Monetary Policy
advertisement

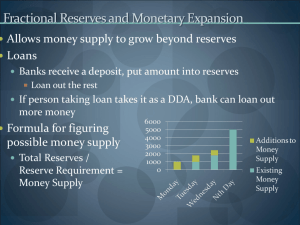
Notebook # 24Economics 15-2 Monetary Policy Monetary Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: • What is the purpose of the Federal Reserve System? • What are the structures of the Federal Reserve System? •What are the functions of the Federal Reserve System? Monetary Policy GPS STANDARDS: SSEMA2- Explain the role and functions of the Federal Reserve System. b.) Define Monetary Policy c.) Describe how the Federal Reserve use the tools of monetary policy to promote price stability, full employment, and economic growth. l The Federal Reserve System • What is the main function of the Federal Reserve? How does the Fed perform this function? 1. The function of the Fed is to control the money supply. 2. The primary instrument the Fed uses to affect the money supply is the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC): a. they make decisions about whether or not to raise or lower interest rates b. or whether or not to expand or contract the money supply l Other Functions of The Federal Reserve 1. The Fed monitors member banks’ reserves. 2. The Fed oversees foreign banks operating in the United States as well as the international operations of U.S. member banks operating in foreign countries 3. The Fed approves bank mergers like when Wells Fargo bought out Wachovia. l Functions of The Federal Reserve • Why might the Fed disapprove of a merger between two large banks? • Because it might limit competition between banks. l Other Functions of The Federal Reserve 5. The Federal Reserve is responsible for extending truth-in-lending disclosures to millions of individuals who purchase or borrow from corporations, retail stores, automobile dealers, and lending institutions. (they tell us the truth about using credit & credit cards) 6. The Federal Reserve is responsible for issuing paper currency. 7. The Federal Reserve is responsible for providing financial services to the federal government. l Monetary Policy • Federal Reserve actions intended to stabilize the economy make up what is called … Monetary policy. •One of the Federal Reserve System’s most important responsibilities is that of Monetary policy. •Monetary policy is the expansion or contraction of the money supply in order to influence the cost and availability of credit. l Monetary Policy • Also, the Fed does not hesitate to change interest rates whenever the economy’s health is threatened. •Monetary policy is a structured process. •In order to understand it better, it helps to understand the fractional reserve system that our banking system is based on. l l Monetary Policy: Fractional Bank Reserves • The United States has a: 1. fractional reserve system which requires banks and other depository institutions to keep “only” a fraction of their deposits in the form of actual monetary legal reserves. l l Monetary Policy: Fractional Bank Reserves • The United States has a: 1. The legal reserves consists of coins and paper currency that banks hold in their vaults. 2. Under this system, banks are subject to a reserve requirement which is a rule stating the percentage of every deposit that has to be set aside as legal reserves (money). l l Monetary Policy: Fractional Bank Reserves • Banks earn money by lending out that portion of their deposits that need not be held as reserves. • Your “physical” money is not at the bank but is being used to provide bank loans to businesses and consumers l l Monetary Policy: Fractional Bank Reserves To earn its profits, a bank usually needs to charge 2-3 percent more for its loans than the rate of interest it pays for its saving accounts and time deposits, interest bearing deposits that cannot be withdrawn by check. l Tools of Monetary Policy • The Fed can affect the money supply by changing the reserve requirement. •This means the Fed increases the supply of money. (The Fed can affect the money supply by buying and selling government securities (open market operations). •The Fed can affect the money supply by changing the discount rate, the interest rate the Fed charges on loans to financial institutions. l Monetary Policy • Every piece of paper money issued in the United States used to have has the name of one of the 12 Federal Reserve banks on it. •Most money in a region had the name of the closest Federal Reserve bank. •Now, newly printed money just says, “United States…Federal Reserve System.” Tools of Monetary Policy l • What is the purpose of monetary policy? 1.The purpose of monetary policy is to influence the cost and availability of credit 2. To keep the economy healthy l Monetary Policy • Changes in the money supply affect the interest rate, the availability of credit, and the price level. l Monetary Policy 1. In the short run, monetary policy affects interest rates and the availability of credit. 2.In the long run, it affects inflation and economic growth, which is one of the Fed’s major concerns. l Monetary Policy: Short-Run Impact Changes in the money supply affect interest rates. Increases in the money supply lowers the interest rate. l Monetary Policy: Short-Run Impact Changes in the money supply affect interest rates. Decreases in the money supply raises the interest rate. Figure 15.7b Effects of Low Interest Rates Generally, low interest rates stimulate the economy because there is more money available to lend. Consumers buy cars and houses. Businesses expand, buy equipment, etc. Why does the Fed lower interest rates? If inflation is in check, lower rates stimulate economic activity, thus boosting economic growth. Effects of High Interest Rates The Fed raises interest rates as an effective way to fight inflation. Inflation—a sustained rise in the general price level; that is, all prices are rising together. Consumers pay more to borrow money, dampening spending. Businesses have difficulty borrowing; unemployment rises. Pages