MOM = Cc 25% chance of a child having curly hair 5. Having a hitchhiker's thumb is a dominant trait (T). If a woman with a straight thumb has a child with a man who is heterozygous for the trait, what are the chances their child will have a hitchhiker's thumb? T t t Tt tt t Tt tt T = Hitchhiker t = Straight DAD = Tt MOM = tt 50% chance of have a child with Hitchhiker’s thumb. 6. What would the phenotypic and genotypic ratios be for two purple (Pp) flowers that were bred together? P p P p PP Pp Pp pp P = Purple p = White DAD = Pp MOM = Pp Phenotype: 3 Purple Flowers 1 White Flowers Genotype: 1 PP : 2 Pp : 1 pp HW: Wizard Genetics PG 75 Essential Question How do I model the predicted inheritance of a single trait? Human Pedigree – A Family Tree Project PG 74 Essential Question: “Why do offspring resemble both of their parents?” • REQUIREMENTS FOR PEDIGREE • POSTER SIZE: Smallest dimensions = 11 x 17 • TITLE: Family Name • KEY: Trait(s) & Gender Symbols • FAMILY MEMBERS: First Names • CONNECTEDNESS: Lines connecting people in the family EXTRA CREDIT!!! - Bring up your semester average to passing or a higher letter grade! Required: Siblings/You Parents Grandparents (0 points extra!) Extra Credit: Cousins/Siblings/You Parents/Aunts/Uncles Grandparents (10 points extra!) Extra Credit: Cousins/Siblings/You Parents/Aunts/Uncles Grandparents/Great Aunts/Great Uncles Great Grandparents (20 points extra!) Going beyond Great, great grandparents will not receive further extra credit. (0 points extra!) Make a cupcake family tree, a 3D model, or a YouTube Video, etc… Let your imagination run WILD!!! (10 points extra!) This activity is adaptable to everyone’s family situation. If you have any questions about how to draw a pedigree for your particular family, please see me. WARNING! Not completing the project will leave you in jeopardy of failing the 3rd Six-Weeks/Semester.