practice worksheet
advertisement

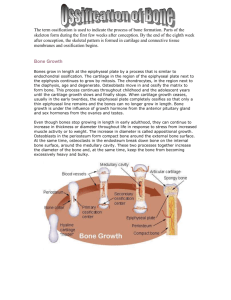
Anatomy SI worksheet 9 (2012) 1. Functions of bone include all of the following except A) storage of mineral and energy reserves B) transport of materials C) production of blood cells D) support and protection 2. Hemopoiesis is the process of A) bone formation B) cartilage formation C) blood cell production D) entrapment of blood vessels by developing bone 3. Hemopoiesis/Hematopoiesis occurs where? A) in yellow marrow B) the myeloid tissue of red marrow C) the periosteum D) the osteogenic layer of bone Hemopoiesis: A biological process in which new blood cells are formed, and is usually takes place in the myeloid tissue of bone marrow. Hematopoiesis: The production of all types of blood cells including formation, development, and differentiation of blood cells. Prenatally, hematopoiesis occurs in the yolk sack, then in the liver, and lastly in the bone marrow. 4. The most abundant mineral in the human body that is stored in our bones is A) calcium B) hydroxyapatite C) phosphate D) sodium 5. The most prevalent salt in bone matrix is _____. A) calcium B) hydroxyapatite C) phosphate D) sodium chloride * Calcium hydroxyapatite is the name of the complex mineral salts present in bone and is comprised of phosphate, carbonate and hydroxyl (OH-)ions. 6. Bone is somewhat flexible due to the presence of A) calcium B) phosphates C) collagen D) hydroxyapatite 7. The production of RBC’s, WBC’s and platelets is a major function of bone A) True B) False 8. The peritoneal area is the only area if the body not protected by bone A) True B) False 9. The epiphyseal plate (growth plate) / epiphyseal line is found in what area of a long bone? A) epiphysis B) metaphysis C) diaphysis 10. An epiphyseal line can be easily seen in the X-ray of a child. A) True B) False 11. Once epiphyseal cartilage cells stop dividing and are replaced by bone, the bony structure that forms is called the A) tuberosity B) epiphyseal line C) osteon D) metaphysis 12. The type of hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of all long bones is called A) articular cartilage B) epiphyseal cartilage C) the periosteum D) synovial cartilage 13. Articular cartilage provides a smooth surface between moving joints to reduce friction. This occurs because this form of hyaline cartilage is very VASCULAR and is DIRECTLY nourished by synovial fluid. A) True B) False 14. Spongy bone is also referred to as _____ bone. A) cancellous B) compact C) cortical D) fibrous 15. Osteogenic or Osteoprogenitor cells: A) are the unspecialized stems cells for bone B) build bone matrix C) breakdown the bone matrix D) are mature bone cells 16. Which of the following are the only bone cells that can divide? A) osteoblasts B) osteoclasts C) osteocytes D) osteogenic 17. Which of the following is not related to (derived from) osteoprogenitor cells? A) osteoblasts B) osteocytes C) osteoclasts 18. Osteoclasts: A) are the unspecialized stems cells for bone B) build bone matrix C) break down the bone matrix D) are mature bone cells 19. When there is too little calcium in blood, which cells begin resorption of bone to release calcium to the blood? A) osteocytes B) osteoclasts C) osteoblasts D) chondrocytes 20. The immature cells that produce osteoid are called A) osteocytes. B) osteoblasts. C) osteoclasts. D) osteons. 21. A small space within compact bone housing an osteocyte is termed a A) lamella. B) lacuna. C) canaliculus. D) medullary cavity. 22. All of the following occur during appositional bone growth EXCEPT A) osteoblasts in the periosteum lay down layers of bone matrix B) the bone widens as the number of circumferential lamellae increases C) growth occurs primarily in the cartilage of the epiphyseal plates D) osteoclasts expand the medullary cavity by resorbing bone matrix 23. As with cartilage growth, a long bone's growth in length is called A) interstitial growth B) appositional growth C) osteoid deposition D) none of the above 24. Interstitial growth of a bone occurs in the A) articular cartilage B) epiphyseal plate C) diaphyseal line D) center of the shaft 25. The nutrient foramen is where the nutrients enter the bone. This area; also called the perforating or volkmann’s canals form which type of ossification center for bone A) primary B) secondary 26. Primary ossification centers arise in the epiphyses of long bones. A) True B) False 27. Secondary ossification centers A) are located in the diaphysis of the bone. B) are located in the epiphysis of the bone. C) are located in the fontanels. D) appear during early fetal development. 28. Endochondral ossification begins with a______ model of bone. A) dense regular connective tissue B) hyaline cartilage C) fibrocartilage D) elastic cartilage 29. Chondrocytes die and stem cells in the perichondrium form osteoblasts during which of these processes? A) appositional growth of cartilage B) interstitial growth of bone C) intramembranous ossification D) endochondral ossification 30. Endochondral ossification A) occurs primarily in the bones of the skull. B) involves calcification of the cartilage matrix. C) produces bone in connective tissue membranes. D) occurs when chondrocytes replace osteoblasts in the matrix. 31. The surface of the medullary cavity of long bones is lined with a connective tissue membrane called A) periosteum. B) epiphyseal plates. C) endosteum. D) perichondrium. 32. The outer layer of bone, composed of dense, irregular, collagenous connective tissue that contains blood vessels and nerves is called A) endosteum. B) concentric lamellae. C) periosteum. D) the epiphyseal plate 33. Bundles of collagen fibers that penetrate the periosteum into the outer part of the bone are called A) endosteums. B) trabeculae. C) fasicles D) perforating fibers. 34. In long bones; new bone is deposited from the epiphysis to the diaphysis; but the actual bone growth occurs from the diaphysis to the epiphysis A) True B) False