f7286625ff5543c

1
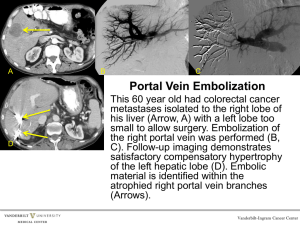
. The neck (L. collum, cervix ) is the transitional area between the head superiorly and the clavicles inferiorly that joins the head to the trunk and limbs.
2
2
. It serves as a major passage for structures passing between them.
3. In addition, several important organs with unique functions are located here: the larynx and the thyroid and parathyroid glands, for example
.
3
Great occipital nerve
(C2)
Lesser occipital nerve
(C2)
Great auricular nerve
(C2,C3)
Transverse cutaneous nerve (C2,C3)
Supraclavicular nerves
(C3,C4)
Skin of the neck (cutaneous nerves)
Platysma muscle
Superficial fascia
Superficial veins
External jugular vein
Tributaries of E.J.V and ant. J.V.
Cervical lymph node
Deep cervical fascia
Major muscles of the neck
Sternomastoi d muscle
11
Important notes
Layers of deep cervical fascia: investing layer, pretracheal, prevertebral and carotid sheath
Investing layer of deep fascia encloses sternomastoid and trapezius muscles
Contents of carotid sheath: CCA and ICA,
IJV and vagus nerve
N.B: all parts of skin of face and scalp infront of the ear innervated by trigeminal nerve except area over the angle of the mandibule and parotid gland innervated by great auricular nerve
Important veins
1. external jugular vein
Begin: just behind angle of the mandible by union of posterior auricular vein and post.division of the retromandibular vein
End: drain into subclavian vein tributaries 1. post.external jugular vein
2. ant. Jugular vein
Important veins
2. internal jugular vein
Begin: as contiuation of sigmoid sinus and leave skull throught jugular foramen
End: join subclavian vein to form brachiocephalic vein
Tributaries:
1. facial vein
2. Lingual vein
3. Pharyngeal vein
4. Thyroid veins
Sternomastoid muscle
Origin : a) Sternal head: Rounded and tendinous from front of manubrium. b) Clavicular head: Thin and fleshy from upper surface of med. ⅓ of clavicle.
Insertion :
Mastoid process and lateral ⅓ of the superior nuchal line.
Action :
1- Unilateral contraction → directs the face to opposite side.
2- Bilateral contraction → tilt the head backwards.
Nerve Supply : → spinal accessory n.
* Injury to the muscle leads to it contracture and shortening → Torticollis.
The oblique position of the sternomastoid divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangle.
A note about the scalene muscles :
Scalenus anterior
Scalenus medius
Scalenus posterior
Origin : transverse processes of cervical vertebrae .
Insertion : first and second ribs .
Action :
1- Lateral flexion of neck .
2- Fixation of ribs during forced inspiration .
Nerve supply : cervical and brachial plexuses .
. The subclavian vein passes infront the of scalenus anterior
. The subclavian artery and brachial plexus pass between scalenus anterior and scalenus medius .