File
advertisement

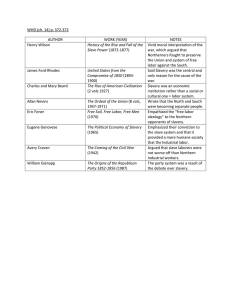
The Civil War THE UNION IN PERIL 1848-1861 • Facts, sequence of events • 4 main causes for why war erupted when it did: • Slavery as a moral issues in North vs. defense, expansion in South • Constitutional disputes over nature of federal union vs. states’ rights • Economic differences b/t N and S • Tariffs, nat’l bank, internal improvements • Political mistakes, extremism Why would war erupt? • Issues of slavery in territories after Mexican War • 1840s • Wilmot Proviso vs. Compromise of 1820 • Balance of 15/15 states • Proviso failed increase in sectional feelings • 3 competing views • Free Soil • Pro-slavery • Popular Sovereignty Territories • N. Dems + Whigs that supported Wilmot Proviso • Believed ALL African Americans should be excluded from Mexican Cession (1848) • Little opposition to slavery in S • West should be kept land of opportunity for whites only • No competition w/ slave labor, free blacks • “Free soil, free labor, and free men” = Free-Soil Party • Also advocate free homesteads, internal improvements Free-Soil Movement • Any restriction of expansion of slavery = violation of constitutional right to take, use property as see fit • Free-Soilers, abolitionists attempting to destroy slavery • Moderates want to see 36/30 extend to Pacific The Southern Position • Promoted by Lewis Cass (Dem. Senator, MI) as compromise • Supported by moderates from N and S • Extension of slavery into territories decided by vote of people who settle there, NOT by Congress • = squatter (popular) soverignty Popular Sovereignty THE ELECTION OF 1848 • 1848- Cass nominated by Dems • Focus solely on popular sovereignty • Whigs nominated Gen. Zachary Taylor • War hero, not political, no position taken on extension of slavery- was a Southerner, slaveholder • Vs. 3rd party Free-Soiler MVB • “conscience” Whigs (opposed slavery), antislavery Dems • Antislavery Dems called “barnburners”- defect threated to destroy Dem. party • Taylor win b/c split vote • Free-Soilers take votes from NY, PA Enter Taylor AGITATION OVER SLAVERY • Gold rush of ‘49 + 100k settlers need for law, order • Draft of state constitution, application for statehood • Banned slavery • Taylor support admission of CA, NM as free • secession talk by “fire-eaters” (S. radicals) • Met in Nashville to discuss secession Compromise of 1850 • Henry Clay step in & organize compromise • CA in as free • Mexican cession divided into Utah, New Mexico & allow slavery determined by pop. sovereignty • Disputed land b/t TX, NM settled- land to new territories in exchange for US assuming $10 mil. Of TX public debt • Slave trade banned in DC • Whites still able to hold slaves as before • New Fugitive Slave Law that will be enforced Enter Clay • Senate debates led by • Henry Clay, Daniel Webster, John C. Calhoun • Webster- for compromise to save Union end of support from abolitionists in MA • Calhoun- vs. compromise, want South to have = rights in territory • N. opposition from younger antislavery lawmakers • William Seward- argue a higher law than the constitution • 1850- death of Taylor brings in Millard Fillmore • Desire compromise • Stephen Douglas step in- pass each part separately Compromise passes • Added to help South accept loss of CA to antislavery forces • Purpose to track down fugitive slaves, capture them, return to owners • Fugitive slave cases under fed.gov. • Authority given to US commissioners to issue warrants, arrest fugitives • No trial by jury if claimed to be free, not fugitive • Enforcement resisted by antislavery groups division b/t N & S on issue • Underground Railroad Fugitive Slave Law • Emotions of people affected by laws, also popular books • Harriet Beecher Stowe- Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Conflict b/t Tom and owner (Simon Legree) • Show slave owners as cruel, inhuman; present MORAL issue of slavery • Could be overcome • Southerners see as “untruth,” proof that N prejudiced against Southern way of life Uncle Tom’s Cabin, 1852 • 1857- Hinton Helper wrote non-fiction, Impending Crisis of the South • Attack slavery through statistics- show as institution that weakened South’s economy • Book banned in South, circulated in North by antislavery, Free-Soilers Southern Antislavery View Category Free States Slave States Slave States as % of Free States Population 18, 484, 922 9,612, 979 52% Patents for New Inventions 1,929 268 14% Value of Church buildings $67, 778, 477 $21,674, 581 32% Newspapers, periodicals 1,790 740 41% Bank Capital $230,100,840 $109, 078, 940 47% Value of Exports $167, 520, 098 $107,480,688 64% • Proslavery whites argue slavery was positive, good for slaves & masters • Slavery sanctioned in Bible, grounded in philosophy & history • Contrast conditions of N. wage workers w/ familial bonds of slavery (patriarchy) • George Fitzhugh- Sociology of the South (1854), Cannibals All! (1857) • Question principle of equal rights for unequal men, attack capitalistic wage system (worse than slavery) Southern Reaction NATIONAL PARTIES IN CRISIS • Division in Dem., Whig party weak • Whigs- Gen. Winfield Scott • Attempt to ignore slavery, focus on improving roads, harbors • Drove out antislavery, Southern factions (fighting party on verge of split) • Dems- Franklin Pierce • Favor compromise, supported Fugitive Slave Law (was a Northerner- NH) • FP win electoral votes in all but 4 states = Whigs on the out Election of 1852 • 1854- Dems control White House, Congress • SD propose bill to split Nebraska Terr. into Kansas & Nebraska, allow settlers to decide slavery based on pop. sovereignty. Passes both houses & pres. • Douglas plan to build RR, promote western settlement • Need southern support to build transcontinental RR through central US and not south • KS, NE both above 36/30 South see as opportunity to expand slavery in areas that had been closed Kansas-Nebraska Act • K-N effectively repeal MO Comp. cap blown off regional tensions • SD assume those into KS antislavery farmers from Midwest • Problem? “Border Ruffians” • Response – New England Emigrant Aid Co. (1855) • FIGHTING b/t pro, antislavery groups • Proslavery gov. in Lecompton • Antislavery gov. in Lawrence • John Brown, Pottawatomie Creek • Other violence: Sumner-Brooks incident Bleeding Kansas NEW POLITICAL PARTIES • Sectional divisions in US + nativist feeling • Ethnic tension from WASP groups vs. immigrant Germans, Irish Catholics • American Party • Oppose Catholics, immigrants • Into N. cities • Support drawn from Whigs weakening of party Know-Nothing Party • 1854- Wisconsin • Response to passage of K-N Act • Free-Soilers + antislavery Whigs & Dems • Purpose to oppose spread of slavery INTO TERRITORIES • Repeal K-N Act, Fugitive Slave Law • Bleeding Kansas + violence abolitionists joining Birth of the Republican Party • Republicans 1st test- Fremont • No expansion of slavery, free homesteads, protective tariff • Know-Nothings- Fillmore • Dems- James Buchanan • Incumbent Pierce, Douglas too close to K-N Act (controversy) • Popular sovereignty • Buchanan take majority of pop. & electoral vote • Freemont- 11/16 free states shows Republicans may not need South to take White House Election of 1856 CONSTITUTIONAL ISSUES • JB seen as weak president (1857-1861) • Challenge in ‘57 to decide on Kansas • Proslavery constitution submitted • JB know majority of setters opposed • JB ask Congress to accept Lecompt. Const. and enter KS as slave • Congress reject • Many Dems agree w/ Republicans & oppose • 1858- settlers reject proslavery constitution in vote Lecompton Constitution • • • • • 1857 Proslavery decision of Taney Court Scott = slave, into free states = freedom? lawsuit against owner Decision? • Scott not a citizen • Slaves = property, so protected by 5th • Congress cannot exclude slavery from territory • MO Comp = unconstitutional Dred Scott v. Sandford