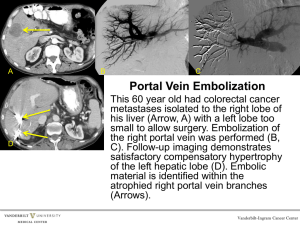
IACUC Procedures FAQs Blood Withdrawals Guidelines for Blood
advertisement

IACUC Procedures FAQs Blood Withdrawals Guidelines for Blood Withdrawals The type of test and amount of blood needed will govern the method and sites of collection. When venipuncture is required, hair should be clipped from the site and the area should be cleaned with alcohol. When collecting blood from the rabbit ear or mouse tail vein, heat (warm water bath) or xylene applied to the area may be helpful. Note: xylene is a dermal inflammatory agent and must be cleaned off with alcohol and water after blood collection is completed. After occluding the vein manually or by tourniquet, the needle is inserted parallel to the vein and the tip directed into the lumen along the longitudinal axis. When withdrawing blood, slow and gentle aspiration helps prevent collapse of the vein. Gauze held firmly in place at the blood collection site for a few minutes after withdrawal of the needle, will prevent the formation of hematomas. The following tables list common blood withdrawal sites and recommended needle length and gauge for use in laboratory animals. Note: Heart puncture and orbital bleeding are acceptable only if the animal is properly anesthetized. Laceration of the marginal ear vein of rabbits is considered to be unnecessarily traumatic and is frequently associated with post-procedural hemorrhage. Heart puncture should be limited to terminal procedures with the exception of the guinea pig. VOLUME OBTAINED* ANIMAL SITE NEEDLE GAUGES Mouse Heart**, tail vein (D), retro-orbital plexus 0.2 - 0.5 ml (least preferred & will required justification) 5/8" 25 ga 5/8" 27 ga Rat Heart** Retro-orbital plexus Tail vein (D) Saphenous vein (D) 5 ml 0.5 - 1 ml 0.5 - 1 ml 0.5 - 1 ml 1" 22 ga Hct tube 5/8" 25 ga 5/8" 25 ga Domestic Fowl Brachial Vein 5 - 10 ml 22 ga