Document
advertisement

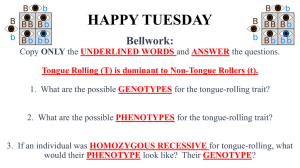
HAPPY THURSDAY BELL WORK: In 33 words, explain how a girl with blue eyes could have two parents with brown eyes. **Turn in your HW – The 2 handouts** Standard: B6F - Predict possible outcomes of genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses. Essential Question: How can I predict genetic outcomes? Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Gregor Mendel is the Austrian monk who was particularly important to understanding biological inheritance. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. From his experiments, Mendel concluded that biological inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from one generation to the next. The chemical factors that determine traits are called genes. The different forms of a gene are called alleles. When mating two organisms, the original pair of organisms is known as the P generation. The “P” in P generation stands for parental. The offspring of the P generation is the F1 generation. “F1” in F1 generation stands for first filial. Filius and filia are the Latin words for son and daughter. The offspring of crosses between parents with different traits are called hybrids. The principle of dominance states that some alleles are dominant while others are recessive. The dominant allele will always be expressed. A capital letter is used to represent a dominant allele. When Mendel crossed the F1 generation with itself, one fourth of the F2 plants showed the trait controlled by the recessive allele. The recessive allele will only be expressed when the dominant allele for the trait is not present. A lower case letter is used to represent a recessive allele. The way in which alleles separate during meiosis does not follow a pattern. It is completely random. The results of genetic crosses can be explained by the principles of probability. Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. Probabilities predict the average outcome of a large number of events. Probabilities cannot predict the exact outcome of an individual event. In probability, sample size eventually determines how close resulting numbers get to the expected values. In probability, past outcomes do not affect future ones. The gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross can be determined by drawing a diagram known as a Punnett square. The types of gametes produced by each F1 parent are shown along the top and left sides of a Punnett square. The possible gene combinations for the F2 offspring appear in the 4 boxes that make up the square. The letters in the Punnett square represent alleles. Punnett squares are used to predict and compare the genetic variations that will result from a cross. Organisms that have two of the same alleles for a trait are homozygous Organisms that have two different alleles for a trait are heterozygous. Homozygous organisms are true-breeding/purebred for a trait. Heterozygous organisms are hybrid for a trait. A phenotype is an organism’s physical characteristics. A genotype is an organism’s genetic makeup. Two organisms can have the same phenotype but different genotypes. Mendel’s assumptions about segregation predicted a phenotypic ratio of 3:1. Mendel’s assumptions about segregation predicted a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1. The fact that genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance is known as independent assortment. The principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. Independent assortment helps account for the many genetic variations observed in many organisms. Punnett Square Steps 1st Step = Identify what letter is being used What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? “P” and “p” Punnett Square Steps 2nd Step = Assign the trait for each letter. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? P= PINK p = WHITE Punnett Square Steps 3RD Step = Match what letters are being used for each parent/gender. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? = PP DAD = pp MOM Let’s sum it up….. 1st = Identify what letters are being used. 2nd = Assign the trait for each letter. 3rd = Match what letters are being used for each parent/gender. 4th = Now fill in your Punnett Square. Punnett Square practice… 1. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)? p p P P Pp Pp Pp Pp P = Pink p = White DAD = PP MOM = pp **When using the letters like “P and p” OR “C and c”, draw the lowercase letter in cursive or just make sure you make them look different. Otherwise, you might confuse the dominant for the recessive ** 2. Long fingers are dominant (F) to short fingers (f). Complete the Punnett square for a homozygous recessive mom and a heterozygous dominant dad. f f F f Ff ff F = Long f = Short ff DAD = Ff MOM = ff Ff 3. In a plant, long stems are dominant (L) to short stems (l). If a homozygous dominant flower and a homozygous recessive plant are crossed, what would be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? l l L L Ll Ll L = Long L = Short Ll DAD = LL MOM = ll Ll 4. Straight hair (C) is dominant to curly hair (c). What would be the probability that a child would have curly hair if both parents are heterozygous dominant? C c C c CC Cc Cc cc C = Straight c = Curly DAD = Cc MOM = Cc 5. Having a hitchhiker's thumb is a dominant trait (T). If a woman with a straight thumb has a child with a man who is heterozygous for the trait, what are the chances their child will have a hitchhiker's thumb? T t t Tt tt t Tt tt T = Hitchhiker t = Straight DAD = Tt MOM = tt 6. What would the phenotypic and genotypic ratios be for two purple (Pp) flowers that were bred together? P p P p PP Pp Pp pp P = Purple p = White DAD = Pp MOM = Pp Can you identify your own genotypes and phenotypes? Hairline: Widow’s peak is dominant to straight hairline Eye Shape: Almond eyes is dominant to round eyes Eyelash Length: Long eyelashes is dominant to short eyelashes Tongue Rolling: CAN roll the tongue is dominant to cannot Hitchhiker’s Thumb: Hitchhiker’s thumb is dominant to straight thumb Lip Thickness: Thick lips are dominant to thin lips